KEFALONIA
Society

Society

Popular destinations GREECE
| Aegina | Alonissos | Andros |
| Chios | Corfu | Crete |
| Hydra | Kalymnos | Karpathos |
| Kefalonia | Kos | Lefkas |
| Lesbos | Mykonos | Naxos |
| Paros | Patmos | Peloponnese |
| Poros | Rhodes | Samos |
| Santorini | Skiathos | Skopelos |
| Spetses | Thasos | Zakynthos |
Society
State structure
 Greece VouliPhoto: Jebulon in the public domain
Greece VouliPhoto: Jebulon in the public domain
The constitution dates from 1975, after which important amendments were made in 1986. Legislative power rests with the unicameral parliament (the "Vouli"), whose 300 members are elected once every four years under an "enhanced right of proportional election". The system favors the strongest party in order to achieve a majority sufficient for government, which, however, encourages a two-party system.
The head of state is the president, who is elected by parliament (a two-thirds majority is required) for a term of five years and is eligible for re-election once. The president appoints and dismisses the prime minister. He may also dissolve parliament and in a state of emergency he can issue laws by decree. His function is largely ceremonial, as head of state he has no executive power. This power rests with the Council of Ministers, which is accountable to parliament for this. There is universal suffrage for all Greeks from the age of 18.
After the military dictatorship, a popular vote on the return of the monarchy to the disadvantage of ex-king Constantine was unfavorable. For the current political situation see chapter history.
Administrative division
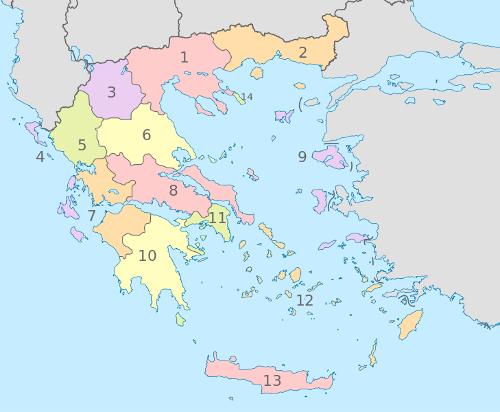 Greece administrative divisionPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Greece administrative divisionPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Greece is divided into 13 administrative divisions, the so-called "Peripheries" (districts). These "Peripheries" are subdivided into prefectures. A prefecture is called a "Nomos", with a "nomoi" at its head. In total there are 51 prefectures. In addition, Greece has one autonomous area under its own administration, namely Agion Oros (Mount Athos) in Chalkidiki (Northern Greece). Greater Athens has a separate status. The other provinces are: Central Greece, Peloponnese, Ionian Islands, Epiros, Thessaly, Macedonia, Thrace, Aegean Islands and Crete.
A place of residence is then called either "Dimos" (municipality, city) or "Kinotita" (community, village). In total there are 900 municipalities and 133 communities.
As of 2011, the Ionian Islands administrative region (map number 7 above) is divided into five regional units (periferiaki enotita) Ithaki (formerly Kefalonia), Kefalonia, Kerkyra, Lefkas and Zakynthos.
Kefalonia has also been a merged municipality since 2011, with the municipalities of Argostoli, Eleios-Pronnoi, Erisos, Leivathos, Omala, Paliki, Pylaros and Sami.
Geographically, Kefalonis belongs to the Ionian Islands group of the same name, together with the larger islands of Ithaca, Corfu, Kythira, Lefkas, Paxi and Zakynthos; the smaller Ionian islands include Antipaxi, Erikoussa, Kalamos, Kastos, Mathraki, Meganisi and Othoni. For the current political situation in Greece, see History.
Education
Kefalonia has a small number of higher education institutions: two Technical Education Institutes in Argostoli and Lixouri, a Maritime School in Argostoli and the Rokos Vergotis Conservatory in Argostoli.
Sources
Wikipedia
Leistra, M. / De Griekse eilanden
Gottmer/Becht
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info