CANADA

Cities in CANADA
| Montreal | Ottawa | Vancouver |
Popular destinations CANADA
| Alberta | British columbia | Manitoba |
| New brunswick | Newfoundland and labrador | Northwest territories |
| Nova scotia | Nunavut | Ontario |
| Prince edward island | Quebec | Saskatchwan |
| Yukon |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Canada is a federal state in North America and a member of the Commonwealth. The total area of Canada is 9,958,319 km2 of which 755,109 km2 is water. Canada is the largest country in the Western Hemisphere and the second largest country in the world, accounting for 7% of the Earth's total land area.
 Canada LandscapePhoto: Public domain
Canada LandscapePhoto: Public domain
Characteristic of the enormous size of the country is the fact that Canada borders the Atlantic, Pacific and Arctic Oceans. It is also almost the same size as the whole of Europe (without Russia). The largest distance from east to west is 5514 kilometers and from north to south 4634 kilometers. Canada borders twelve states of the United States to the south and Alaska to the west (8893 kilometers, including 2477 kilometers with Alaska). The total coastline of Canada is 243,791 kilometers. The largest province in Canada is Quebec with approximately 1,650,000 km2 and the smallest province is Prince Edward Island with 5,657 km2.
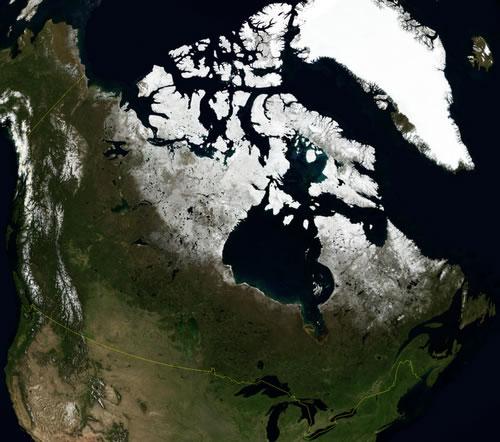
Canada originated from the oldest land masses in the world: the cup-shaped Canadian Shield, which covers a large part of the country, is 1 billion years old. It covers 5 million km2 around Hudson Bay. To the north and west, the continent of Canada is transformed into an archipelago of large, mostly low, islands called the Arctic Archipelago. The largest islands are Baffin, Ellesmere, Victoria, Newfoundland and Vancouver. More than 40% of Canada is north of the tree line (60 ° N.Br.)
Hudson Bay penetrates deep inland with its 1,220,000 km2.
The Canadian Rocky Mountains are the younger part of the Western Cordillera, a wide, mountainous strip running from Mexico to Canada. The mountain range was created between 120 and 20 million years ago and includes some of Canada's highest peaks, the 389 km2 Columbia Icefield and glacial lakes.
Canada has six time zones with a difference of four and a half hours between the east and west coasts. From east to west, the Newfoundland, Atlantic, Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific time zones are known. If it's midnight in Western Europe, it's 4:00 pm in British Columbia, 7:00 pm in Ontario, and 8:00 pm in Nova Scotia.
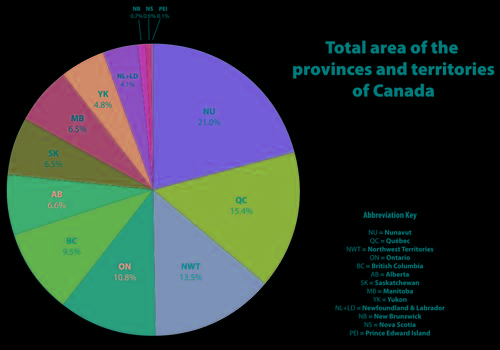 Size Canadian provincesPhoto: Connormah CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Size Canadian provincesPhoto: Connormah CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Landscape description per province
ALBERTA

The east side of Alberta still belongs to the prairies, but beyond Calgary the Canadian Rocky Mountains suddenly appear. Here lie four national parks close together: Banff, Jasper, Kootenay and Yoho.
Alberta is bordered to the west by British Columbia with its high, expansive Rocky Mountains. To the east, Alberta borders Saskatchewan with its flat prairies. Alberta borders the U.S. state of Montana to the south, the hilly north to the province of Northwest Territories, the west to British Columbia, and the east to Saskatchewan. The greatest distance from north to south is 1220 kilometers, from east to west 650 kilometers.
Located in the middle of the Rocky Mountains, Banff National Park is also known for its sulphurous hot springs. The water in the Upper Hot Springs Pool at Sulfur Mountain averages 38 ° C. Very remarkable are the 'hoodoos', more than 20,000 year old slate rocks in the form of high tables.
Jasper National Park is the largest and most northerly of the four national parks in the Rocky Mountains. It covers an area of 10,878 km2 with mountains, valleys, glacial lakes and the Columbia Icefield, a 400-year-old ice sea with a thickness of approximately 400 meters. Miette Hot Springs has the warmest spring water (up to nearly 54 ° C) of the Rockies with a high mineral content.
The Athabasca Glacier is the largest glacier in the Rocky Mountains, six kilometers long and with a total area of 300 km2. The glacier is an offshoot of the Columbia Icefield, the largest field of ice and snow in North America outside of the polar regions. Elk Island was established in 1906 as Canada's first animal sanctuary. The nature in the park consists of rolling meadows, forests and "wetlands". Wood Buffalo National Park is Canada's largest national park, roughly the same size as Denmark (44,807 km2). Declared a World Heritage Site in 1983 by UNESCO, the park encompasses three types of landscape: a highland, a plateau of swamps and streams, and the Peace and Athabasca river delta, filled with sediments, swamps and shallow lakes.
Located in Calgary, Fish Creek National Park is one of the largest urban parks in the world (1189 hectares).
Outside the valley of the Red Deer River stretches the "badlands" of Alberta, a stone desert with ravines, table mountains, plateaus and rock pillars, the so-called "hoodoos". This lunar landscape is one of the richest dinosaur fossil sites in the world.
BRITISH COLUMBIA
 Canada Pacific Rim National Park British ColumbiaPhoto: Dbaer in the public domain
Canada Pacific Rim National Park British ColumbiaPhoto: Dbaer in the public domain
British Columbia is Canada's westernmost province, covering nearly 950,000 km2. British Columbia is bordered on the east by the province of Alberta, on the south by the U.S. states of Montana, Idaho and Washington, on the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the northwest by the U.S. state of Alaska and on the north by the Yukon Territory and the Northwest Territories. The largest length of the province is 1300 kilometers; the largest width 700 kilometers. It is the third largest province after Quebec and Ontario. Approx. three quarters of this province is mountainous; more than half of the province is above 1250 meters. The only flat area is to the northeast on the Peace River. More than half of British Columbia is covered by forests. On the coast mainly Douglas fir trees and red cedar trees; inland forests with pine trees, firs and conifers. Approx. 10% of British Columbia is grassland or under cultivation; almost 2% of the area consists of rivers and lakes. There are approximately 11,000 rivers and streams and 7,000 lakes along the entire coast of British Columbia.
Just off the southwest coast of British Columbia, Vancouver Island is about the same size as the Benelux. Lengthwise a mountain ridge runs across the island with long mountain fjords on the west coast. The island is also famous for its beautiful sandy beaches and dense forests. In the large Strathcona Provincial Park are the highest waterfalls (440 meters) in North America, the Della Falls. The Pacific Rim National Park Reserve encompasses three areas: Long Beach with its rugged and windy beaches, the West Coast Trail with rainforests and deep gorges, and the Broken Group Islands, an archipelago of approximately 100 islands. The Queen Charlotte Islands are located north of Vancouver Island.
The north of the province is mountainous and the central interior consists of a high plateau with dense forests. A number of mountain ranges run from east to northwest.
Southeastern British Columbia, Kootenay consists of mountain ranges such as the Rocky Mountains (with the highest mountain in the Canadian Rockies, Mount Robson at 3954 meters), Purcells, Selkirks, and Monashees. Rivers like the Columbia River and the Arrow Lakes lie between them. Yoho Park is home to one of Canada's highest waterfalls, the 254-meter high Takakkaw Falls. The city of Kimberley is 1117 meters, making it Canada's tallest city. The Kootenay region is known for its many hot springs, but there is also the Glacier National Park (1350 km2) with about 400 glaciers and on the 3390 meter high Mount Dawson there is an average of 23 meters of snow in winter.
The Lower Mainland is a lagoon between the mountains of Vancouver Island and the Coast Mountains on the mainland. The Fraser River, the longest river in British Columbia at 1,368 kilometers, has created a long delta here.
The Okanagan Similkameen region is formed by Okanagan Valley, one of the foothills in a hill country between the Cascade Mountain Range to the west and the Monashee Mountain Range to the east. The Valley extends over a length of 250 kilometers and actually consists of a series of valleys, which are connected by a number of lakes.
In addition to the Fraser River and the Columbia River, the 611 km Peace River and the rivers Skeena, Yukon and Liard also flow in this province. The Liard River Hot Springs are located along the Alaska highway. Surface water seeps through the crevices and breaks to the red-hot rocks of the Earth's crust, which can be as high as 1,000 °C. The Charlotte Islands (approx. 150 islands) are located halfway along the British Columbia coastline; Because of the warm Gulf Currents from Asia, the climate here is always very humid and fog often hangs between the ancient rainforests with thousand-year-old firs and cedars.
Wells Gray National Park is one of the most beautiful natural areas in British Columbia and is characterized by mountain meadows, waterfalls and high mountains with glaciers. Mount Edziza Provincial Park is made up of volcanic landscapes, including lava flows and basalt plains. About a third of Atlin Provincial Park is covered by ice plains and glaciers.
MANITOBA
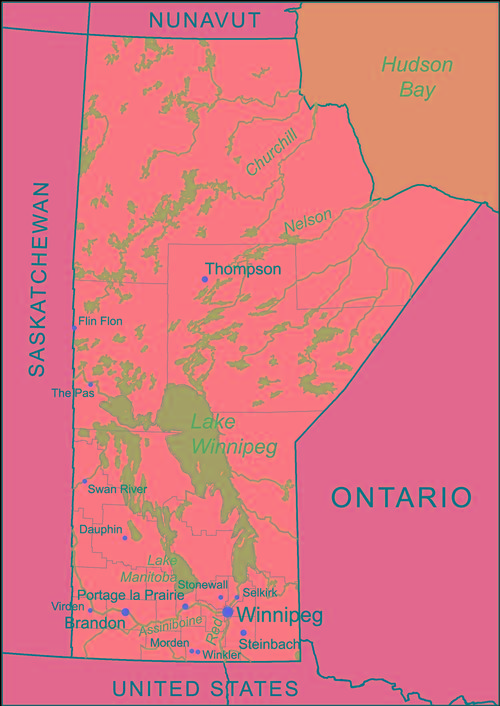 Map of ManitobaPhoto: Kmusser CC 3.0 Unported no changes
Map of ManitobaPhoto: Kmusser CC 3.0 Unported no changes
Manitoba is 650,000 km2 in size, making it the eighth largest province in Canada. The most central prairie province, Manitoba is located between Saskatchewan and Ontario. To the north, Manitoba borders the Nunavut Territory, to the northeast Hudson Bay, to the south to the U.S. states of Minnesota and North Dakota. The longest length is 1224 kilometers and the largest width is 793 kilometers. The highest point is Baldy Mountain (831 meters).
Manitoba's landscape forms the transition between the Saskatchewan prairies and the rolling hills and forests of Ontario. South Manitoba has mainly flat prairie land with large rivers such as the Red River and the Assiniboine. Important rivers are the Churchill River, the Hayes River, the Nelson River, the Saskatchewan River and the Winnipeg River. On the border with the American state of North Dakota is the International Peace Garden, which is the geographical center of the North American continent. To the north are forests and approximately 10,000 lakes with sandy beaches. In total, about half of Manitoba's area is forested with predominantly pine, aspen, silver birch and spruce trees. The Hudson Bay Lowland around the Hudson Bay is a flat and almost treeless tundra area where only moss, grass and lichens grow. There is an extensive agricultural area around the capital Winnipeg.
Lake Winnipeg is a huge 350-kilometer-long lake that connects southern Manitoba to Hudson Bay via the Nelson River. The northern half of the lake is surrounded by wilderness and the southern half is scattered with long white sandy beaches.
Near the town of Churchill, Canada's northernmost deep harbor lies at the mouth of the Churchill River and Hudson Bay, which was discovered by Henry Hudson in 1610. The Northern Lights or Aurora Borealis can be seen here from September to April.
NEW BRUNSWICK
 Grand Falls, New BrunswickPhoto: Benson Kua (CC BY-SA 2.0) no changes made
Grand Falls, New BrunswickPhoto: Benson Kua (CC BY-SA 2.0) no changes made
The very wooded New Brunswick covers almost 75,000 km2 and is the easternmost and largest of the Atlantic maritime provinces. The province is bounded on the north by Chaleur Bay and the province of Quebec; to the east by the Gulf of St. Lawrence, the Northumberland Strait and the province of Nova Scotia; to the south by the Fundy Bay; to the west by the US state of Maine.
A portion of the seacoast has dangerous cliffs and rocky shores. The coast also consists of dunes, sandy beaches and saltwater marshes. Furthermore, the province consists of agricultural areas and a mountainous interior with impenetrable forests.
New Brunswick is surrounded on three sides by water (2,400 miles of shoreline) and faces major tidal differences. The tides at Fundy Bay near Aukac are among the highest in the world with an ebb and flow difference of ten to sixteen meters. The high tide line is characterized by rugged seaweed-covered cliffs, caves and steep rock formations. The effect of the water has created rock formations in the form of flower pots, the so-called "Flower Pots" in Rocky Provincial Park. Twice a day, more than 100 billion tons of water wash in and out of the bay, the so-called "tidal bore".
New Brunswick is home to Canada's oldest city, Saint John. The River Valley Scenic Drive runs along the 724-kilometer Saint-John River. Along the route are the Grand Falls, hilly arable land, peninsulas and islands.
NEWFOUNDLAND & LABRADOR
 Canada Gros Morne Fjord Newfoundland and LabradorPhoto: Gilad.rom CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Canada Gros Morne Fjord Newfoundland and LabradorPhoto: Gilad.rom CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The province of Newfoundland includes not only the island of Newfoundland and Labrador (112,300 km2), but also the much larger Labrador (300,000 km2) on the mainland. The distance between the northernmost tip of Labrador, Cape Chidley, and the southeastern part of Newfoundland, Cape Pine, is approximately 1800 kilometers.
Newfoundland & Labrador is Canada's easternmost province with wild open spaces, high peaks and vast landscapes. The county is made up of the island of Newfoundland and the greater Labrador region on the mainland. The two parts are separated by the fifteen kilometers wide strait Strait of Belle-Isle. The area of this province is just over 400,000 km2.
The 25,000-kilometer coast is rocky with cliffs, fjords and inlets. In the sea to the east and south lies the large continental shelf Grand Banks, the richest fishing area in the world. This is due to the fusion of the cool Labrador Current and the warm Atlantic Gulf Stream. The landscape of Newfoundland & Labrador consists of semi-polar tundra and mountains in Northern Labrador to prairies, low mountains, dense forests, and rugged rocky outcrops in eastern New Foundland. The central plateau is a gigantic forest area, intersected by a number of rivers, the largest of which are the Humber, the Exploits and the Gander. The highest points, up to 814 meters above sea level, are in the western part of Newfoundland.
A World Heritage Site, the Gros Morne National Park is home to spectacular fjords, high cliffs and waterfalls. The coastal mountains are among the oldest in the world. The Long Range Mountains consist of mountainous tundra, covered with polar alpine flora. At Shallow Bay along the Green Gardens Trail are beaches and dunes.
The name of the vast Labrador peninsula comes from the Portuguese Corte Real, which referred to the relatively fertile area as 'terra de laborador'. It forms the extreme northeast of the North American continent, between Hudson Bay in the west, Hudson Strait and Ungava Bay in the northeast, and Belle Isle St and St. Lawrence Bay in the south. Most of the country consists of a high plateau, which is 300-700 meters above sea level, with a glacier-like relief and dotted with countless lakes. It is an important part of the Canadian Shield.
Off the coast, at the bottom of Newfoundland, there are two islands that belong to France, St. Pierre and Miquelon. These are the last remnants of the French empire in North America. About 6,000 people live there who have one Member in the French Parliament.
NORTHWEST-TERRITORIES
 Skyline Yellowknife Northwest-TerritoriesPhoto: Trevor MacInnes CC 1.0 Generic no changes made
Skyline Yellowknife Northwest-TerritoriesPhoto: Trevor MacInnes CC 1.0 Generic no changes made
The total area of this huge province is 3.3 million km2. The Northwest Territories, commonly referred to as NWT, are therefore ten times the size of Germany and cover more than a third of Canada's total area. The entire province is above the Arctic Circle, north of the 60th parallel. In the north is the unnamed highest peak of the Northwest Territories (2762 meters). A large part of the Territories consists of tundra area or "barren lands" and ice plains. The longest river in Canada, the Mackenzie River, flows through the Northwest Territories at 1,800 kilometers. One of the deepest lakes in the world can also be found here, namely the Great Slave Lake with a depth of over 600 meters. The highest waterfalls in Canada also occur in this province, from almost 90 meters high the water falls in the South Nahanni River.
Both the northern geographic pole and the north magnetic pole are located in this province. The geographic pole (Big Nail) is the place on top of the Earth where all imaginary lines converge. The magnetic pole can only be determined with the compass, and can vary considerably every year.
The Northern Lights or Aurora Borealis are clearly visible here in autumn and winter; due to colliding, electrically charged particles with atoms and molecules outside the stratosphere, dancing lights in various colors can be seen in the sky after sunset.
Ellesmere Island National Park Reserve is an area of glaciers and mountains, but there are also thermal oases.
The Northern Frontier region is located around the northernmost city in Canada, the capital Yellowknife. There are thousands of small lakes in this region.
The main rivers are the Mackenzie River, the Coppermine River, the Back River and the Thelon River.
NOVA SCOTIA
 Grafton, Annapolis Valley in Nova ScotiaPhoto: Public domain
Grafton, Annapolis Valley in Nova ScotiaPhoto: Public domain
Nova Scotia is one of the maritime provinces (Maritime Provinces), a peninsula of over 55,000 km2. Part of Nova Scotia, Cape Breton, is an island, separated from the rest of the province by the Strait of Canso. The rest is connected to the mainland by the isthmus of Chignecto. The province is hilly and forms the northern end of the Appalachian Mountains. The coastline is rocky with many coves or coves and islets. There are 400 lakes inland. Central Nova Scotia covers the coastline along the Northumberland Strait, where there are many warm seawater beaches. The coast of the Minas Basin has one of the highest tides in the world with an ebb and flow difference of 15 meters in some places.
Dartmouth is a city with no fewer than four hundred lakes and lakes within its borders. The 330-kilometer Lighthouse Route passes bays, inlets and fjords. Kejimkujik National park is a reserve with beaches, low tides, salt banks, green forests and lagoons. The town of Amherst overlooks the largest wetland area in the world, Tantramar. Cape Breton, the largest island in Nova Scotia, is one of the most impressive in Canada in terms of natural beauty. The park is located across the width of the tip of the island. Between the two coasts is a "highland plateau" of forests, lakes, swamps and river valleys.
Halifax is the province's capital and largest city, located on a huge seaport that is ice-free all year round. Sister city Darmouth is on the other side of the bay; the two cities are connected by two suspension bridges.
NUNAVUT
 Clyde River, NunavutPhoto: Ansgar Walk CC 2.5 Generic no changes made
Clyde River, NunavutPhoto: Ansgar Walk CC 2.5 Generic no changes made
The total area of Nunavut, including all water surfaces, is 1,982,182 km2, which is more than a fifth of the total area of Canada.
On April 1, 1999, Canada's newest territory became a reality: the Inuit country of Nunavut. Nunavut is made up of many islands, some of them the size of England. In Nunavut, the magnetic pole can be found at about 79 degrees north latitude. At 82.5 degrees latitude, Alert is the military base, the northernmost settlement in the world.
Victoria Island is part of the Northwest Territories and part of Nunavut. There are two towns on the island: Inuit Cambridge Bay belongs to Nunavut, Holman to the Northwest Territories. Nunavut has hills up to 500 meters high in the east and north.
Baffin Island has an area of 500,000 km2, making it the fifth largest island on Earth. More than half of the island is above the Arctic Circle. Auyuittuq National park is Canada's third largest national park with 21,470 km2. It is one of the few national parks above the Arctic Circle with many mountains, valleys and fjords. On Baffin Island, mountains occur up to more than 2500 meters.
On the coast at the Beaufort Sea there is a famous series of pingos or frost hills, created by the accumulation of the bottom under the pressure of ice underneath. The Mackenzie Delta pingos, the largest of which are 40 meters high and 300 meters in diameter at the base, are among the most impressive in the entire Arctic.
At Summit Lake, huge perpendicular walls of Mount Asgard can be seen. Mount Thor even has the highest continuous rock face on Earth.
ONTARIO

Ontario is the southernmost province in Canada and the second largest province in Canada with over one million km2. Ontario is bordered on the north by Hudson Bay and James Bay, on the east by Quebec, on the south by the St. Lawrence River, Lake Ontario, the US states of New York, Ohio and Michigan, Lake Erie, Lake Huron, Lake Superior, and to the west by the province of Manitoba. The largest distance from east to west is 1690 kilometers and from east to west 1610 kilometers.
To the south of this province are the great lakes of Lake Superior, Huron, Michigan, Erie and Ontario, which in turn connect the great rivers of St. Lawrence, Niagara, Ottawa and Rideau.
Lake Erie is approximately 400 kilometers long and 60 kilometers wide on average. It is the shallowest of the Great Lakes and separates Canada from the United States. Lake Superior or Bovenmeer is the westernmost of the Great Lakes, and the largest freshwater reservoir in the world at 82,000 km2.
Ontario is home to the most famous waterfall in the world, Niagara Falls, and more than 250,000 lakes, large and small. The Canadian Horseshoe waterfall is 54 meters deep and 675 meters wide; the American waterfall is 56 meters deep and 320 meters wide. Every minute, 115 million liters of water fall into the Horseshoe Falls.
Uninhabited northern Ontario, Algoma land is an area of forests, waterfalls, ravines and mountains. Located in the landscape of the Northern Canadian Shield, the Sudbury Basin is home to many metals and minerals, including gold, silver, platinum, cobalt and especially nickel.
In the St.-Lawrence River lie the Thousand Islands, an area with more than 1000 islands. Prince Edward County Island has 25-meter-high fine sand dunes; they are considered to be one of the most important freshwater dune areas in the world.
The Algonquin Provincial Park is the oldest and most famous park in Ontario with an area of 7725 km2 of untouched nature and more than 1000 lakes. Located just off the north shore of Lake Huron, Manitoulin Island is the largest island in a lake in the world with an area of 2,800 km2.
St. Lawrence Islands National Park is located in the river of the same name, where it forms the border with the state of New York. The park consists of 18 wooded islands and some eighty rocky small islands.
Important rivers in Ontario are the Abitibi, the Albany, the Attawapiskat, the Montréal, the Moose, the Niagara, the Ottawa, the Thames, the Trent and the Winisk.
PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND
 Coastal landscape Cavendish, Prince Edward IslandPhoto: Chensiyuan CC 4.0 International no changes made
Coastal landscape Cavendish, Prince Edward IslandPhoto: Chensiyuan CC 4.0 International no changes made
Prince Edward Island is the smallest province in Canada with an area of 5657 km2. Prince Edward Island measures approximately 200 kilometers from east to west; the width varies from 6 to 65 kilometers. The island lies in the St. Lawrence gulf and is only connected to the mainland by a bridge, the Confederation Bridge (13 kilometers long). It is the longest continuous arch bridge over the sea in the world. Prince Edward Island has only been an island for about 500 years, when rising sea levels created Northumberland Strait. The Bonshaw Hills are about 120 meters high diagonally across the island. The highest point is 147 meters above sea level. The soil is rusty brown due to the ferrous soil.
Prince Edward Island National Park is Canada's smallest national park, located along the shoreline of the St. Lawrence gulf.
The park spans 40 km2 of rugged dunes that are constantly shifting places due to the stormy winds, and further saltwater swamps, rocks and vast beaches. Prince Edward Island also has huge agricultural areas.
QUEBEC
 Boreal landscape in Northern QuebecPhoto: Peupleloup CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Boreal landscape in Northern QuebecPhoto: Peupleloup CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The largest province in Canada is Quebec with approximately 1.5 million km2. Quebec is bordered on the north by the Hudson Strait, Ungava Bay and the Atlantic Ocean, on the east by the Province of Newfoundland, on the south by the Gulf of St. Lawrence, the Province of New Brunswick and the US states of Maine, New Hampshire , Vermont and New York, and to the west by the province of Ontario, James Bay and Hudson Bay. The greatest distance from east to west is 1570 kilometers and from north to south 1970 kilometers. Approx. 90% of the province belongs to the Canadian Shield. Half of the province consists of extensive (maple) forests, tundra, lakes and rivers. Quebec is so long that the northern part is in the polar region and is part of the eternally frozen Canadian Shield. The highest points are in the south with Laurentides Park at 1100 meters and Mont Tremblant at 960 meters.
The northern peninsula of Gaspé or popularly called La Gaspésie is 240 kilometers long and lies at the mouth of the St. Lawrence River (French: Fleuve St. Laurent) and the Gulf of St. Lawrence. It is a rugged area with wooded mountain ridges of the Monts Chic-Choc, with the highest peaks Mont Richardson (1173 meters) and Mont Jacques Cartier (1268 meters).
In the Gulf of St. Lawrence are the Îles de la Madeleine (Magdalen Islands), an archipelago consisting of twelve islands. In summer, the water sinks so far that the islands of Ile de l'Est, Ile du Havre-aux-Maisons, Ile du Capaux-Meules and Ile-du-Havre-Aubert are connected by dunes. Ile d'Anticosti is the largest island in the Gulf of St. Lawrence and also a nature reserve.
The Laurentians are part of the Canadian Shield whose hilly area of the Saint-Laurent Lowlands contains many lakes and mountains. The highest mountain of the Laurentians is Mont Tremblant with 978 meters.
The Saint Lawrence Seaway (completed in 1959), which connects Canada's major industrial area (Ontario) to the Atlantic Ocean, is the most heavily inland waterway used for transportation and of great importance to the economy. The Seaway is the longest inland waterway in the world at 553 kilometers. Other important rivers are the Ottawa, the Saint Maurice, the Saguenay and the George River.
The maple forests turn beautifully red and orange in autumn; in the spring the famous maple syrup is harvested. The maple leaf is the national symbol of Canada and has also been on the flag since 1965.
Chute Montmorency is Quebec's most famous waterfall, higher than Niagara Falls at 86 meters. The Charlevoix coast is a UNESCO World Biosphere Reserve because of the boreal (northern or arctic) forest that grows here. Nearby is the Jardin des Grands Jardins with a complex of lakes and an evergreen taiga forest.
Central Quebec is characterized by a rocky, fir-covered wasteland. In 1984, the islands of the Mingan Archipelago became Canada's first national island park. The islands have become known for the bizarre limestone monoliths that have the shape of flower pots, among other things.
At Charlevoix, a meteorite with a diameter of more than two kilometers hit 350 million years ago. In less than a minute, he hit a 5-kilometer-deep crater with a 55-kilometer diameter, making the Charlevoix crater one of the largest on Earth.
SASKATCHEWAN
 Saskatchewan LandscapePhoto: Public domain
Saskatchewan LandscapePhoto: Public domain
One of the prairie provinces, Saskatchewan is flat, characterized by many forests, lakes and almost endless wheat fields, which account for much of Canada's grain and bread production. The total area of this province is nearly 650,000 km2 and the Saskatchewan River flows right through it. Saskatchewan is bordered on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, on the south by the U.S. states of North Dakota and Montana, and on the west by Alberta.
The north is flat, virtually uninhabited and is part of the Canadian Shield. The Cypress Hills form the highest point in the province at 1386 meters. The Prince Albert Provincial Park contains approximately 10,000 lakes. Yesterday is also good to see the transition from Southern to Northern Canada. The southern part is made up of birch and prairie forests, the northern part is wetter, with lakes, pines and spruces, the beginning of the vast forests of Northern Canada. In the southwest is Cypress Hills Provincial Park, a mountain range of 1389 meters high in a desert-like environment with many dunes and sand creeks. From the Diefenbaker Lakes to the eastern border of the province we only encounter flat prairie land.
In the southwest of the province lies Grasslands National Park with one of the last authentic grasslands in North America. The temperature in the park varies widely, from 40 °C in summer to -40 °C in winter.
Just north of Regina, the Qu'Appelle River valley is attractive. The river separates the flat meadows to the south of the more hilly grassland north of the river. Major rivers are the Churchill River, the North Saskatchewan River and the South Saskatchewan River.
YUKON TERRITORY
 Yukon River LandscapePhoto: Dave Bezaire & Susi Havens-Bezaire CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Yukon River LandscapePhoto: Dave Bezaire & Susi Havens-Bezaire CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The province covers an area of 483,450 km2 and is the province with the highest mountains in Canada. Yukon Territory borders the Beaufort Sea to the north, from Northwest Territories to the east, and British Columbia to the south, and part of the US state of Alaska. The greatest length from north to south is 1050 kilometers, from east to west 930 kilometers. In the southwest of Yukon is Kluane National Park, with twenty peaks higher than 4,200 meters and Canada's highest mountain, Mount Logan, at 5,959 meters. Said national park is again part of the St. Elias Mountains.
The Hubbard and Lowell Glaciers are the largest non-polar ice fields in the world with an area of approximately 8,500 km2 in 1.6 kilometers thick. Drainage of most of the Yukon Territory takes place through the immense river system of the 3,185-kilometer Yukon River and its side arms.
Northeast of the capital Whitehorse is the Carcross Desert, the smallest desert in the world. The presence of the rare Lazulite crystal is remarkable.
Rivers and lakes
Canada's rivers and lakes are one of the largest inland water areas in the world. The Mackenzie River system is the longest in Canada at approximately 4,250 km and drains about a quarter of Canadian territory into the Arctic Ocean. The drainage of the Canadian Shield area and the Interior Plains is largely via Hudson Bay on the Atlantic Ocean. Of this area, the Nelson River system is the largest, with rivers such as the Saskatchewan, Assiniboine, Red Deer and the Bow.
The waters of the Maritime Provinces and of Southeastern Quebec are largely oriented towards Canada's largest river, the Saint Lawrence, which drains into the Atlantic Ocean. The Rocky Mountains form the watershed between the Shield area and the Pacific drainage basin, and the main rivers here are the Yukon in northwestern Canada and the Columbia and Fraser in the southwest.
The many lakes, about two million, are remnants from the post-glacial period and often connected by rivers. The largest lakes in Canada are the four Great Lakes, namely Lake Superior or Upper Lake, Lake Huron, Lake Erie and Lake Ontario, as well as Lake St.-Clair and Lake Winnipeg.
In the south, the rivers and lakes are covered with ice for about five months of the year; in the north, on the other hand, only the largest rivers are ice-free for one to two months.
Sources
Canada
The Reader’s Digest
Canada
Cambium
Heetvelt, A. / Canada
ANWB
Ivory, M. / Canada
Kosmos-Z&K
Jepson, T. / Canada
Van Reemst
Njio, F. / Canada
Kosmos-Z&K
Roy, G. / North Canada
Bradt Wal, C.P.F. van der / Canada van A tot Z : praktische informatie over wonen en werken in Canada
DEN, Stichting Dienstverlening Emigratie Nederland
Weber, Wolfgang R. / West-Canada : Alberta, British Columbia
Lannoo
Zuilen, A.J. van / Gids voor Canada
Gottmer
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info