MOROCCO
Society

Society
Cities in MOROCCO
| Marrakech |
Society
State Structure
 Parliament Building MoroccoPhoto: Anass Sedrati CC 4.0 International no changes made
Parliament Building MoroccoPhoto: Anass Sedrati CC 4.0 International no changes made
According to the 1972 constitution, Morocco is a constitutional, democratic and social monarchy with male succession. Head of state, spiritual head and commander in chief of the armed forces is the king. He composes the cabinet, issues laws and royal decrees and has the power to dissolve the parliament and issue plebiscites. Of the 333 members of the unicameral parliament, 222 members are directly elected, according to universal suffrage, the others are appointed by electoral colleges of municipal councils, chambers of commerce and employee organizations. Freedom of association is guaranteed in the Constitution, but is often restricted in practice.
Administrative division
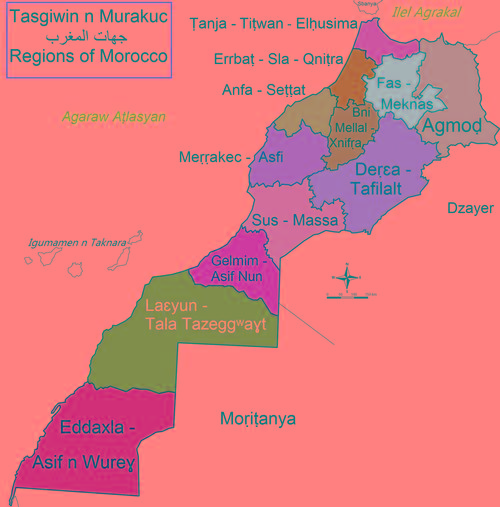 Regions of MoroccoPhoto: Tussna (CC BY-SA 3.0) no changes made
Regions of MoroccoPhoto: Tussna (CC BY-SA 3.0) no changes made
The country is divided into 39 provinces (40 including the Spanish Sahara) and eight city prefectures, each with a governor and two prefectures. Morocco is a member of the United Nations. It is also a member of the Organization of African Unity, the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank. Special ties are maintained with France, and although Morocco is a non-aligned country, it has special relations with the United States, based on a friendship treaty dating from 1787, the oldest international treaty in United States history. Morocco has the status of associate member of the EU. An administrative reclassification took place in 2010 and Morocco consists of 12 regions.
Politics
There is a wide variety of political parties compared to other North African countries. The main ones are: the royalist center-right Union Constitutionelle (UC), founded in 1982; the Rassemblement National des Indipendents (RNI), a mass movement in support of the king's policies; the Parti National Democrate (PND), social democratic spin-off from the RNI, established in 1981. These are the so-called royal parties. Furthermore, since 1984 the Mouvement Popular has been part of the government coalition. This is a movement of several royalist organizations. The main opposition parties are the Istiqlal Party (moderate socialist and nationalist). The Union Socialiste des Forces Populaires (USFP) advocates, among other things, nationalization. The Union National des Forces Populaires (UNFP) advocates even more radical reforms. All these parties are represented in parliament. The fundamentalist Muslim party Adl wa Lihsane is banned. The unions are limited in their freedom of movement.
The current political situation is described in the chapter on history.
Sources
Encarta Encyclopedia
Lehmann, L. / Marokko
Van Reemst
Macguinness, J. / Morocco handbook
Passport Books
Wilkins, F. / Morocco
Chelsea House
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info