ANDORRA
Economy

Economy

Cities in ANDORRA
| Andorra la vella |
Economy

Economically, Andorra has always been strongly oriented towards Spain and under the Franco-régime the mountain state flourished as a tax haven or smuggling nest between the EU members France and Spain. At present, most of the trade in goods and services is still settled with Spain and, to a lesser extent, France. A trade agreement was signed with the European Union in June 1990 and a customs union was introduced for industrial products as well as special arrangements for agricultural products. This framework agreement with the EU was amended and expanded in 1991 and 1995.
After the political upheaval in Spain and accession to the EU, Andorra lost part of its special economic position. What remained was the significance of the country as the seat of commercial banks, as a tax haven and tourist (winter) attraction. Tourism (especially winter sports) and related sectors- retail, services- remain the main pillars of the economy, accounting for about 80% of GDP. About thirteen million tourists visit the principality every year. The GNP per inhabitant is $ 49,900 per year (2017).

After tourism, the banking sector is the most important economic sector due to Andorra's attractive tax environment. The 1993 constitution shifted from an economy based primarily on tax-free shopping to one based on the international banking sector and the financial offshore. The government, in the absence of income tax and other direct taxes, imposes duties on imports and financial transactions in order to generate state revenue.
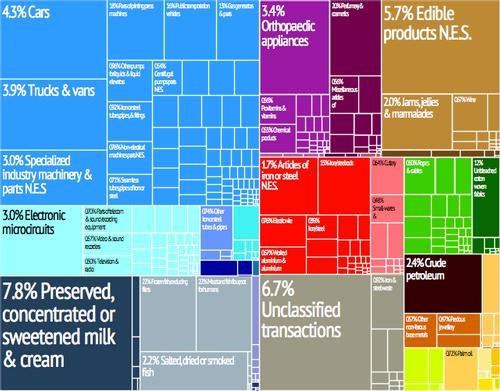
There are hardly any other economic sources: neither agriculture nor industrial industry (tobacco processing, furniture production) are of any relevant size. Tobacco is mainly grown in the valley of Sant Juliàthe Lòria, up to 1600 meters altitude. The government is therefore struggling with financial shortages and a backlog of investments in insufficient infrastructure. Infrastructure, especially a missing airport, is therefore a major priority given the millions of tourists every year.
Due to declining economic activities, the government receives less income from import tax, which should account for 3/4 of the total income. Due to the narrow economic base and the fact that Andorra cannot meet its own domestic needs for industrial and agricultural products, economic growth is very small. The capital Andorra la Vella is the trading center of Andorra where many shopping tourists also make their trade. Andorra does not know airports or railways;most places can be reached via a bus connection.
Unemployment is still virtually nil: because Andorra cannot provide for its own labor needs, many French and Spaniards work there.
Sources
Allemann, F.R. / Catalonië : kunst en cultuur in Barcelona en wijde omgeving
Cantecleer bv
Joosten, T. / Wandelgids Spaanse Pyreneeën : Catalaanse Pyreneeën en Andorra : in 50 wandelingen
Elmar
Maarle, R. van / Pyreneeën
ANWB
Pyreneeën en Andorra
Touring/Lannoo
Zuid-Europa
The Reader’s Digest
Zuidwest-Frankrijk : Toulouse, Lourdes, Andorra, Pyreneeën
Lannoo
Wikipedia
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info