CANADA
Economy

Economy

Cities in CANADA
| Montreal | Ottawa | Vancouver |
Popular destinations CANADA
| Alberta | British columbia | Manitoba |
| New brunswick | Newfoundland and labrador | Northwest territories |
| Nova scotia | Nunavut | Ontario |
| Prince edward island | Quebec | Saskatchwan |
| Yukon |
Economy
General
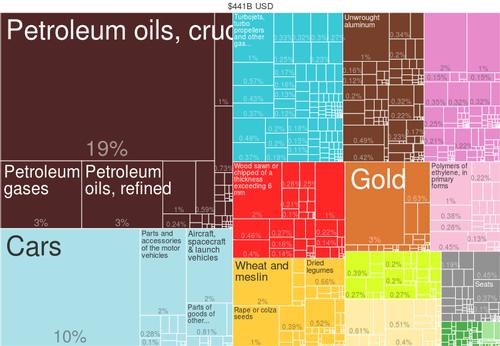 Export CanadaPhoto: The Atlas of Economic Complexity CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Export CanadaPhoto: The Atlas of Economic Complexity CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Canada has a highly developed industrial market economy, which is strongly export oriented and closely linked to the economy of the United States. With a gross national product (GDP) per capita of $48,300 (2017), Canada ranks among the wealthiest countries in the world.
In less than half a century, Canada has transformed from a country predominantly dependent on agriculture, forestry and fur trade into one of the most important industrialized countries in the world. In addition, many resources and resources are not yet available.
Most of the Canadian economic activity, like the population, can be found in a strip of about 160 kilometers wide along the border with the United States. The industry is mainly concentrated in the central provinces of Ontario and Québec and in the western provinces of British Columbia and Alberta. The province of Ontario is the center of the Canadian economy due to its large industrial concentration and large agricultural sector, while Toronto is the financial center of Canada. The Atlantic provinces are mainly oriented towards fisheries and agriculture, Saskatchewan and Manitoba are mainly oriented towards agriculture.
The enormous capital required for this is largely covered by the United States; almost all non-agricultural economic activities are financed by the wealthy southern neighbor.
The Canadian government and the Bank of Canada have pursued tight monetary policies for years, aimed at promoting price stability and keeping inflation under control. Due to the low and stable inflation, people are able to maintain the monetary value, which leads to an increase in the standard of living.
What also hinders national economic policy is the great degree of independence of the individual provinces, which have powers in the field of wage and price development and taxation.
In 2017, about 76% of the workforce was employed in the services sector, 19.0% in industry, and only 2% in the agricultural sector.
Agriculture
 Canada WheatPhoto: Akshay.paramatmuni1987 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Canada WheatPhoto: Akshay.paramatmuni1987 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The economic importance of agriculture has declined drastically in the past few decades, and now amounts to approximately 2% of GDP. The highly mechanized sector produces for the domestic market and increasingly for exports.
Canada has approx. 280,000, often large farms (average 247 ha), which use approx. 8.5% cultivated land. Since the 1980s, total production, which increases by approximately 2.5% annually, has intensified further; fewer farms with more and more land The main agricultural areas are located in the provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. Other areas of high agricultural activity include Southern Ontario, Southern Quebec, the mountain valleys of British Columbia, and the Atlantic provinces.
The most important product is still wheat, largely from the prairie provinces mentioned above. About 75% of the wheat produced there is exported. Other important products are: oats, barley, mixed grains, corn (especially in Ontario), rye, potatoes, oilseeds such as flax and rapeseed, and to a much lesser extent legumes, sugar beets, vegetables, tobacco (Ontario), feed grains and fruits.
Federal and provincial governments provide support to agricultural businesses in almost every field, including through irrigation works, research, measures to promote price stability, and the provision of favorable credits.
Animal husbandry

The Canadienne, also known as Black Canadienne, French Canadienne, or Black Jersey, is the only cow type bred in Canada. This type of cow dates back to the 16th century, when French colonists transported livestock to Canada from France. The Canadians remained the most used cow species in Canada until the late 19th century. After that, other species, such as the Hereford and the Holstein, began to displace the Canadienne from the scene.
Although the Canadienne can still be found all over Canada, the species is becoming increasingly rare and can only be found on a larger scale in the province of Quebec. Breeding organizations and the Quebec have in recent years made every effort not to let the species go extinct.
Areas with highly developed livestock farming are Ontario and Quebec, where the greater population density offers outlets for meat and dairy products. However, beef cattle breeding largely takes place in Alberta and Saskatchewan. Animal husbandry is the largest source of income for the Canadian agricultural sector, with cattle trade accounting for over 40% of sales. Cattle and pig farming are mainly focused on the export of animals, while the production of dairy farming is much more focused on the domestic market. Cattle farming is mainly concentrated in Alberta, the dairy industry and pig breeding in Ontario and Québec.
Fisheries
 Cod CanadaPhoto:Patrick Gijsbers CC 4.0 International no changes made
Cod CanadaPhoto:Patrick Gijsbers CC 4.0 International no changes made
In the mid-1980s, fisheries employed, apart from the fish processing industry, around 60,000 professional fishermen, two thirds of whom work on the Atlantic coast and around 20% on the west coast; approx. 5% fish in inland waterways. The Atlantic coast with important fishing grounds such as the Newfoundland Bank provides almost 70% of the total fish production, the Pacific coast more than 20% of this and the inland fishing mainly on the Great Lakes and Manitobamers about 10%.
The most commonly caught species are cod and herring on the Atlantic coast, salmon on the Pacific coast, perch, sturgeon and trout. Overfishing has put pressure on catches.
Fur hunting
 Atlantic seal CanadaPhoto: Public domain
Atlantic seal CanadaPhoto: Public domain
Hunting fur animals has long been Canada's largest economic resource. However, economic hunting (kicks) is increasingly being abandoned in favor of the much more lucrative breeding of fur animals on farms, mainly in Southern Canada. The farms mainly produce mink, chinchilla and silver fox fur.
The main hunted fur animals are beavers, lynxes, bisam rats, foxes, squirrels, otters, martens and seals. Seals have declined in the early 1980s, partly as a result of a European boycott. In 1987, the government ended the highly controversial hunt for young seals. However, the hunt for older animals continues unabated.
Forestry
Approx. 45% of Canada is covered by forests (400 million ha), which form an approx. 1000 to 2000 km wide belt from the east to the west coast. This is 10% of the world's forests. This enormous area consists mainly of different types of softwood and is approximately 70% exploitable. Canada is the largest exporter of timber and timber products. The forestry sector and employs approximately 35,000 people.
Sources
Canada
The Reader’s Digest
Canada
Cambium
Heetvelt, A. / Canada
ANWB
Ivory, M. / Canada
Kosmos-Z&K
Jepson, T. / Canada
Van Reemst
Njio, F. / Canada
Kosmos-Z&K
Roy, G. / North Canada
Bradt Wal, C.P.F. van der / Canada van A tot Z : praktische informatie over wonen en werken in Canada
DEN, Stichting Dienstverlening Emigratie Nederland
Weber, Wolfgang R. / West-Canada : Alberta, British Columbia
Lannoo
Zuilen, A.J. van / Gids voor Canada
Gottmer
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info