NORWAY
Society

Society

Cities in NORWAY
| Oslo |
Society
State structure
The Norwegian constitution dates from 1814 along the lines of that of the United States. In 1884, the parliamentary system was introduced, whereby the government is accountable to the representatives of the people. In 1898 universal male suffrage was introduced, in 1913 as the second country in Europe after Finland, also female suffrage. A referendum can be held on important issues. In 1994 the majority of Norwegians voted against membership of the European Community. The Kingdom of Norway has existed since 1905 and is a constitutional monarchy with an elected parliament (Storting). Legislative power rests with the 165-member Storting, elected by universal suffrage under a district system for four years. Parliament building NorwayPhoto:Ggcardinal from Norway CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Parliament building NorwayPhoto:Ggcardinal from Norway CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Norway has a mixture of one- and two-chamber system: there is only one chamber, but it divides itself into a Lagting (3 of the members) and an Odelsting (H). Usually the Storting meets in full, but bills are discussed first in Odelsting and then in Lagting. Executive power is formally vested in the king, but the state councilor determines the content of the royal decrees, which must be co-signed by the prime minister. The king appoints the members of the privy council (government), who is answerable to parliament. For the current political situation, see chapter history. Meeting room Storting, NorwayPhoto: Smuconlaw CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Meeting room Storting, NorwayPhoto: Smuconlaw CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Administrative division
The country is divided into nineteen provinces (fylker), headed by a governor (fylkesmann). The smallest administrative units are the 439 municipalities. Svålbard (Spitsbergen) has a special status and is administered by a governor (sysselmann), who falls directly under the government in Oslo. Oslo is an independent province. The island of Jan Mayen in the Arctic Ocean also belongs to Norway.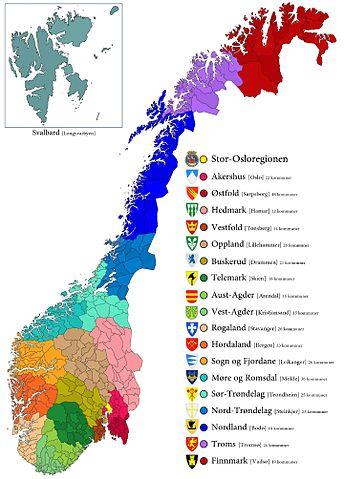 Regions NorwayPhoto: Antonio Ciccolella CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Regions NorwayPhoto: Antonio Ciccolella CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Education
Children attend a nine-year, usually public elementary school from kindergarten age. From the fourth grade, the children learn the English language. In the eighth grade they can still choose a foreign language. Secondary school lasts three years. Primary school in Stord off the southeast coast of NorwayPhoto: Wolfmann CC 4.0 International no changes made
Primary school in Stord off the southeast coast of NorwayPhoto: Wolfmann CC 4.0 International no changes made
After secondary school, one can study at various universities and colleges. The oldest university is Oslo, which dates back to 1813. Main building Oslo UniversityPhoto: Riaz CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Main building Oslo UniversityPhoto: Riaz CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The University of Tromso was founded in 1969 especially for the residents of Northern Norway. Campus Universitetet i Tromsø, NorwayPhoto: Maja Sojtaric CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Campus Universitetet i Tromsø, NorwayPhoto: Maja Sojtaric CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Sources
Dominicus, J. / Noorwegen
Gottmer
Hoogendoorn, H. / Noorwegen
ANWB
Meesters, G. / Zuid-Noorwegen
ANWB media
Schagen, K. / Noorwegen
Kosmos-Z&K
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Last updated June 2025Copyright: Team The World of Info