ALBERTA
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | English |
| Capital | Edmonton |
| Area | 661.848 km² |
| Population | 4,442,879 (2021) |
| Currency | Canadian dollar (CAD) |
| Web | .ca |
| Code. | CA-AB |
| Tel. | +1 |

Popular destinations CANADA
| Alberta | British columbia | Manitoba |
| New brunswick | Newfoundland and labrador | Northwest territories |
| Nova scotia | Nunavut | Ontario |
| Prince edward island | Quebec | Saskatchwan |
| Yukon |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Alberta, also known as the 'Princess Province', is a province in western Canada with an area of 661,848 km², Canada's largest province after Quebec (1,542,056 km²), Ontario (1,076,395 km²) and British Columbia (944,735 km²). Alberta is not adjacent to the sea and the total area consists of 642,317 km² of land and for 19,531 km² out of water. Alberta belongs to the so-called prairie provinces, along with Manitoba and Saskatchewan.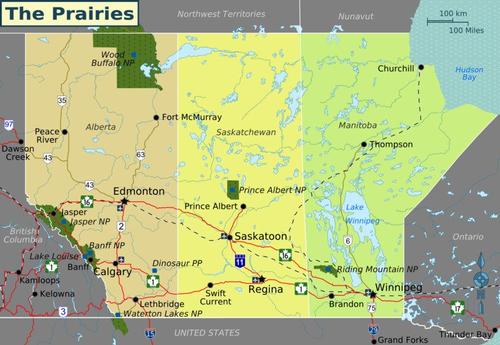 Canadian prairie provincesPhoto: Shaund CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Canadian prairie provincesPhoto: Shaund CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Alberta is three times the size of Great Britain, and the same size of France, Switzerland, Belgium and the Netherlands together. The greatest distance from north to south is 1,221 kilometers, from east to west 634 kilometers.
Alberta is bordered to the west by British Columbia, to the east on Saskatschewan (1,223 km), in the south to the US state of Montana (298 km) and in the north to the Northwest Territories (644 km). Alberta's northernmost village is Indian Cabins, 9 miles from the Northwest Territories border.
Canada is divided into six time zones, Newfoundland Time (-4.5 hours), Atlantic Time (-5 hours), Eastern Time (-6 hours), Central Time (-7 hours), Mountain Time (-8 hours), and Pacific Time (-9 hours);Alberta is in the Mountain Time time zone.
Landscape
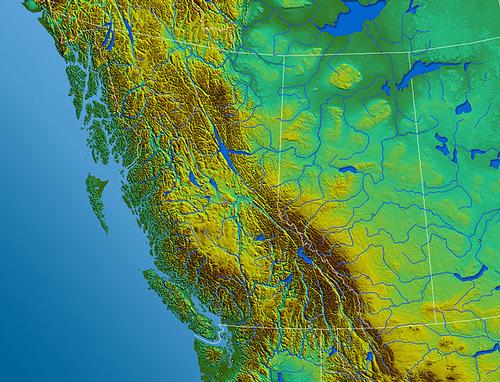 Alberta elevation mapPhoto: Qyd in the public domain
Alberta elevation mapPhoto: Qyd in the public domain
Combining physiography, climate, soil, and vegetation, Alberta has identified four biophysical regions.
The prairie region, which extends into the US state of Montana, encompasses most of Southern Alberta, more precisely the area south and east of an arc extending from Waterton in the southwest corner to the Saskatchewan border east of Red Deer. This gently sloping almost treeless grassland is relatively dry, but this landscape is interrupted in places by deep river valleys and heights from about 300 meters in the northeast to more than 1,460 meters in the Cypress Hills in the southeast. Prairadic areas with the original vegetation can only be found sporadically, they have been cultivated almost everywhere over the years to serve as a 'granary'.
Vegetation-free, erosion-damaged barren spots in the prairie with canyons, ravines and hoodoos are called the 'Alberta Badlands'. This area is east of Calgary and stretches south. It is also one of the most important paleontological regions in the world because of the many dinosaur finds.
 Alberta Prairie LandscapePhoto: Brett Snyder CC1.0 Generic no changes made
Alberta Prairie LandscapePhoto: Brett Snyder CC1.0 Generic no changes made
Parkland, called 'Aspen Parkland' and a transition zone between forests in the north and prairie in the south, is predominant in central Alberta and is in the shape of a crescent moon west and north of the prairie region, including a much of the catchment area of the North Saskatchewan River.
The parkland ranges from lowlands formed by dry lake bottoms to rolling landscapes with numerous lakes and depressions. It contains both wooded areas, especially aspen, aspen and spruce, as well as grassy areas, with a soil that is extremely suitable for agricultural activities due to favorable climatic conditions.
 Central Alberta ParklandPhoto: Paulhami CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Central Alberta ParklandPhoto: Paulhami CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The northern half of Alberta is covered with arctic forests, especially taiga coniferous forests, and peatlands. Together with many lakes and large rivers that flow towards the Arctic Ocean, they define the landscape. Soil and harsh climatic conditions make farming difficult in this part of Alberta, except in the Pacific Northwest area, where parkland allows grain to be grown on the world's most northerly acreage. This relatively flat land is interrupted by the Swan Hills (max. Altitude 1200 meters), the Birch Mountains and the Caribou Mountains (max. Altitude 1030 meters).
 Typical Canadian Rocky Mountains Landscape in AlbertaPhoto: Gorgo in the public domain
Typical Canadian Rocky Mountains Landscape in AlbertaPhoto: Gorgo in the public domain
To the west of the prairie, after a hilly area, the Rocky Mountain Foothills, loom the true Rocky Mountains, which lie in the provinces of British Columbia and Alberta as far as Canada is concerned. This strip of mountains, sometimes over 3,700 meters high, starts in Alberta near the city of Grande Prairie and runs south along Alberta's western border with British Columbia.
Most of Alberta's mountains are found in the southwestern part of the province on the eastern slopes of the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Other areas of mountains include the Caribou Mountains and the Cypress Hills. Mount Columbia, located on the border with British Columbia, is the highest mountain in Alberta at 3747 meters and the second highest mountain in the Canadian Rocky Mountains (Mount Robson in British Columbia, 3954 meters). The Highwood Pass is located in Kananaskis Country, at 2206 meters the highest mountain pass in Canada with a paved road over it. The average elevation of Alberta is 725 meters. Alberta's lowest point (152 meters) is located in the northeast of the province at the Slave River in Wood Buffalo National Park. The city of Banff is the highest city in Canada (1,383 m), the village of Lake Louise is even higher, at 1,534 m.
On the border of British Columbia and Alberta are the 384-meter Takakkaw Falls, the Canada's second highest waterfall fed by meltwater from the Wapta Icefield. Other high or spectacular waterfalls are Crypt Falls (Waterton Lakes National Park, 150m), Upper Falls and Lower Falls (Banff National Park), Weeping Wall (Banff National Park, 100m), Bridal Veil Falls (Banff National Park), Panther Falls (Banff National Park), Upper Sunwapta Falls and Lower Sunwapta Falls (Jasper National Park), Athabasca Falls (Jasper National Park, 23 m).
 Cypress HillsPhoto: Erik Lizee in the public domain
Cypress HillsPhoto: Erik Lizee in the public domain
The Caribou Mountains are located in northern Alberta and form an elevated plateau in an otherwise flat landscape of wetlands. The mountains here reach a height of up to 1030 m, rising almost 700 m above the otherwise flat environment. In the far northwest of Alberta lies the Hay-Zama Lakes Wildland, a complex network of lakes, swamps and rivers, together an 800 km²large freshwater wetlands, one of the largest in Canada. About 300,000 ducks and geese reside here during the fall migration.
Covered with grassland and woodland, the Cypress Hills are located in southeast Alberta on the border with Saskatchewan and form the highest area between the Rocky Mountains and Labrador in the far west of Canada. The Cypress Hills reach a maximum height of 1468 meters.
Below are the top ten highest mountains in Alberta
| Name | Height |
| Mount Columbia | 3747 meters |
| Twin Peaks Massif | 3684 meters |
| Mount Alberta | 3619 meters |
| Mount Forbes | 3612 meters |
| Mount Temple | 3543 meters |
| Mount Brazeau | 3525 meters |
| Snow Dome | 3520 meters |
| Mount Kitchener | 3505 meters |
| Mount Lyell | 3504 meters |
| Mount Hungabee | 3492 meters |
 Mount Columbia, Alberta's highest mountainPhoto: Geoffl in the public domain
Mount Columbia, Alberta's highest mountainPhoto: Geoffl in the public domain
Rivers and lakes
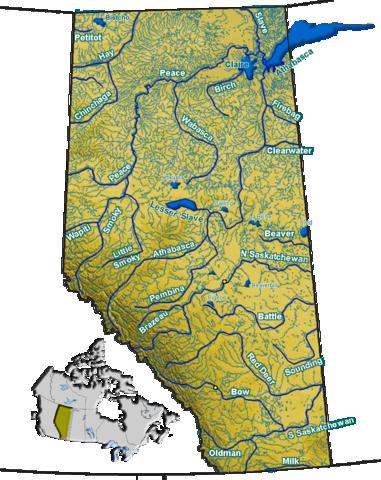
Alberta has 245 rivers that flow into three different waters, the Arctic Ocean, Hudson Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. That there is no riverand outflows from Alberta into the Pacific is through the 'Continental Divide', 'Great Divide' or 'Continental Divide', a mountain ridge that leads to Mexico via Alaska, Canada (including Alberta) and the United States. Rivers west of the Continental Divide waters drain into the Pacific or Pacific Ocean; rivers east of this dividing line drain into the Atlantic Ocean. Most of the Continental Divide follows the Rocky Mountains in Canada and the United States. The Athabasca River Delta is the second largest river delta in the world after the Amazon River.
Below is an overview of Alberta's main rivers
| River name | Catchment area | Length |
| Athabasca River | Alberta | 1231 km |
| Beaver River | Alberta and Saskatchewan | 491 km |
| Hay River | Alberta and Northwest Territories | 702 km |
| Milk River | Alberta and Montana | 1173 km |
| North Saskatchewan River | Alberta and Saskatchewan | 1287 km |
| Peace River | Alberta and British Columbia | 1923 km |
| Slave River | Alberta and Northwest Territories | 434 km |
| South Saskatchewan River | Alberta and Saskatchewan | 1392 km |
Rivers of AlbertaPhoto: Qyd in the public domain
Alberta has some 600 lakes, mainly formed in the last Ice Age, about 12,000 years ago. There are several lake types in Alberta, from glacial lakes in the Rocky Mountains, small shallow lakes on the prairies, lakes with brown water in the northern arctic forests, 'muskeg' swamp lakes to large lakes with sandy beaches in Central Alberta.
The largest lake that lies entirely within Alberta territory is Lake Claire. The vast Lake Athabasca is mostly in the province of Saskatchewan, but the Alberta portion is still much larger than Lake Claire. One of the most beautiful lakes in Canada and a real tourist attraction is the emerald green mountain lake Lake Louise, which lies at the foot of Mount Victoria and is named after Queen Victoria's daughter, Louise Caroline Alberta.
It is special in Jasper National Park located Medicine Lake, which drains into an underground cave system during the fall and winter and rises again in the Maligne Canyon.
Ten Largest Lakes in Alberta
| Name | Location | Area |
| Lake Athabasca | Alberta and Saskatchewan | 7850 km²(2295 km²in Alberta) |
| Lake Claire | Alberta | 1436 km² |
| Lesser Slave Lake | Alberta | 1160 km² |
| Bistcho Lake | Alberta | 426 km² |
| Utikuma Lake | Alberta | 296 km² |
| Cold Lake | Alberta and Saskatchewan | 280 km²(248 km²in Alberta) |
| Lac la Biche | Alberta | 236 km² |
| Beaverhill Lake | Alberta | 139 km² |
| Calling Lake | Alberta | 134 km² |
| Winefred Lake | Alberta | 123 km² |
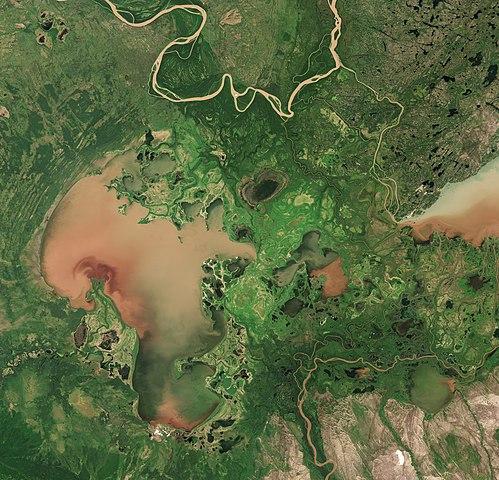 Satellite image of Lake Claire ( right part of Lake Athabasca) Photo: Copernicus Sentinel-2, ESA CC 3.0 IGO no changes made
Satellite image of Lake Claire ( right part of Lake Athabasca) Photo: Copernicus Sentinel-2, ESA CC 3.0 IGO no changes made
 One of the most beautiful lakes: Lake LouisePhoto: Orlandkurtenbach in the public domain
One of the most beautiful lakes: Lake LouisePhoto: Orlandkurtenbach in the public domain
National Parks
Alberta has the most park areas in Canada with its five national and 62 provincial parks. The national parks are Banff National Park, Elk Island Park, Jasper National Park, Waterton Lakes National Park and Wood Buffalo National Park.
Banff National Park (6641 km2) was Canada's first national park (1885) and worldwide the third. The national park is located in the middle of the Rocky Mountains and, in addition to mountains, valleys, glaciers, forests, rivers, lakes and grasslands, is also known for its sulfuric hot springs. The water of the Upper Hot Springs Pool at Sulfur Mountain averages 38°C. Particularly noteworthy are the ‘hoodoos’ , over 20,000 year old slate rock formations in the form of high tables. The highest point of Banff National Park is Mount Forbes (3612 m), the largest lake is the 28 km long Lake Minnewanka, there are 320 km of roads through the park and approximately 1500 km of hiking trails.

Established in 1907 and a national park since 1930, Jasper National Park is the largest and most northerly of the four national parks in the Rocky Mountains. It covers an area of 10,878 km² with mountains, valleys, glacial lakes, Columbia Icefields, a 400 year old ice sea, 325 km² large with a thickness of up to 400 meters, and the 30 meter high Athabasca Falls.
Columbia Icefields is one of the largest non-polar icy seas in the world. Miette Hot Springs has the warmest spring water (to nearly 54°C) in the Rockies with a high mineral content. Jasper National Park has about 1000 km of hiking trails and thousands of camping spots.
 Athabasca Glacier, AlbertaPhoto: Carlos Delgado CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Athabasca Glacier, AlbertaPhoto: Carlos Delgado CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The Athabasca Glacier is the largest glacier in the Rocky Mountains, six kilometers long and with a total area of 300 km². The glacier is an offshoot of the Columbia Icefield, the largest field of ice and snow in North America outside of the polar regions.
Elk Island National Park (194 km²), less than an hour's drive from Edmonton, was established in 1906 as Canada's first animal sanctuary. The nature in the park consists of rolling meadows, forests, ‘wetlands’ and some 250 lakes; about 20% of the surface consists of water. Elk Island Park, in addition to being a haven for moose, wood bison and prairie bison, is a true bird paradise with about 250 different species, including the trumpeter swan. The rare pygmy shrew is also found here.
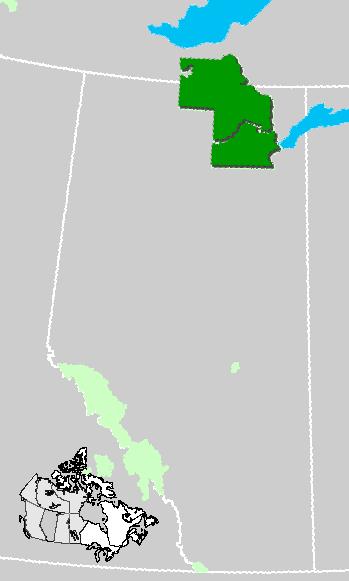
Location Wood Buffalo National Park, AlbertaPhoto: Qyd in the public domain
Wood Buffalo National Park (established 1922) is the largest national park in Canada and one of the largest in the world (44,807 km2), about the same size as Denmark (The largest national park in the world is the Greenland Northeast Greenland National Park, 972,001 km2). The park was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1983 and encompasses three types of landscape: a highland, a plateau with marshes and streams and the Peace and Athabasca river delta, full of seals, marshes and shallow lakes. Several thousand forest bison live in this national park. With a length of 800 meters, this is home to the largest beaver dam in the world.
Waterton Lakes National Park, founded in 1895, is a relatively small national park with 525 km2. Here are a number of elongated lakes that extend into the American Montana. Waterton Lakes National Park has formed the Waterton Glacier International Peace Park since 1932, together with the Glacier National Park in Montana. This entire area was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1995.
 Prince of Wales Hotel in Waterton Lakes National Park, AlbertaPhoto: Jon Sullivan in the public domaein
Prince of Wales Hotel in Waterton Lakes National Park, AlbertaPhoto: Jon Sullivan in the public domaein
Fish Creek, located in CalgaryProvincial Park is one of the largest city parks in the world (1189 ha).
 Winter scenery in Fish Creek Park, AlbertaPhoto: Cszmurlo CC 3.0 no changes made
Winter scenery in Fish Creek Park, AlbertaPhoto: Cszmurlo CC 3.0 no changes made
Outside the valley of the Red Deer River stretch the ‘badlands’ from Alberta, a stony desert with ravines, table mountains, plateaus and rocky pillars, the so-called ‘hoodoos’ . This lunar landscape is one of the richest dinosaur fossil sites in the world.
 Badlands AlbertaPhoto: Dingy CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Badlands AlbertaPhoto: Dingy CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Sources
Canada
Cambium
Canada
Lonely Planet
Hempstead, Andrew / Calgary
Avalon Travel
Hempstead, Andrew / Edmonton & Northern Alberta
Avalon Travel
Pashby, Christie / Frommer's Alberta
Wiley
Struijk, Aad / West-Canada
Elmar
Teuschl, Karl / Canada-West : Rocky Mountains, Vancouver
Uitgeverij Unieboek/Het Spectrum BV
Veldt, Marc / Canada
Gottmer/Becht
Wagner, Heike / West- Canada
Lannoo
Wikipedia
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info