CALIFORNIA
Society

Society
Cities in CALIFORNIA
| Los angeles | San francisco |
Popular destinations USA
| Arizona | California | Florida |
| Hawaii | Utah |
Society
State structure United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic, with power shared between the president as head of state and government, the United States Congress and the judiciary. The federal government, in turn, shares sovereignty with the state governments of all 50 individual states. The president of the executive branch is the president; Congress as a legislative power sits in two chambers, the House of Representatives and the Senate; the judiciary, which interprets and assesses the constitution, federal laws, is in the hands of the Supreme Court as the supreme body, under which the lower federal courts rule.
The President of the United States is indirectly elected by the American population. The voters in the various states do not rely on the presidential candidate, but on electors who support a particular president candidate. The number of electors of a state is equal to the number of Congressmen of that state. California is the most important state for some electoral votes, as many as 55. The candidate who obtains the most votes in a state can send all electors to the Electoral College. In total there are 538 electors to win, the candidate with at least 270 electors behind him will become president of the United States.
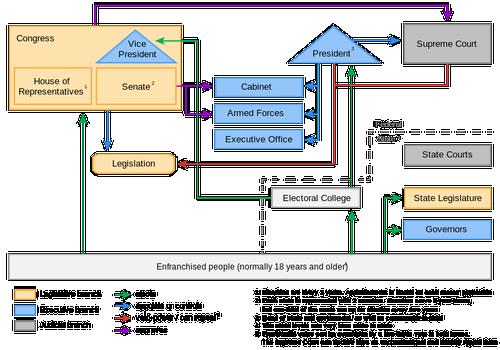 United States political system overviewPhoto: 111Alleskönner CC BY-SA 3.0 de no changes made
United States political system overviewPhoto: 111Alleskönner CC BY-SA 3.0 de no changes made
Government California
In the United States, the Democratic and Republican Parties have ruled since the American Civil War (1860-1865). That applies to both the federal government and the state governments. Below is an overview of the governors and their party since 1849. Until now, California had 21 governors of republican rule, 17 governors of Democratic background, one governor of the American Party and one governor of the Progressive Party.
| Name | In function | Party |
| Peter Hardeman Burnett | 20-12-1849 till 9-1-1851 | Democrat |
| John McDougall | 9-1-1851 tlll 8-1-1852 | Democrat |
| John Bigler | 8-1-852 till 9-1-1856 | Democrat |
| John Neely Johnson | 9-1-1856 till 8-1-1858 | American Party |
| John B. Weller | 8-1-1858 till 9-1-1860 | Democrat |
| Milton Latham | 9-1-1860 till 14-1-1860 | Democrat |
| John Gately Downey | 14-1-1860 till 10-1-1862 | Democrat |
| Leland Stanford | 10-1-1862 till 10-12-1863 | Republican |
| Frederick Low | 10-12-1863 till 5-12-1867 | Republican |
| Henry Huntly Haight | 5-12-1867 till 8-12-1871 | Democrat |
| Newton Booth | 8-12-1871 till 27-2-1875 | Republican |
| Romualdo Pacheco | 27-2-1875 till 9-12-1875 | Republican |
| William Irwin | 9-12-1875 till 8-1-1880 | Democrat |
| George Clement Perkins | 8-1-1880 till 10-1-1883 | Republican |
| George Stoneman | 10-1-1883 till 8-1-1887 | Democrat |
| Washington Bartlett | 8-1-1887 till 12-9-1887 | Democrat |
| Robert Waterman | 12-9-1887 till 8-1-1891 | Republican |
| Henry Markham | 8-1-1891 till 11-1-1895 | Republican |
| James Budd | 11-1-1895 till 4-1-1899 | Democrat |
| Henry Gage | 4-1-1899 till 7-1-1903 | Republican |
| George Pardee | 7-1-1903 till 9-1-1907 | Republican |
| James Gillett | 9-1-1907 till 3-1-1911 | Republican |
| Hiram Johnson | 3-1-1911 till 15-3-1917 | Progressive Party |
| William Stephens | 15-3-1917 till 8-1-1923 | Republican |
| Friend Richardson | 9-1-1923 till 4-1-1927 | Republican |
| Clement Calhoun Young | 4-1-1927 till 6-1-1931 | Republican |
| James Rolph | 6-1-1931 till 2-6-1934 | Republican |
| Frank Merriam | 2-6-1934 till 2-1-1939 | Republican |
| Culbert Olson | 2-1-1939 till 4-1-1943 | Democrat |
| Earl Warren | 4-1-1943 till 5-10-1953 | Republican |
| Goodwin Knight | 5-10-1953 till 5-1-1959 | Republican |
| Pat Brown | 5-1-1959 till 2-1-1967 | Democrat |
| Ronald Reagan | 2-1-1967 till 6-1-1975 | Republican |
| Jerry Brown | 6-1-1975 till 3-1-1983 | Democrat |
| George Deukmejian | 3-1-1983 till 7-1-1991 | Republican |
| Pete Wilson | 7-1-1991 till 4-1-1999 | Republican |
| Gray Davis | 4-1-1999 till 17-11-2003 | Democrat |
| Arnold Schwarzenegger | 17-11-2003 till 3-1-2011 | Republican |
| Jerry Brown | 3-1-2011 till 7-1-2019 | Democrat |
| Gavin Newsom | 7-1-2019 till present | Democrat |
The fifty states of the United States are divided into so-called 'counties'. The fifty states are made up of 3,007 counties, averaging 62 per state, California has 58, and Texas has the most, 254. The division of power between states, counties, cities and towns is determined in the constitutions of each state.
Every US state, except for the state of Nebraska, has its own congress with a bicameral parliament, a House of Representatives and a Senate. the number of seats per state varies greatly, senators usually have a term of office of four years, deputies often only two years. The state administration is headed by a directly elected governor. The governor has a lot of power in his or her four-year, sometimes two-year term.
Administrative division
Overview California counties
 Counties CaliforniaPhoto: Júlio Reis,CC 3.0 Unportedno changes made
Counties CaliforniaPhoto: Júlio Reis,CC 3.0 Unportedno changes made
| county | main town | since | surface |
| Alameda County | Oakland | 1853 | 1.911 km² |
| Alpine County | Markleeville | 1864 | 1.914 km² |
| Amador County | Jackson | 1854 | 1.536 km² |
| Butte County | Oroville | 1850 | 4.248 km² |
| Calaveras County | San Andreas | 1850 | 2.642 km² |
| Colusa County | Colusa | 1850 | 2.981 km² |
| Contra Costa County | Martinez | 1850 | 1.865 km² |
| Del Norte County | Crescent City | 1857 | 2.611 km² |
| El Dorado County | Placerville | 1850 | 4.434 km² |
| Fresno County | Fresno | 1856 | 15.444 km² |
| Glenn County | Willows | 1891 | 3.406 km² |
| Humboldt County | Eureka | 1853 | 9.254 km² |
| Imperial County | El Centro | 1907 | 10.813 km² |
| Inyo County | Independence | 1866 | 26.397 km² |
| Kern County | Bakersfield | 1866 | 21.088 km² |
| Kings County | Hanford | 1893 | 3.600 km² |
| Lake County | Lakeport | 1861 | 3.258 km² |
| Lassen County | Susanville | 1864 | 11.805 km² |
| Los Angeles County | Los Angeles | 1850 | 10.515 km² |
| Madera County | Madera | 1893 | 5.537 km² |
| Marin County | San Rafael | 1850 | 1.347 km² |
| Mariposa County | Mariposa | 1850 | 3.758 km² |
| Mendocino County | Ukiah | 1850 | 9.088 km² |
| Merced County | Merced | 1855 | 9.088 km2 |
| Modoc County | Alturas | 1874 | 10.215 km² |
| Mono County | Bridgeport | 1861 | 7.884 km² |
| Monterey County | Salinas | 1850 | 8.604 km² |
| Napa County | Napa | 1850 | 1.953 km² |
| Nevada County | Nevada City | 1851 | 2.481 km² |
| Orange County | Santa Ana | 1889 | 2.046 km² |
| Placer County | Auburn | 1851 | 3.893 km² |
| Plumas County | Quincy | 1854 | 6.615 km² |
| Riverside County | Riverside | 1893 | 18.669 km² |
| Sacramento County | Sacramento | 1850 | 2.502 km² |
| San Benito County | Hollister | 1874 | 3.597 km² |
| San Bernardino County | San Bernardino | 1853 | 51.960 km² |
| San Diego County | San Diego | 1850 | 10.888 km² |
| San Francisco County | San Francisco | 1850 | 122 km² |
| San Joaquin County | Stockton | 1850 | 3.623 km² |
| San Luis Obispo County | San Luis Obispo | 1850 | 8.557 km² |
| San Mateo County | Redwood City | 1856 | 1.163 km² |
| Santa Barbara County | Santa Barbara | 1850 | 7.091 km² |
| Santa Clara County | San Jose | 1850 | 3.344 km² |
| Santa Cruz County | Santa Cruz | 1850 | 1.155 km² |
| Shasta County | Redding | 1850 | 9.806 km² |
| Sierra County | Downieville | 1852 | 2.468 km² |
| Siskiyou County | Yreka | 1852 | 16.283 km² |
| Solano County | Fairfield | 1850 | 2.145 km² |
| Sonoma County | Santa Rosa | 1850 | 4.082 km² |
| Stanislaus County | Modesto | 1854 | 3.872 km² |
| Sutter County | Yuba City | 1850 | 1.562 km² |
| Tehema County | Red Bluff | 1856 | 7.643 km² |
| Trinity County | Weaverville | 1850 | 8.234 km² |
| Tulare County | Visalia | 1852 | 12.494 km² |
| Tuolumne County | Sonora | 1850 | 5.791 km² |
| Ventura County | Ventura | 1872 | 4.781 km² |
| Yolo County | Woodland | 1850 | 2.621 km² |
| Yuba County | Marysville | 1850 | 1.632 km² |
There are also major differences at the county and local level. At city level, three forms can be distinguished, which also occur in combination:
Council and mayor: the council members are sometimes appointed, sometimes elected, and have budget rights. They also draw up general policy guidelines and monitor the city council. The mayor is almost always elected and has a veto, among other things.
-Commission: a committee of 3 to 7 elected members, one of which acts as chairman, is both legislative and executive.
City Manager: This figure is hired indefinitely and executes decisions of an elected council.
Many referendums are held at provincial and local level in all American states, and in California a great many. They are often citizen initiatives.
Sources
BBC - Country Profiles
Benson, Sara / California
Lonely Planet
Benson, Sara / Discover California
Lonely Planet
Californië
Uitgeverij Cambium B.V.
CIA - World Factbook
Elmar Landeninformatie
Hansen, Preben / 100% Californië & West-USA
Mo'Media
Heetvelt, Angela / Zuidwestelijke staten van Amerika
Gottmer/Becht
Mangin, Daniel / Californië : de reisgids voor een actieve & culturele vakantie
Wat & Hoe
Ominalowska, Malgorzata / Californië
Uitgeverij Unieboek/Het Spectrum
The Rough Guide to California
Rough Guides Ltd.
Schmidt-Brümmer, Horst / Lannoo's autoboek Californië en Zuidwest-USA : on the road
Lannoo
Vlahides, John A. / Northern California
Lonely Planet
Wikipedia
Zuidwest-USA
Uitgeverij Terra Lannoo
Copyright: Team The World of Info