USA
Economy
Economy
Cities in USA
| Atlantic city | Boston | Dallas |
| Detroit | Las vegas | Memphis |
| Nashville | New york | Seattle |
Popular destinations USA
| Arizona | California | Florida |
| Hawaii | Utah |
Economy
General
The American economy rests on the pillars of the free market and private entrepreneurship ("free enterprise"), whereby the influence of the government is very limited. Railways, electricity companies, telephone and the like are largely privately owned. However, the government certainly does not completely refrain from influencing economic life. For example, it has a decisive say in the rates charged by the utilities to its customers, and the central banking system was pulled into the government sphere by the Federal Reserve System by a 1913 law.
Trust has also been rigorously monitored over time, prohibiting market separations, monopolization and price fixing. The government also influences economic life through taxation, labor protection laws, quality requirements and consumer protection provisions. There are no real state-owned companies in the United States.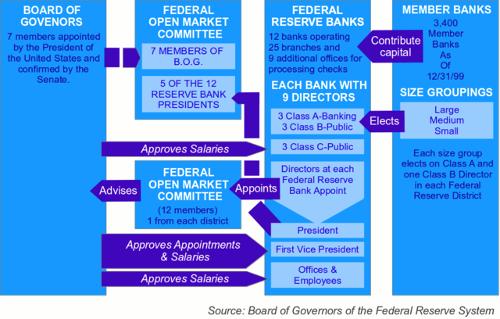 Federal Reserve System, USAPhoto: Kimse84 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Federal Reserve System, USAPhoto: Kimse84 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The United States has become the wealthiest country in the world over time. The vast expanse, the many possibilities for agriculture, the presence of almost all major minerals (only oil is a problem) and an enterprising and resourceful population, have made the country the most powerful economic power in the world, taking up almost a quarter of world production. Only Japan has come somewhat close to the United States in recent decades.
For several years after the severe recession of 1982, the US economy experienced a period of continuous expansion, with an average growth of 4% per year. The new economic government policy was based on stimulating the supply side on the market. Lower taxes and deregulation led to increased business investment, and cutbacks on several federal programs, including those in the social sector. The fall in oil prices, interest rates and the dollar further contributed to the recovery of the economy. But at the same time the budget deficit also increased enormously. The trade deficit widened from $ 35 billion in 1982 to $ 800 billion in 2017. Tighter monetary policy was pursued to help curb the increasingly slow-growing economy, including to contain inflation. The United States suffered from the housing crisis in the 21st century, followed by the credit crunch. Nevertheless, GDP per capita ($ 59,800 in 2017) is one of the highest in the world. Yet in 2017, 15.1% of the population lived below the poverty line. Poverty is particularly high among the non-white population. Approx. 22% of Indians, blacks and Hispanics can be classified as poor. About 40% of the poor live in major cities. In 2017, the labor force was 0.7% active in agriculture, 20.3% in industry and 79% in services.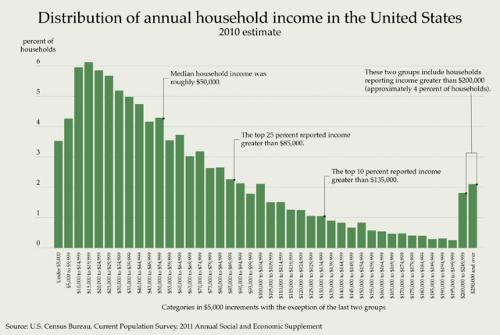 Distribution of annual household income in the USAPhoto: Vikjam CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Distribution of annual household income in the USAPhoto: Vikjam CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The US economy is developing quite favorably with growth of around 2% per year, 2.2% in 2017). Unemployment is at 4.4% and prices are stable.
Agriculture, livestock farming, forestry and fishing
The US agricultural sector contributes only 0.9% (2017) to the GDP of the United States. The massive volume of agricultural production has made the United States the world's largest exporter of agricultural products for a long time, a position that expanded further in the 1980s. Medium and large farms predominate; far-reaching mechanization and application of the latest agricultural methods are characteristic of these companies. Small, traditional farms have been displaced by larger, efficient and technologically equipped farms. The number of agricultural companies is declining. Grain silos in North Dakota, USAPhoto: Mark Goebel from Taos, New Mexico, USA CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Grain silos in North Dakota, USAPhoto: Mark Goebel from Taos, New Mexico, USA CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Climatic and physical-geographical conditions have created different agricultural zones. The northeastern states and the Great Lakes regions belong to the dairy zone, the so-called "dairy belt". The east coast has many horticulture, fruit and poultry farming. South of the dairy belt, the corn and soybeans, which are important for livestock farming, are grown in the corn soy belt. The large cotton plantations in the once famous 'cotton belt' have now largely given way to mixed agricultural companies. Due to better agricultural methods, the yield of the still existing cotton plantations is higher than before. Citrus fruits, sugar cane and rice are grown on the coast of Florida and Texas. The Middle West is the breadbasket, known as the "wheat belt". California has extensive vegetable and fruit farms, while viticulture has become of great importance there.
The main products from the arable farming sector are maize, soybeans, wheat, tobacco, cotton, sorghum, potatoes, rice, oats and sugar beet.
The United States is also the largest producer in the world in livestock farming and is therefore of equal importance to the agricultural sector as arable farming. The US animal husbandry sector is mainly focused on supplying its own domestic market. Cattle farming takes place in Texas, Iowa, Nebraska, Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma, and Wisconsin. Livestock farming is extensively practiced in the west.
In the south and the west mainly beef cattle are kept, in the north and northeast and in the large cities dairy cattle are kept. Pig farming is mainly carried out in the north. Of great significance is poultry farming, which is concentrated in California, New England, North Carolina and Georgia. Cattle in Ohio USAPhoto: U.S. Department of Agriculture CC 2.0 General no changes made
Cattle in Ohio USAPhoto: U.S. Department of Agriculture CC 2.0 General no changes made
Approx. 30% of the country's surface is still covered with forests. This makes the United States, after the Russian Federation and Brazil, one of the most wooded countries in the world. Two thirds of these can be exploited commercially and 73% of this is privately owned. The timber industry owns significant forest areas and is also committed to expanding them. Nevertheless, wood production has been declining for years.
Commercial forestry mainly takes place in the great coniferous forests of Northern California, Washington and Oregon, which also has the largest sawmills in the world, mainly working for the paper industry and in the mixed forests of the Southeast. A third important forest area is the Rocky Mountains.
The forest areas are used for wood extraction, but also for food supply, nature management, drinking water supply and recreation.
Fishing in itself makes only a modest contribution to the US economy, and the products are mainly used for local consumption. The United States has fishing grounds in the Atlantic Ocean, where it mainly catches cod, mackerel, herring and sole. The main fishing areas are the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
The main import products are shrimp, salmon, crab, lobster and tuna. The main import countries are Canada, Thailand, China, Chile, Vietnam, Mexico and Indonesia.
The Fishery Conservation and Management Act of 1976 declared a zone 200 miles offshore prohibited from foreign fishermen.
Mining and energy supply
The United States is very rich in resources and one of the most important mining countries in the world. They take first place in the extraction of magnesium, phosphate and molybdenum. The extraction of natural gas, oil, lead, copper, gold and coal are also very important to the economy. The United States has the largest coal supply in the world, and the center of gravity of extraction is in Pennsylvania. Coal is also extracted in the Rocky Mountains.
Besides the normal extraction of petroleum, the extraction of shale gas is important. Major natural gas reserves are in Texas and Louisiana.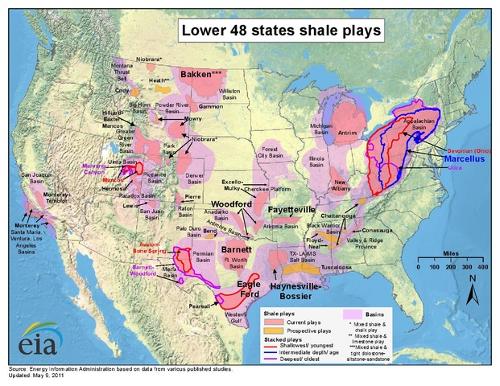 locations in the USA where shale-gas is extractedPhoto: U.S. Energy Information Administration May, 2011 in the public domain
locations in the USA where shale-gas is extractedPhoto: U.S. Energy Information Administration May, 2011 in the public domain
Iron ore mining, mainly taking place in the North and in the Appalachians, Utah, Nevada and Southern California, is also no longer sufficient to cover domestic demand. This also applies to the mining of copper ore that takes place in Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada and Montana, where gold and silver are also mined. Bauxite is mainly found in Arkansas and Georgia, but not enough to meet the demand of the aluminum industry. Uranium ore is found in the Rocky Mountains.
Some minerals are mainly imported, especially from Canada and Mexico: including manganese, bauxite, platinum, tungsten, chromium, potassium and nickel.
The United States currently uses 27% of total world energy production. Not surprising when you consider that per capita consumption is almost four times higher than the world average. Power is supplied mainly from cogeneration plants, the majority of which are fed by petroleum, natural gas and coal. Nuclear energy only provides a small part of the total energy supply.
Renewable energy sources provide for a limited part of the power generation capacity of the United States. Hydroelectric power stations, such as those in the Tennessee River, also provide a substantial share of the energy supply. Biomass and solid urban waste on the one hand and solar, wind and geothermal energy on the other hand each provide approximately 1% of the total capacity. The total amount of sustainably generated energy remains limited to date. Hydroelectric power plant Glendo State Park, Wyoming, USAPhoto: Wusel007 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Hydroelectric power plant Glendo State Park, Wyoming, USAPhoto: Wusel007 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Industry in general
The United States is also the largest industrial nation in the world. The core area of the industry is the manufacturing belt, in the triangle formed by New York, Chicago and St. Louis. Texas is the center of the petrochemical industry, while the western states, particularly the areas around Los Angeles, San Francisco and Seattle, have attracted many industrial establishments in recent decades.
Characteristic of the American industry are the large industrial companies that are often merged into large groups. These concentrations mainly occurred in the car industry, the telephone, aircraft, steel and cigarette industries.
Chemistry and plastics
The chemical industry is one of the largest industries in the United States, with more than 1 million employees. There are hundreds of chemical companies that have more than 13,000 production units. Major states include California, Texas, Florida, Illinois, New Jersey, Ohio and Pennsylvania, and the chemical industry is also the largest exporting industry. The production and sales turnover of the plastics industry is still increasing every year. About 60,000 people work in this branch of industry. Midland, Michigan, USA with Dow Chemical plant and headquartersPhoto: Doc Searls from Santa Barbara, USA CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Midland, Michigan, USA with Dow Chemical plant and headquartersPhoto: Doc Searls from Santa Barbara, USA CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Biotechnology
The most interesting developments in biotechnology are in the sub-sectors dedicated to the development of medicines and vaccines, genetically modified crops, food and pesticides.
American agriculture relies heavily on biotechnology. Many genetically modified crops are grown.
Most biotechnology companies are located in the northeast of the country and in and around the major cities along the west coast.
Computer industry
The United States is the world leader in computer technology and innovation. A large part of the world market in this sector is owned by American companies. The US computer industry employs 2 million people worldwide, of which more than 1 million are in the United States. A number of US computer companies have moved production to Asian countries for competitive reasons due to much lower production costs.
The majority of microprocessors and software are still being developed in the United States. The technological innovation from Silicon Valley, where many leading companies have their headquarters, is world famous.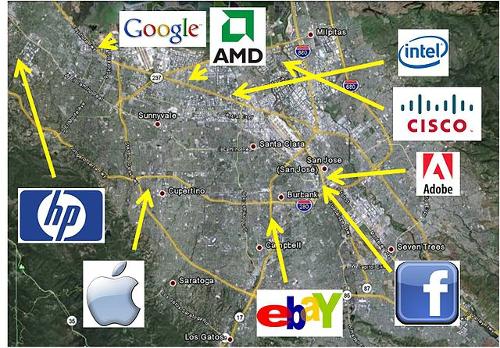 Leading (computer)companies all together in Silicon Valley, USAPhoto: Samykolon CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Leading (computer)companies all together in Silicon Valley, USAPhoto: Samykolon CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Machine industry
About 1.4 million employees work in more than 20,000 machine factories, producing approximately $ 500 billion annually. However, much is also imported from abroad. The major states of revenue are Illinois, Ohio, California, Michigan and New York.
Automotive industry
The United States is one of the major automobile manufacturers in the world. This industry accounts for about a quarter of total world production and that share is only increasing. The three largest US automakers are General Motors, Ford and Chrysler. Automotive production mainly takes place in the north of the Midwest.
Aerospace industry
The aerospace industry is one of the most successful industries in the United States, with enormous market value. Airplanes and aircraft parts are the main products in this industry.
About 35% of its total production is supplied to the United States Department of Defense, and more than half of its production is sold abroad. Major companies include Lockheed Martin, Raytheon, Boeing, Honeywell and Northrop Grumman. Boeing Factory in Washington USA, where Boeing-wide bodies are fabricatedPhoto: Piergiuliano Chesi CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Boeing Factory in Washington USA, where Boeing-wide bodies are fabricatedPhoto: Piergiuliano Chesi CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Trade
Foreign trade - compared to domestic trade - is relatively small in size, as approximately 90% of all agricultural and industrial products are consumed in the United States itself. Trade with foreign countries has only increased since the mid-1980s and forms an increasingly important part of the economy. The huge export surplus in the 1960s has now turned into a trade deficit.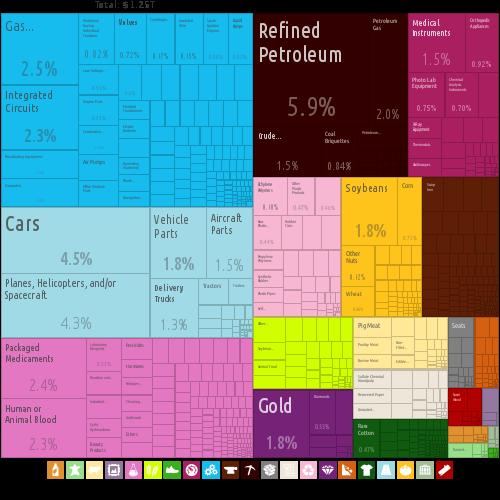 Main export products USAPhoto: Alexander Simoes, Cesar Hidalgo, et. al. CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Main export products USAPhoto: Alexander Simoes, Cesar Hidalgo, et. al. CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The United States is still one of the largest exporting countries in the world, exporting $ 1.553 billion in 2017. The main export partners were Canada, Mexico, China and Japan. The main export products are: machinery, cars and car parts, aircraft, chemicals and food products, including grain. Imports are mainly cars and car parts, electrical appliances, petroleum and petroleum products, chemical and agricultural products. Total value of imports in 2017 was $ 2.361 billion. The main import partners were China, Canada, Mexico, Japan and Germany.
Traffic
The United States has the largest road network and the highest motorization rate in the world. For daily short-distance passenger transport, the car is still the most frequently used and preferred means of transport. The facilities required for this have had far-reaching consequences, especially for urban planning. Due to the large number of private cars and the extensive use that is made of them (e.g. for commuting), public transport is poorly developed in some urban areas such as Los Angeles.
The leisure activities of the Americans are also influenced by the car. The east in particular has a very dense road network. For longer distances, the "interstate highways" (6 million kilometers) are important, of which a large number are toll roads. The core of this system is the toll-free interstate freeways. Bus traffic plays an important role in particular for passenger transport over longer distances (Greyhound and Continental Trailways). Greyhound bus, USAPhoto: SounderBruce CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Greyhound bus, USAPhoto: SounderBruce CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The significance of the railways for passenger and freight transport has declined rapidly after the advent of cars and air travel. Due to a complex of causes, the private railway companies lost the competition with the car and later the plane. Investments, extensions and adaptation of the network and renewal of the equipment were not carried out, as a result of which the passenger and goods supply fell even further.
As far as freight transport is concerned, the rail lines are the most important transport lines. Approx. 35% of the volume of commercial freight transport is accounted for by the train. Amtrak, national train company USAPhoto: User:DanielHolth CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Amtrak, national train company USAPhoto: User:DanielHolth CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Inland navigation is of great importance for the transportation of goods, especially in the catchment areas of the Ohio, Missouri and Mississippi and on the Great Lakes. A waterway network with a total length of 40,000 kilometers is available.
A number of major canals connect key seaports and industrial areas, such as the St. Laurence Seaway, the Illinois Waterway and the Intracoastal Waterway. Chicago is the largest inland port. The major seaports are: New York, New Orleans, Houston, Baltimore, Newport, San Francisco and Los Angeles.
Aviation is of great importance for domestic passenger transport. In fact, domestic passenger transport by air accounts for nearly 50% of total global air traffic. There are a large number of airlines (the largest US Airlines-United Airlines, American Airlines and Delta Air Lines) and more than five hundred cities have airports. The busiest airports are: Chicago, Dallas, Los Angeles, Atlanta, New York (J.F. Kennedy), San Francisco, Denver, Miami, New York (La Guardia) and Boston. US Airways, USAPhoto: Aero Icarus from Zürich, Switzerland CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
US Airways, USAPhoto: Aero Icarus from Zürich, Switzerland CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Sources
Phillipson, O. / USA
Heinemann Library
Sandak, C.R. / Verenigde Staten van Amerika
Corona
Stanic, S. / De Verenigde Staten
Schuyt & Co
Supermachten
Stichting Teleac 1: Verenigde Staten van Amerika
Verenigde Staten
Uitgeversmaatschappij The Reader’s Digest NV
Webb, M. / The United States
Lucent Books
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Last updated February 2026Copyright: Team The World of Info