LESBOS
Society

Society
Popular destinations GREECE
| Aegina | Alonissos | Andros |
| Chios | Corfu | Crete |
| Hydra | Kalymnos | Karpathos |
| Kefalonia | Kos | Lefkas |
| Lesbos | Mykonos | Naxos |
| Paros | Patmos | Peloponnese |
| Poros | Rhodes | Samos |
| Santorini | Skiathos | Skopelos |
| Spetses | Thasos | Zakynthos |
Society
State structure
 Greece VouliPhoto: Jebulon in the public domain
Greece VouliPhoto: Jebulon in the public domain
Greece received a new administrative division on January 1, 2011 as part of an overall administrative reform named after Kallikratis, a Greek architect from the mid-5th century BCE.
Greece has been divided into 13 administrative regions, known as "peripheries," since 2011. These administrative regions are in turn divided into 74 regional units, the "perifereiaki enotita". The regional units, which no longer have their own administration, are in turn subdivided into 325 municipalities or "demoi. In addition, since 1926 Greece has had one autonomous area under its own Greek Orthodox administration, namely Agion Oros or the monastic state of Athos in Chalkidiki (northern Greece).
Administrative division
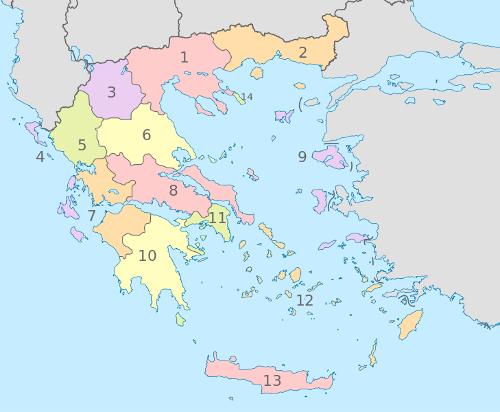 Greece administrative divisionPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Greece administrative divisionPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The 13 administrative regions of Greece are Attica (1), Central Greece (2), Central Macedonia (3), Crete (4), Eastern Macedonia and Thrace (5), Epirus (6), Ionian Islands (7), Northern Aegean Islands (8), Peloponnese (9), Southern Aegean Islands (10), Thessaly (11), Western Greece (12) and Western Macedonia (13).
Through the 2011 administrative reorganization, Lesbos became a regional unit of the North Aegean Islands Administrative Region, which further consists of the regional units of Chios, Ikaria, Limnos and Samos.
The merged municipality of Lesbos consists of the 13 boroughs of Agia Pareskevi, Agiasos, Gera, Eresos-Antissa, Evergetoulas, Kalloni, Loutropoli Thermis, Mandamados, Mithymna, Mytilini, Petra, Plomari and Polichnitos. For the current political situation in Greece, see history section.
Education
Scientific Education
After the Peace of Moudros was signed (October 17/30, 1918), Greece was designated by the Allies to maintain control of the area around Turkish Smyrna and ensure peace and stability. In this context, in 1919 the internationally renowned mathematician Constantine Caratheodory, then working at the University of Berlin, proposed the establishment of a new university in Smyrna, the "Ionian University.
Athens was at that time the only educational center for scientific education in that area of the Mediterranean, and so he proposed three possible sites for the new university: Smyrna, Thessaloniki and Chios. The Greek government decided to establish the Ionian University, located in Smyrna, present-day Izmir, Asia Minor (Turkey), on December 1, 1920. However, the Ionian University would never open its doors to the students. The Turks, led by Mustafa Kemal (Atatürk), revolted against the presence of the Greeks in Turkey. On August 26, the Turks attacked Smyrna and within hours the Greeks had been driven into the sea and a terrible slaughter of the Greeks ensued and the thousands of years of Greek presence in Asia Minor came to a definitive end.
The University of the Aegean is the continuation of the initial vision of Constantine Caratheodory. Reestablished in 1984, the university now has 17 faculties and has become one of the largest universities in the country. The central administration of the university is located in the capital of Lesbos, Mytilene, while the various institutes are located in Chios, Karlovassi (on the island of Samos), Rhodes, Syros and Mytilene.
Mytilene houses the faculties of Social Sciences and Environmental Studies. The faculty has the institutes of social anthropology and history, geography, sociology and cultural technology and communication. The faculty of environmental studies has the institutes of food and nutrition, environment and maritime sciences (on Lemnos).
Miscellaneous Education
The Girls School of Mytilene is located in the historic center of Mytilene and was funded by Z. Vournazos, the architect of the school building is not known. The building was completed in 1899 and has since served as an elementary and secondary school for girls. The main entrance of the building is decorated with stone neo-classical elements such as columns, pediments and lintels.
The northern Aegean region includes 155 kindergartens, 177 elementary schools, 49 high schools, 30 colleges and 18 technical schools.
Sappho, poet of Lesbos
Sappho (c. 615-562 B.C.), probably born in Eresoú, is generally considered one of the best lyric poets of all time. She was a daughter of noble parents, who allowed her much artistic freedom. Her poems were known throughout the Mediterranean during her lifetime, but were banned by the Church at the end of antiquity. Her poems have been preserved only in short quotations from others and on remnants of papyrus. She often wrote poems about women and is therefore known as the first literary lesbian, although it is not certain that she was a lesbian. In ancient times, she was also called the "Tenth Muse.
Sources
Dubin, Marc S. / Griekse eilanden
Van Reemst
Greek islands
Lonely Planet
Griekse eilanden
Lannoo
McGilchrist, Nigel / Greece : the Aegean islands
Somerset Books
Midgette, Anne / Griekse eilanden : Egeïsche Zee
Het Spectrum
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info