KARPATHOS
Society

Society

Popular destinations GREECE
| Aegina | Alonissos | Andros |
| Chios | Corfu | Crete |
| Hydra | Kalymnos | Karpathos |
| Kefalonia | Kos | Lefkas |
| Lesbos | Mykonos | Naxos |
| Paros | Patmos | Peloponnese |
| Poros | Rhodes | Samos |
| Santorini | Skiathos | Skopelos |
| Spetses | Thasos | Zakynthos |
Society
State structure
 Greece VouliPhoto: Jebulon in the public domain
Greece VouliPhoto: Jebulon in the public domain
The constitution dates from 1975, after which important amendments were made in 1986. Legislative power rests with the unicameral parliament (the "Vouli"), whose 300 members are elected once every four years under an "enhanced right of proportional election". The system favors the strongest party in order to achieve a majority sufficient for government, which, however, encourages a two-party system.
The head of state is the president, who is elected by parliament (a two-thirds majority is required) for a term of five years and is eligible for re-election once. The president appoints and dismisses the prime minister. He may also dissolve parliament and in a state of emergency he can issue laws by decree. His function is largely ceremonial, as head of state he has no executive power. This power rests with the Council of Ministers, which is accountable to parliament for this. There is universal suffrage for all Greeks from the age of 18.
After the military dictatorship, a popular vote on the return of the monarchy to the disadvantage of ex-king Constantine was unfavorable. For the current political situation see chapter history.
Administrative division
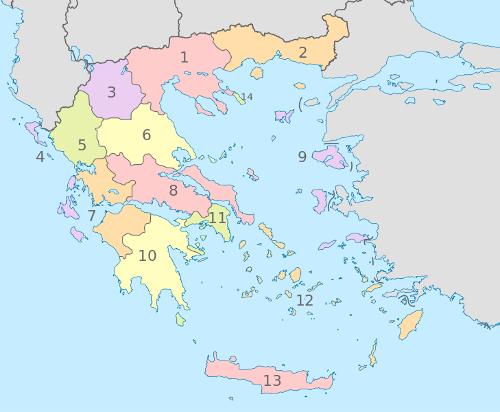 Greece administrative divisionPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Greece administrative divisionPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Greece is divided into 13 administrative divisions, the so-called "Peripheries" (districts). These "Peripheries" are subdivided into prefectures. A prefecture is called a "Nomos", with a "nomoi" at its head. In total there are 51 prefectures. In addition, Greece has one autonomous area under its own administration, namely Agion Oros (Mount Athos) in Chalkidiki (Northern Greece). Greater Athens has a separate status. The other provinces are: Central Greece, Peloponnese, Ionian Islands, Epiros, Thessaly, Macedonia, Thrace, Aegean Islands and Crete.
A place of residence is then called either "Dimos" (municipality, city) or "Kinotita" (community, village). In total there are 900 municipalities and 133 communities.
Through the administrative reorganisation of 2011, Karpathos became a regional unit of the administrative region of South Aegean Islands, which further comprises the islands of Andros, Kalymnos, Kea-Kythnos, Kos, Milos, Mykonos, Naxos, Paros, Rhodes, Santorini (Thira), Syros, and Tinos. The merged municipality of Karpathos consists of the parishes of Karpathos Town and Olympos or Olympos Karpathou.
Karpathos is geographically part of the Dodecanese archipelago, together with the islands of Kalymnos, Kos, Patmos and Rhodes, among others. For the current political situation in Greece see chapter history.
Besides the capital Karpathos Town or Pigadia, there are twelve villages on Karpathos: Ammopi, Aperi, Arkassa, Diafani, Lefkos, Menetes, Mesohori, Olympos, Othos, Piles, Spoa and Volada.
Eduction
The 16th century monastery of Agios Georgios once housed the first school of Karpathos.
Naturally, Karpathos also has a number of diving schools.
Due to the isolated location of Karpathos and its poor economic situation and prospects, in the course of time many inhabitants of the island emigrated to the United States and later also to Australia. A considerable part of these emigrants has meanwhile returned to Karpathos, often with a lot of money and a good education. The population of Karpathos has one of the highest percentages of university graduates in Europe.
Sources
Wikipedia
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info