SURINAME
Society

Society
Society
State structure
 National Assembly SurinamePhoto:nBrokopondo in the public domain
National Assembly SurinamePhoto:nBrokopondo in the public domain
Suriname's form of government is parliamentary democracy. Under the 1987 constitution, supreme power rests with the president elected for five years by the United People's Assembly (an extended parliament), who is head of state and commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The latter position is held ex officio by the vice-president. The National Assembly is the highest state body and has 51 members.
Administrative division
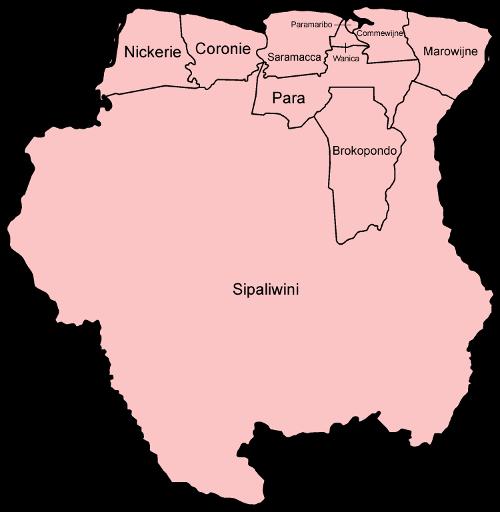 Districts of SurinamePhoto: Golbez CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Districts of SurinamePhoto: Golbez CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Suriname is divided into ten districts plus the capital. The districts are Paramaribo, Brokopondo, Commewijne, Coronie, Marowijne, Para, Wanica, Sipaliwini, Saramacca and Nickerie. The districts are administered by a district commissioner. The district is an administrative part of the central government in Paramaribo, and the district commissioner receives his instructions from the Minister of District Administration and Decentralization. The districts themselves are subdivided into areas that fall under an administrative official with a permanent position. There is no municipal division. Within a district, however, different communities are distinguished, such as settlements (old plantations), village communities, water boards and villages (lands).
Politics
 Precidential Palace SurinamePhoto: Ian Mackenzie CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Precidential Palace SurinamePhoto: Ian Mackenzie CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The following political parties played an important role before the military coup of 1980 and after the redemocratization in 1987. The Kaum Tani Persatuan Indonesia, now called Kerukanan Tulodo Pranatan Ingil (KTPI = Party for National Unity and Togetherness of the Highest Order). This party is strong with the Javanese population group. The National Party of Suriname (NPS), the largest party for the Creoles. The Progressive Reform Party (VHP), based on the Hindustani population group. Together these three parties form the New Front for Democracy and Development. There are also the National Democratic Party (NDP) associated with army leader Bouterse and the Democratic Alternative '91 (DA '91), a combination of four parties.
The trade union movement has traditionally played an important role in social life. The most important trade unions are the General Union of Trade Unions in Suriname, 'the Mother Union', the Centrale 47 (C-47) and the Centrale van Landsdienaren Organizations. These three unions united in 1987 in the Council of Trade Unions Suriname.
The current political situation is described in the chapter history.
Sources
Beatty, N.B. / Suriname
Chelsea House
Encarta Encyclopedie
Leuwsha, T / Reishandboek Suriname
Elmar,
Noordegraaf, W / Suriname
ANWB
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info