NIGERIA
Society
Society

Society
State structure
 Nigeria ParliamentPhoto: Kabusa16 CC 4.0 International no changes made
Nigeria ParliamentPhoto: Kabusa16 CC 4.0 International no changes made
Nigeria is a republic headed by a president who is elected for four years. The new Constitution was established in May 1999. At the national level, the Constitution provides for a Senate with 109 seats and a House of Representatives with 360 seats. At the federal level, Nigeria has 36 states, each with its own legislature and an elected governor. Three political parties, all established in 1998, set the political scene in Nigeria. These are the People's Democratic Party (PDP), the All People's Party (APP) and the Alliance for Democracy (AD). The APP has a lot of support from former Abacha supporters. The AD finds its support mainly among the Yoruba of the southwestern states.
Politcs
 Oilindustry Niger DeltaPhoto: Sixoone CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Oilindustry Niger DeltaPhoto: Sixoone CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Immediately after taking office in 1999, President Obasanjo took numerous confidence-building measures within the political system and the military. The country continues to suffer greatly from corruption at all levels of society. Hot issues such as the redistribution of federal allowances to the 36 states and the institutional issues associated with the introduction of Sharia in the North have continued to stalemate after the 2005 National Political Reform Conference.
One problem is endemic violence in the Niger Delta, including hostage-taking of oil company personnel and attacks on oil installations. This violence is both criminal and political in nature and is partly due to the underdevelopment of the area, corruption and lack of good governance. The population attributes the underdevelopment to a lack of (financial) contributions from the oil companies. They argue that their legally required remittance of a significant part of the oil revenues to the government through corruption (including at the government organization Niger Delta Development Commission) only partially benefits the population.
“Illegal bunkering” by criminal gangs, with the cooperation of police and military, generates a lot of money for the purchase of weapons for criminal actions.
The current political situation is described in the chapter history.
Economy
 Oil factory NigeriaPhoto: Xeon CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Oil factory NigeriaPhoto: Xeon CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Oil remains at the heart of the Nigerian economy and the state's financial base. Nigeria is Africa's main oil and gas exporter; the oil determines more than 75% of the state's income. Due to the high oil prices in recent years, the government is generally keeping up with the economic tide. Many other sectors, especially agriculture, have been neglected. There is still much room for improvement in Nigeria, especially in the areas of a transparent government, an effective tax system, the fight against corruption and reforms in the Nigerian institutions. Economic growth was 0.8% in 2017. GDP was $ 5,900 per capita in the same year.
Nigeria has presented an ambitious socio-economic reform plan, the National Economic Empowerment and Development Strategy (NEEDS), reflected at the state level in the State Economic Empowerment and Development Strategy). NEEDS focuses on sustainable growth and poverty reduction by means of improvement of social infrastructure, economic growth and improvement of the functioning of the government. The program focuses on the private sector and aims to improve the business climate, increase productivity and competitiveness, diversify the economy and reduce government intervention.
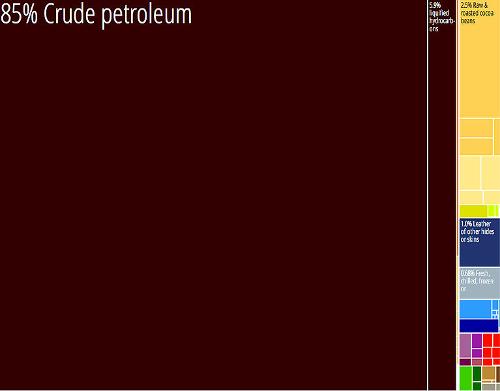 Nigeria ExportPhoto: R Haussmann, Cesar Hidalgo, et. al CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Nigeria ExportPhoto: R Haussmann, Cesar Hidalgo, et. al CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
NEEDS also provides for a Fiscal Responsibility Bill (tabled in Parliament, but still met with opposition from state governors), a Procurement Bill (aimed at making large transactions more transparent) and an Oil Revenue Transparency Bill (not yet adopted by the Parliament). NEEDS is positively valued by the IMF, but there are doubts about implementation at state level (SEEDS), by governors whose (political) agenda is not always in line with that of the federal government.
Nigeria has recently intensified its economic relations with China. Both countries agreed that China will be the first choice in selling the exploitation rights to four oil fields at Kaduna in exchange for a $ 4 billion investment in infrastructure. The Chinese oil company Cnooc has taken a 45% interest in a large offshore oil installation for 2.7 billion dollars. Exports were worth $ 146 billion in 2017. The main export partners are the United States, India, China, Spain and the Netherlands. Imports were worth $ 32.7 billion in 2017. The main import partners are China, Belgium, the United States and South Korea.
Sources
Elmar Landeninformatie
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Last updated June 2024Copyright: Team The World of Info