GAMBIA
Society

Society

Society
State structure
The Gambia has been a republic since April 26, 1970, with a president as head of state who is also head of government. The Gambia has one chamber (National Assembly) with 45 members who are elected by the people for five years. There are as many as there are administrative areas (45). The National Assembly is further expanded with eight members who do not have the right to vote: the Minister of Justice, a chairman, a deputy chairman and five deputy members. There are also five district chiefs (Chiefs) in the National Assembly.
General elections were held for the first time in 1964. Just like in England, the elections are held according to a district system. The Gambia is administratively divided into six “divisions” (provinces). These are divided into 45 districts. For the current political situation see chapter history.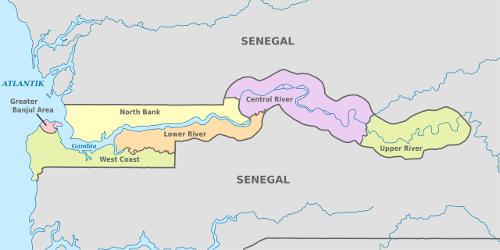 Administrative division in The GambiaPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Administrative division in The GambiaPhoto: TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Education
Just over a quarter of the population has finished school. A much larger percentage can read and write. There is no compulsory education, and it does not matter when children go to school for the first time. Usually at the age of five or six. Further education is followed by only 25% of the children in rural areas. Six-year primary education is free. It is mandatory to wear a school uniform, the cost of which must be paid by the parents. There are private schools as well as schools funded by the government. The Quran is taught in mostly Islamic schools, which is why Arabic lessons are compulsory. Red Cross school, GambiaPhoto: Lars Curfs CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Red Cross school, GambiaPhoto: Lars Curfs CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
In the interior there are still mission schools. The secondary and higher schools pass on their costs in full to the parents. Secondary education is divided into three years of “junior secondary school”. After that, one can continue at the “senior secondary school”.
The higher courses take an average of five years. Higher in the case of Gambia means administrative training and technical secondary education. HBO courses and university education are possible since 1999. The University of The Gambia was established by an Act of the National Assembly of the Gambia in March 1999. The enactment, which was a bold step to fulfill a long-standing desire of the people of The Gambia and to respond to several years of advocacy both within and outside the country for a university, ended years of indecision on the university question. Logo University of The GambiaPhoto: Gatherinformation CC 4.0 International no changes made
Logo University of The GambiaPhoto: Gatherinformation CC 4.0 International no changes made
Although the number of schools is growing rapidly, there is still a chronic shortage. There are more than 200 primary schools. About 70,000 children attend this education. There are 25 secondary schools and 10 higher education schools. Only 15,000 students attend secondary education and even fewer, 1,500 students, attend higher education.
Sources
Derksen, G. / Gambia, Senegal
Gottmer
Hesseling, G. / Senegal/Gambia : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen
Waard, P. de / Reishandboek Gambia
Elmar
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info