GAMBIA
Economy

Economy
Economy
The Gambia's economy is among the weaker in the world. Per capita GDP was $ 2,600 in 2017. The Gambia's economy is mainly agricultural. Most important export products are still peanuts and peanut products such as peanut oil and animal feed. This monoculture means that The Gambia is highly dependent on peanut prices on the world market and therefore the economy has a shaky foundation. With the support of mainly British development funds, efforts are being made to improve production methods and stimulate the cultivation of other crops. The emphasis is on the development of agriculture and irrigation of the marshes around the Gambia River. Peanuts are still important for the conomy of The GambiaPhoto: Peter van der Sluijs CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Peanuts are still important for the conomy of The GambiaPhoto: Peter van der Sluijs CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Small quantities of spices, papayas, mangoes, cotton, millet, bananas and palm tree products are also exported. However, most agricultural products such as cereals are grown for domestic use. Important trading partners for the Gambia are Guinea-Bissau, Great Britain, the Netherlands, France, Mali and Senegal (also smuggling trade). Total exports in 2017 were $ 72.9 million. Other important exports are fish and fish products, in particular dried fish, most of which go to countries in the region.
Many goods and products are imported, especially food, beverages and tobacco. Furthermore, among others machines, oils and fats, chemical products and textiles. Important trading partners in terms of imports are China, Great Britain, the Netherlands, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Belgium and Senegal. Total imports were $ 377 million in 2017.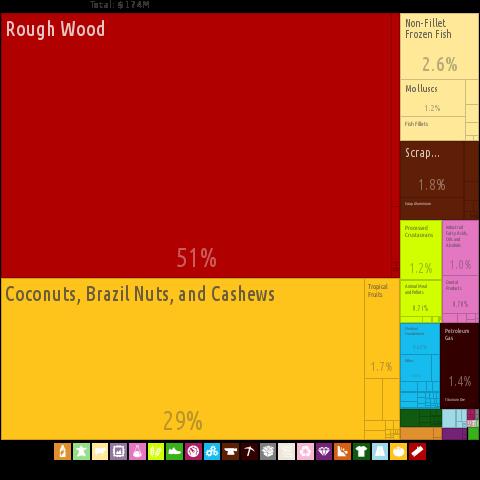 Export products The GambiaPhoto: Alexander Simoes, Cesar Hidalgo, et. al. See CC 3.0 no changes made
Export products The GambiaPhoto: Alexander Simoes, Cesar Hidalgo, et. al. See CC 3.0 no changes made
Most of the working people in The Gambia have two sources of income. Firstly, an official job and secondly, income from the sale of mainly home-grown agricultural products. Nearly 500,000 people earn from the market and 150,000 of them have a business or shop.
The industry is not much in the Gambia yet. There is some agricultural manufacturing industry and some packaging factories.
In The Gambia, almost half of the population lives below the poverty line, which means that they are unable to provide for their basic needs.
For shipping, only the port of Banjul at the mouth of the Gambia river is important; the river is especially important for inland navigation. Of the roads (2386 km in total), 750 km can be used all year round. There are two routes from west to east through The Gambia. One of them runs north of the Gambia River and is unpaved. The other route runs south of the Gambia River and is paved. The only significant airport is Yundum, near Banjul. Banjul International Airport, GambiaPhoto: Sal73x at it.wikipedia CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Banjul International Airport, GambiaPhoto: Sal73x at it.wikipedia CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Sources
Derksen, G. / Gambia, Senegal
Gottmer
Hesseling, G. / Senegal/Gambia : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen
Waard, P. de / Reishandboek Gambia
Elmar
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info