SINGAPORE
Economy

Economy

Economy
General
 Singapore central business districtPhoto: Zairon CC 4.0 International no changes made
Singapore central business districtPhoto: Zairon CC 4.0 International no changes made
Due to its geographic location, Singapore has become an international center for industry and trade. Singapore has the advantage of a deep harbor and is located on one of the busiest trade routes from the east to the west. Furthermore, Singapore has a free market economy in which private business occupies the largest place and a well-developed communication and financial infrastructure. The government nevertheless has a great influence on economic development through legislation, special bodies such as the Economic Development Board (EDB), the provision of subsidies and tax breaks.
The importance of the port has declined somewhat in recent years, but this is more than offset by the development of Singapore as the center of business and financial services (75.2% of the gross national product (2017).
Singapore is still a draw for foreign investors. As early as the 1960s and 1970s, the government has taken up economic development with great success. Foreign investors were encouraged by favorable circumstances such as a large and well-educated workforce, low wages, a stable working environment, attractive investment subsidies and tax incentives to settle in Singapore to have part of their mass production carried out there.
Agriculture and Fisheries
 Indoor vertical farming SingaporePhoto: Lianoland Wimons CC 4.0 International no changes made
Indoor vertical farming SingaporePhoto: Lianoland Wimons CC 4.0 International no changes made
Agriculture plays a subordinate role in the economy, partly due to the limited available land area. About 6% of the total land area is used for agricultural activities. In particular, a lot of meat, fish, vegetables, fruit and eggs must be imported. It is significant that only 6% of all required vegetables are grown in Singapore itself. In order to get the most out of the 273 farms, a lot of money has been invested in agrotechnology in recent years. Furthermore, traditional mixed farms are being replaced by specialized intensive farms. The few forests have no economic significance. The fishery is not very developed. Orchids and aquarium fish are the only exports of interest in the agricultural sector.
Industry
 Industry SingaporePhoto: Jacklee CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Industry SingaporePhoto: Jacklee CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The processing industry supplies more than 24.8% (2017) of the gross national product and about 25.6% of the working population finds a job there. The main branch is the petroleum processing industry, followed by the electronics industry, chemicals and shipbuilding and repair. The country's economic growth is mainly based on its ports and service companies. The seven ports of Singapore together are among the largest in the world. They are home to the largest export refining complex in Asia, processing more than a million barrels per day.
Trade and Banking
 Export SingaporePhoto: Celinaqi CC 4.0 International no changes made
Export SingaporePhoto: Celinaqi CC 4.0 International no changes made
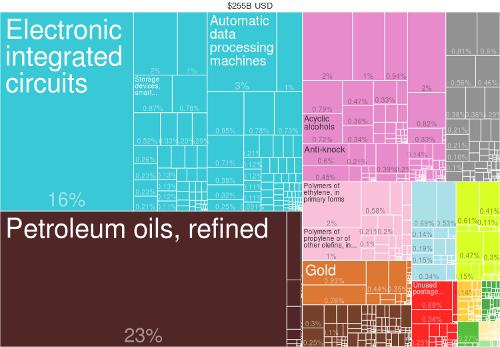
Trade is the second important economic sector, namely the bonded warehouse of rubber, tropical hardwood and pepper, with Singapore serving as a transit port for Malaysia.
Main exports are: petroleum products, machinery and transport equipment, textiles, rubber, iron ore, tin and copra. In 2017, exports amounted to $ 397 billion. Main export partners are the United States, Malaysia, Hong Kong, Japan, Taiwan, Thailand, Great Britain, China and Germany. Main import commodities are petroleum, raw materials, machinery and food. In 2017, imports were worth $ 380 billion. Main import partners are the United States, Japan, Malaysia, Thailand, China, Taiwan, Germany and Saudi Arabia.
Singapore is an international financial center, home to a large number of foreign banks and financial institutions. Since 1968, Singapore has had an important Asian dollar market and a gold exchange has been established. The Monetary Authority of Singapore and the Board of Commissioners of Currency jointly exercise the function of central bank.
Traffic
 Singapore Changi AirportPhoto: Calvin Teo CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Singapore Changi AirportPhoto: Calvin Teo CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
A 25 km long railway line connects Singapore with the mainland Malaysian rail network via a bridge over the Johore Strait.
In order to restrict car traffic, only passenger cars with at least four occupants may enter the city center free of charge.
The extensive public transport network is maintained by the Singapore Bus Service. Construction of a 67 km long metro network was completed in 1990.
Singapore has one of the busiest ports in the world, which makes it vital to the economy. Singapore has a distribution port with shipping lines to more than 600 ports around the world. It is one of the most important transhipment ports in Asia and is also of increasing importance for shipping traffic to China. There are oil piers for super tankers and modern container terminals. The Port of Singapore Authority manages the seven ports.
Due to its location, Singapore's natural harbor has also developed into a major departure point for cruises to destinations in Southeast Asia.
Chiangi Airport (1981) often ranks first in the rankings of “best airports in the world”.
Singapore International Airport serves 133 cities in 53 countries.
The national airline Singapore Airlines (SIA) is one of the most successful airlines in the world. SIA flies to 98 cities in 46 countries.
Sources
Beliën, H. / Maleisië : Singapore
Gottmer
Hellander, P. / Singapore
Lonely Planet,
Oon, H. / Singapore
Van Reemst
Singapore
Ministry of Information and the Arts
Wee, J. / Singapore
Chelsea House Publishers
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info