PHILIPPINES
Geography and Landscape
Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | Filipino (Tagalog), English |
| Capital | Manila |
| Area | 299.764 km² |
| Population | 112,018,293 (2021) |
| Currency | Philippine peso (PHP) |
| Web | .ph |
| Code. | PHI |
| Tel. | +63 |
Cities in PHILIPPINES
| Manila |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
The Philippines (Filipino: Republica ñg Pilipinas; Spanish: República de Filipinas; English: Republic of the Philippines) is a republic in Southeast Asia. The country is an archipelago and consists of 7,107 counted large and small islands in the Pacific or Pacific, of which about 1000 are permanently or temporarily inhabited. Most of the islands are nothing more than uninhabited sandbanks and rocky reefs; many of these islands don't even have a name yet!
The total land area is approximately 300,000 km2. The total coastal length is approximately 34,500 km. The Philippines extends north-south for a length of 1850 km, and east-west for a length of 1060 km. It is remarkable that the capital Manila with an area of 636 km2 is one of the largest cities in the world.
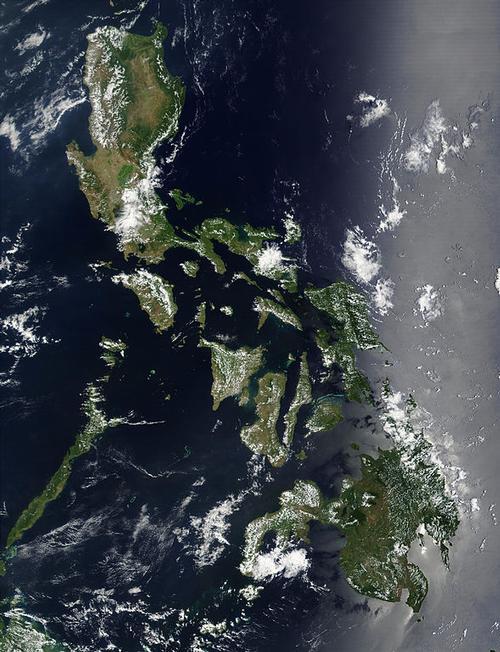

About two-thirds of the total area is occupied by the islands of Luzon (104,700 km2; north-south 830 km, east-west maximum 240 km2) in the north and Mindanao (94,600 km2) in the south. The islands that lie between the two largest islands are called the Visaya Islands or Visayas. Other large islands are (in order of size): Palawan (14,896 km2), Panay (12,327 km2), Mindoro (10,245 km2), Samar (9,949 km2), Negros (9,225 km2), Leyte (6,268 km2), Cebu (5,088) km2), Bohol (4,117 km2) and Masbate (4,047 km2).
The Philippines, named after Philip II of Spain, is located south of Hong Kong, Taiwan (150 km away), Japan and South Korea; north of Brunei, Malaysia (Borneo at 25 km), Indonesia (at 60 km) and Singapore; east of Vietnam (960 km), Thailand and the South China Sea; west of the Pacific.
Landscape
The landscape of the Philippines consists largely of mountains and hills. Approx. a third of the archipelago consists of lowlands.
The important Cordillera Central runs from north to south on the island of Luzon, the highest peak of which is the Pulog (2928 m). To the east of this lies the Sierra Madre on the coast, with the highest peak being Anacuao (1850 m). The longest river in the Philippines, the Cagayan (354 km), flows between the two mountain ranges. Central Luzon is occupied by the Central Plain, which is home to a large part of the population and is home to an important rice-growing area. Luzon Island is also home to the largest lake in the Philippines, Laguna de Bay (922 km2); the largest lake in Mindanao is Lake Lanao (357 km2). In the south there are still a few volcanoes, of which the Mayon is the best known (2421 m).
The landscape of the Visaya Islands and Palawan is, except for a coastal strip, hilly and mountainous. The highest peak here is the Kanlaon volcano (2465 m).
 Mount Apo, PhilippinesPhoto: Unknown CC 3.0 no changes made
Mount Apo, PhilippinesPhoto: Unknown CC 3.0 no changes made
Mindanao Island is also mountainous, but has two large and fertile lowland areas, the Angus Valley and the Cotabato Valley. The Cotabato Valley is bisected by the Mindanao or Rio Grande de Mindanao, a river with an extensive catchment area. Mindanao is also home to the highest mountain in the Philippines, the stratovolcano Mount Apo (2954 m).
The Philippines has 132 short, fast-flowing rivers that are generally unnavigable. The coasts are characterized by the presence of many bays and are largely fringed by coral reefs.
Earthquakes and volcanoes
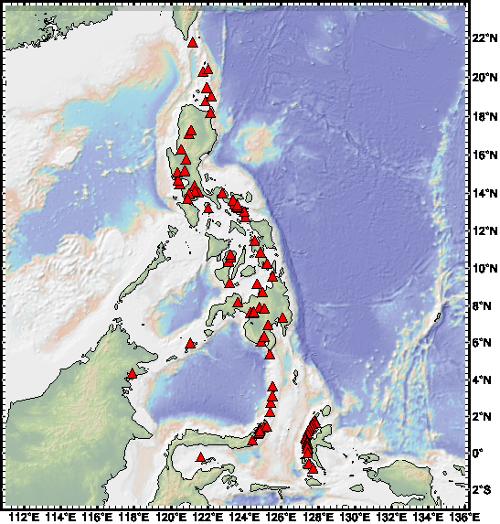 Map of volcanoes in the PhilippinesPhoto: LkwkarenHKU CC 4.0 International no changes made
Map of volcanoes in the PhilippinesPhoto: LkwkarenHKU CC 4.0 International no changes made
The archipelago of the Philippines, like Taiwan and the islands of Japan, is part of a fault zone that runs from Kamchatka in the far north to New Zealand in the deep south. There are also a number of very deep troughs in the ocean along all these islands. Southeast of the Philippine island of Leyte is the 1800 km long Mindanao trough with a depth of 10,497 meters.
Earthquakes and volcanism are a "normal" phenomenon in such fault zones, and the Philippines is also regularly affected and is one of the most geologically troubled areas on the planet. The last major earthquake dates back to 1990, when large areas of the northern Philippine city of Baguio were destroyed and more than a thousand people were killed.
The Philippines archipelago has 37 volcanoes, including the highest mountain in the Philippines, the working volcano Mount Apo (2954 m), located in the Apo massif in Mindanao. At least 18 of these volcanoes are still active and the last very large volcanic eruption dates back to June 1991 when the Luzon volcano, Mount Pinatubo, spewed about 5 billion tons of rock and 19 million tons of sulfur dioxide into the air to an altitude of more than 20 km. About a hundred people were killed, many were missing and there were nearly one million homeless. The Taal is one of the most dangerous volcanoes in Southeast Asia; it has erupted about thirty times since the arrival of the Spaniards.
Sources
Filippijnen
Het Spectrum
Philippines
Lonely Planet
Poppe, D. / Reishandboek Filippijnen
Elmar
Rodell, P.A. / Culture and customs of the Philippines
Greenwood Press
Wee, J. / Philippines
Chelsea House
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info