BRITISH COLUMBIA
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | English |
| Capital | Victoria |
| Area | 944,735 km² |
| Population | 5,147,712 (2020) |
| Currency | Canadian dollar (CAD) |
| Web | .ca |
| Code. | CA-BC |
| Tel. | +1 |
Popular destinations CANADA
| Alberta | British columbia | Manitoba |
| New brunswick | Newfoundland and labrador | Northwest territories |
| Nova scotia | Nunavut | Ontario |
| Prince edward island | Quebec | Saskatchwan |
| Yukon |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
British Columbia (commonly referred toby the initials BC) is Canada's westernmost province, covering 944,735 km2. Worldwide there are only about 30 countries that are larger than British Columbia. Together with the US states of Washington and Oregon, this area is called the 'Pacific Northwest'.
British Columbia is bordered on the east by the Canadian province of Alberta, on the south by the American states of Montana, Idaho and Washington, on the west by the Pacific Ocean for a total length of approximately 27,000 km, on the northwest by the US state of Alaska and to the north by Yukon Territory and the Northwest Territories. The distance from the north to the south of British Columbia is a maximum of 1,300 kilometers; the maximum distance from east to west is 700 kilometers. British Columbia is Canada's second largest province after Quebec and Ontario.

Landscape
 Canada Pacific Rim National Park British ColumbiaPhoto: Adam Jones, Ph.D. CC 3.0 no changes made
Canada Pacific Rim National Park British ColumbiaPhoto: Adam Jones, Ph.D. CC 3.0 no changes made
Approx. three quarters of British Columbia is mountainous; more than half of the province is above 1250 meters. The only flat area is in the northeast on the Peace River. More than half of British Columbia is covered in forests. On the coast mainly Douglas fir and red cedar trees; inland forests of pines, spruces and conifers. Approx. 10% of British Columbia is grassland or is being cleared; almost 2% of the surface consists of rivers and lakes. Along the more than 7,000 km long coast of British Columbia are approximately 11,000 rivers and streams and 7,000 lakes. The largest lake in British Columbia is the 200 km long Williston Lake, also the largest man-made lake in North America.
Just off the southwest coast of British Columbia is Vancouver Island, the largest island along the west coast of North America and just slightly larger than Belgium (31,285 km2 to 30,528 km2; approx. A ridge runs longitudinally across the island, the Vancouver Island Ranges, with long mountain fjords on the west coast. The longest fjord in British Columbia is Gardner Canal (114 km). Vancouver Island is separated from mainland British Columbia and the United States by the Johnstone Strait and Queen Charlotte Street to the north and northeast, the Strait of Georgia to the southeast, and the Strait of Juan de Fuca to the southwest. The island is also famous for its beautiful sandy beaches and dense forests. In the large Strathcona Provincial Park, the oldest provincial park in British Columbia (1911) lies the highest waterfalls in North America, the Della Falls (440 m along three cascades). The highest point on Vancouver Island is also located in Strathcona Provincial Park, the Golden Hinde (2197 m). Near Gold River is the Quatsino Cave, the deepest vertical cave in North America at 152 meters. The deepest 'common' caves are also found in British Columbia, Heavy Breather System (653 m), Arctomys Cave (536 m), Close to the Edge (472 m) and Thanksgiving Cave on Vancouver Island (416 m).
The Pacific Rim National Park Reserve includes three areas: Long Beach with its rugged and windswept beaches (here is the only surfing beach in British Columbia), West Coast Trail with rainforests and deep rock canyons and the Broken Group Islands, an archipelago consisting of approximately 300 islands and rocky outcrops, spread over an area of about 80 km2. North of Vancouver Island are the Queen Charlotte Islands, officially referred to as Haida Gwaii, "Islands of the Haida People" since 2010. The main islands are Graham Island to the north and Moresby Island to the south. Furthermore, there are several hundred small islands from north to south over a distance of 300 km. Half of the population is Haida.
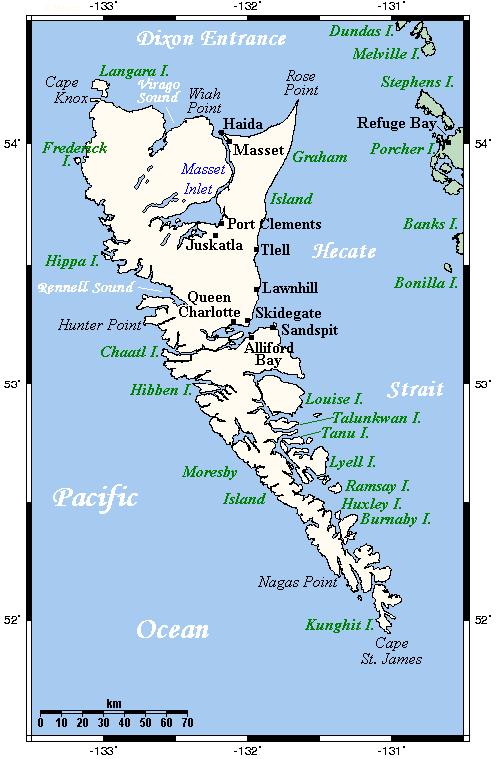 Queen Charlotte Islands of Haida Gwaii, British ColumbiaPhoto: Public domain
Queen Charlotte Islands of Haida Gwaii, British ColumbiaPhoto: Public domain
The Gulf Islands is a group of islands in the Strait of Georgia, also known as the Salish Sea or Gulf of Georgia, that lie between Vancouver Island and mainland British Columbia. The Gulf Islands can be divided into the Northern and the Southern Gulf Islands. The Southern Gulf Islands consist of about two hundred most uninhabited islets and rocky outcrops. A small number of larger islands are inhabited, including Salt Spring Island, the largest and most populous, North Pender Island, South Pender Island, Saturna Island, Mayne Island, Gabriola Island, and Galiano Island. Notable islands of the Northern Gulf Islands include Denman Island, Hornby Island, Lasqueti Island, and Texeda Island. Quadra Island also appears to belong to the Gulf Islands in terms of location, but is generally considered to be the Discovery Islands, also an archipelago between Vanouver Island and mainland British Columbia. Most of the islands are unpopulated or very sparsely populated, only to Quadra Island, the largest and most populous island, and Cortes Island run by ferries. The larger islands include Hardwicke Island, East Thurlow Island, Stuart Island, Maurelle Island, West Redonda Island, Marina Island, Hernando Island, Savary Island, and the Twin Islands.
Northern British Columbia is mountainous and the central interior consists of a high plateau with dense forests. A number of mountain ranges run from east to northwest. Southeastern British Columbia, Kootenay, is made up of mountain ranges such as the Rocky Mountains (including the highest peak in the Canadian Rockies, the 3,954m Mount Robson), Purcells, Selkirks, and Monashees. In between flow rivers like the Columbia River and the Arrow Lakes. Yoho Park is home to one of Canada's tallest waterfalls, the 384-meter-high (including a 254-meter-tall drop) Takakkaw Falls, which is fed by the glacial meltwater from the Daly Glacier flowing into the Yoho River. Near Whistler, in Shannon Falls Provincial Park, British Columbia's third-highest waterfall plunges, Shannon Falls (335m), six times the height of the famed Niagara Falls. The third waterfall is Hunlen Falls (260 m) in Tweedsmuir Provincial Park, whose water flows into the Atnarko River.
 Takakkaw Falls, British ColumbiaPhoto: Michael Rogers CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Takakkaw Falls, British ColumbiaPhoto: Michael Rogers CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The city of Kimberley is located at 1117 meters, making it the highest city in Canada. The Kootenay region is known for its many hot springs (including Harrison Hot Springs near the town of Harrison Lake), but here is also the Glacier National Park (1350 km2) with 422 glaciers (the most famous of which are Asulkan and Illecillewaet Glacier) and on the 3391 meter high Mount Dawson falls on average 23 meters of snow in winter. Due to the steep mountain walls, this area is one of the most active avalanche areas in the world. Mount Waddington (4,019 meters) is British Columbia's highest mountain located entirely in the province. At 4,671 meters, Mount Fairweather is much higher, but that mountain is partially located in Alaska. In the Stawamus Chief Provincial Park is the 652-meter high rock wall Stawamus Chief, the second largest granite monolith in the world.
The Lower Mainland is a lagoon between the mountains of Vancouver Island and the Coast Mountains on the mainland. The Fraser River, British Columbia's longest river at 1,368 kilometers, has created a long delta here and then flows into the Strait of Georgia. The Okanagan Similkameen Region is formed by the Okanagan Valley, one of the foothills in a hill country between the Cascade Range to the west and the Monashee Range to the east. The Okanagan Valley stretches for 215 kilometers and is actually a series of valleys connected by a number of lakes. One of those lakes is Osoyoos Lake, Canada's warmest freshwater lake with temperatures in August of 26-33°C and sometimes a bit higher.
Surrounding the lake is the Okanagan Desert, a distant offshoot of the Sonoran Desert, which begins in Mexico and stretches north across five U.S. states to eventually British Columbia. Typical desert flora such as desert sage, blackberry and cacti can be found here. Another remarkable lake is the blue/green colored Kalamalka Lake or 'Lake of a Thousand Colours', one of the few marl lakes in the world. Also in this area is the lake with the highest average summer temperature in Canada, Christina Lake (23°C).
 Okanagan Desert around Lake Osoyoos, British ColumbiaPhoto: Spatial Mongrel CC 2.0 Genericno changes made
Okanagan Desert around Lake Osoyoos, British ColumbiaPhoto: Spatial Mongrel CC 2.0 Genericno changes made
In addition to the Fraser River and the Columbia River, which originate in Columbia Lake, this province also contains the 611 kilometer long Peace River and the Skeena, Yukon and Liard rivers. The Kootenay River rises in Kootenay National Park and eventually joins the Columbia River. The Liard River Hot Springs are located along the Alaska Highway. Surface water seeps through the fissures and fractures to the red-hot rocks of the Earth's crust, which can reach 1000°C.
Halfway along the British Columbia coastline are the Queen Charlotte Islands (about 150 islands); Due to the warm gulf streams from Asia, the climate here is always very humid and there is often fog between the ancient rainforests with thousand-year-old spruce and cedars.
Wells Gray Provincial Park (5200 km2) is one of the most beautiful natural areas in British Columbia and is characterized by mountain meadows, more than 250 waterfalls and high mountains with glaciers. Mount Edziza Provincial Park consists of volcanic landscapes, including lava flows and basalt plains. About a third of Atlin Provincial Park is covered by ice sheets and glaciers.
British Columbia has potentially active volcanoes, but the last eruption dates back more than 2,000 years. Another eruption of Mount St. Helens occurred in Washington state, bordering British Columbia.
Earthquakes, on the other hand, still occur regularly in British Columbia, but with barely visible consequences. Yet it was only a few decades ago (1949) that the Queen Charlotte Islands in particular off the coast of British Columbia were hit by an earthquake measuring 8.1 on the Richter scale. These earthquakes are caused by two tectonic plates rubbing against each other off Canada's west coast.
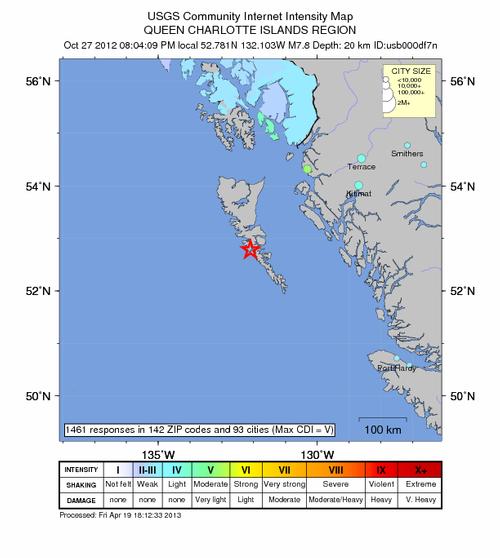 Data from a 2012 earthquake off the Queen Charlotte Islands, British ColumbiaPhoto: Public domain
Data from a 2012 earthquake off the Queen Charlotte Islands, British ColumbiaPhoto: Public domain
Sources
BBC - Country Profiles
British Columbia and the Rockies
Michelin Apa Publications
Canada
Cambium
Canada
Lonely Planet
CIA - World Factbook
Elmar Landeninformatie
Jepson, Tim / Vancouver en de Canadese Rockies
Wat & Hoe
Leigh Fleming, Janet / British Columbia : a walking guide
Cicerone
Ohlhoff, Kurt Jochen / Canada west & Alaska
ANWB
Phenix, Penny / Canada
Wat & Hoe
The rough guide to Canada
Rough Guides
Struijk, Aad / West-Canada
Elmar
Veldt, Marc / Canada
Gottmer/Becht
Ver Berkmoes, Ryan / British Columbia & the Yukon
Lonely Planet
Wagner, Heike / West-Canada : Alberta, British Columbia
Lannoo
Wikipedia
Last updated February 2026Copyright: Team The World of Info