MANITOBA

Popular destinations CANADA
| Alberta | British columbia | Manitoba |
| New brunswick | Newfoundland and labrador | Northwest territories |
| Nova scotia | Nunavut | Ontario |
| Prince edward island | Quebec | Saskatchwan |
| Yukon |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Manitoba is 650,000 km2 in area, making it the eighth largest province in Canada.
Manitoba is the most central prairie province and lies between Saskatchewan and Ontario. Manitoba borders the Nunavut Territory to the north, Hudson Bay to the northeast and the US states of Minnesota and North Dakota to the south. Its greatest length is 1224 kilometres and its greatest width 793 kilometres. The highest point is Baldy Mountain (831 metres).
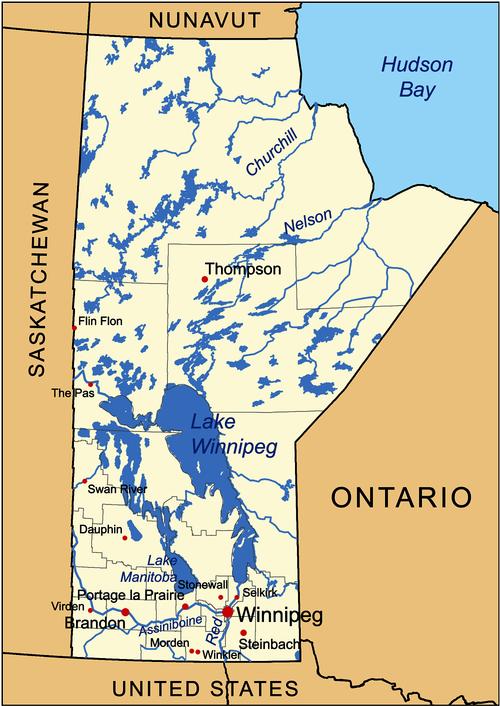 Map of Manitoba with main citiesPhoto: Kmusser CC BY-SA 3.0 no changes made
Map of Manitoba with main citiesPhoto: Kmusser CC BY-SA 3.0 no changes made
Landscape
Manitoba's landscape is a transition between the prairies of Saskatchewan and the rolling hills and forests of Ontario. Southern Manitoba has mainly flat prairie land with large rivers like the Red River and the Assiniboine. Other important rivers are the Churchill River, the Hayes River, the Nelson River, the Saskatchewan River and the Winnipeg River. On the border with the American state of North Dakota is the International Peace Garden, where the geographical centre of the North American continent is located. Further north are forests and about 10,000 lakes with sandy beaches. In total, about half of Manitoba's surface is forested with mostly pine, aspen, silver birch and fir trees. The Hudson Bay Lowland around the Hudson Bay is a flat and almost treeless tundra area where only moss, grass and lichens grow. Around the capital Winnipeg is an extensive agricultural area.
Lake Winnipeg is a huge 350-kilometre-long lake that connects southern Manitoba to Hudson Bay via the Nelson River. The northern half of the lake is surrounded by wilderness and along the southern half are scattered long white sandy beaches.
 Sunset over Lake WinnipegPhoto: Non-dropframe CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Sunset over Lake WinnipegPhoto: Non-dropframe CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Near the town of Churchill is Canada's northernmost deep-water port at the mouth of the Churchill River and Hudson Bay, which was discovered by Henry Hudson in 1610. From September to April, the Northern Lights or Aurora Borealis can be seen here.
Climate and Weather
The climate in Manitoba is generally characterised by warm, sunny summers and cold winters. In July and August the temperature rises to about 25°C, but in the middle of winter it remains below freezing.
The temperatures in a number of places are as follows:
average january minimum and average july maximum
Brandon -19.7°C 18.8°C
The Pas -22,7°C 17,7°C
Thompson -26.6°C 15.6°C
Churchill -27.5°C 11.8°C
In Manitoba it is warmer in the south and cooler in the north than, for example, in the neighbouring province of Saskatchewan.
This is because Hudson Bay provides a less extreme continental climate. The highest temperature ever recorded is 33.9°C. In 1964 the temperature dropped to -45.4°C.
The climate in Manitoba can vary considerably: from 30°C in the summer to -40°C in the winter. The average annual snowfall, especially in the south of the province, is over 100 cm (Winnipeg 126 cm, Brandon, 117 cm). Most snow falls in northeastern Manitoba, east of the Bissett-Churchill line, and in the Duck and Riding Mountains, about 160 cm per year. More than half of all precipitation falls in summer, often in short heavy showers. The south of Manitoba has, on average, very many hours of sunshine per year, which is normal for a prairie area.
Plants and Animals
The marshy part of Grand Beach Provincial Park is home to many bird species, including the rare and endangered whooping plover. The Oack Hammock Marsh is home to bird species such as the garganey and the Ammospiza caudacuta, a special species of sparrow.
The Narcisse Wildlife Management Area has been established to safeguard the habitat of thousands of garter snakes. An evergreen spruce and pine forest in Riding Mountain National Park provides habitat for elk, wapitias and a small herd of bison. Elms, oaks and maples grow on the eastern side of the park, sheltering a rich understory of shrubs, vines and ferns, a habitat almost unheard of on the prairies.
Churchill is also known as the 'Polar Bear Capital of the World'. As autumn approaches, polar bears migrate to the bay east of Churchill, and around 150 pass through the town.
Between June and September, about 3000 belugas or white dolphins gather at the mouth of the Churchill River.
The Spruce Woods Provincial Park is home to rare animals such as hook-nosed snakes, garlic toads and northern prairie skinks.
The plant symbol of Manitoba is the prairie crocus.
Sources
Elmar Landeninformatie
Wikipedia
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info