CAMBODIA
Cities in CAMBODIA
| Phnom-penh |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Cambodia (officially: Preah Réchéanachâkr Kampuchea = the Kingdom of Kampuchea) is a kingdom in Southeast Asia. The total area of Cambodia, including a number of islands, is 181,035 km2. Cambodia is the smallest country in Southeast Asia after Singapore and Brunei.
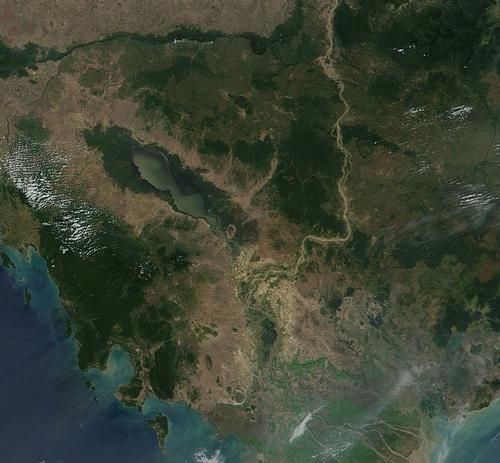
The maximum distance between the east and the west is 580 km; from north to south 450 km. Cambodia is bordered in the north and west by Thailand (803 km), in the north by Laos (541 km), in the east by Vietnam (1228 km), in the south by the Gulf of Thailand (443 km).
Landscape
 Cambodia Angkor WatPhoto: Bjørn Christian Tørrissen CC 4.0 International no changes made
Cambodia Angkor WatPhoto: Bjørn Christian Tørrissen CC 4.0 International no changes made
At the heart of the Cambodian landscape are fertile alluvial lowlands that make up two thirds of the country's surface. These lowlands are surrounded in the north by the last foothills of the Himalayas; in the north the Dangrek mountains (max. 500 meters high), in the east by the Moi hills, in the southwest by the Elephant chain or Phnom Damrei (max. 900 meters high) and in the west by the highest mountain range in Cambodia, the Cardamom Mountains or Chuor Phnom Kravanh. The lowlands and the mountains, especially in northern Cambodia, are separated from each other by a transition zone of savanna and low-lying hills or "phnom". The highest peak in Cambodia is Phnom Aural at 1,813 meters.
Approx. 5% of present-day Cambodia consists of rivers and lakes. The largest rivers are the Mekong, which flows through the country in a north-south direction, and the Tonlé Sap, which forms the lake of the same name in the center of western Cambodia, the area of which varies according to rainfall from 2500 to 6500 km2. The Mekong (Cambodian: Tonlé Thom, the Great River) flows through Tibet, China, Myanmar (formerly: Burma), Thailand and Laos to Cambodia.
At the capital Phnom Penh, the Mekong splits west into Lower Mekong and east into Bassac. Both arms flow into the South China Sea via the south of Vietnam. The Mekong flows about 500 km through Cambodia and in some places is 5 km wide.
 Tonle Sap Lake CambodjaPhoto:David Sim CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Tonle Sap Lake CambodjaPhoto:David Sim CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
A striking feature of the Cambodian landscape is the 2500 km2 Tonlé Sap Lake (the Big Lake). Located in the western part of the central plain, the lake is connected to the Mekong via the 100 km long Tonlé Sap river. The fish-rich Lake of Tonlé Sap is the largest freshwater lake in Southeast Asia.
The special feature of the lake is that it has two currents, depending on the season. In the dry season, from November to April, the lake's water flows southeast to the Mekong. In the rainy season, the Tonlé Sap river changes its flow direction and the excess water discharges into the Tonlé Sap lake.
During the monsoon season, the Tonlé Sap river is fourteen meters deep and has an area of about 10,000 km2, during the dry season the lake is barely two meters deep and has an area of about 3000 km2.
Sources
Canesso, C. / Cambodia
Chelsea House Publishers
Colet, J. / Cambodia handbook
Footprint Handbooks
Green, R. / Cambodia
Lucent Books
Kleinen, J. / Cambodja
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen ; Novib
Peterse, L. / Cambodja
Gottmer/Becht,
Wulf, A. / Cambodja, Laos
Het Spectrum
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info