AFGHANISTAN
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | Dari, Pashto |
| Capital | Kabul |
| Area | 652.230 km² |
| Population | 39,835,428 (2021) |
| Currency | Afghani (ALL) |
| Web | .af |
| Code. | AFG |
| Tel. | +93 |

Cities in AFGHANISTAN
| Kabul |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Afghanistan, the 'Land of the Afghans' is located in South Central Asia and is bordered to the northeast by China (91 km), to the west by Iran (921 km), to the north by Uzbekistan (144 km), Tajikistan ( 1357 km) and Turkmenistan (804 km), and in the east and south to Pakistan (2670 km). The river Amu Darya, which flows into the Aral Sea on the border of Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan, forms the border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Pakistan over a length of about 1000 km.
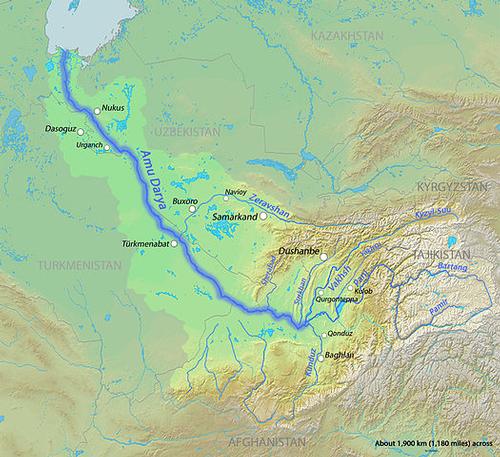 Course of the river Amu Darja, AfghanistanPhoto: DEMIS Mapserver CC 4.0 I no changes made
Course of the river Amu Darja, AfghanistanPhoto: DEMIS Mapserver CC 4.0 I no changes made
A historical buffer area is the Wakhan Corridor, an at first sight curious promontory of about 300 km long and varying in width from 16 to 60 km, which just connects Afghanistan with the Chinese province of Xinjiang and borders Tajikistan and Pakistan.
The surface of Afghanistan is 647,500 km2, making the country slightly larger than France. Afghanistan is 41st on the list of the largest countries in the world. The longest distance from north to south is 1012 km and from east to west 1320 km. Afghanistan is a long way from the sea and surrounded entirely by the above countries.

One of the most famous mountain passes in the world is the Khyber Pass, which runs for about 50 km and at a maximum height of 1070 meters through the Hindu Kush from the Afghan city of Torkham to the Pakistani city of Peshawar. Other high passes are Wakhjir (4923 m), Baroghil (3798 m), Kachin (5639 m), Shotorgardan (3720 m), Bazarak (2713 m), Khawak (3550 m), Anjuman (3858 m), Hajigak (2713) m) and Unai (3350 m).
 Khyber passPhoto: James Mollison CC 2.5 Generic no changes made
Khyber passPhoto: James Mollison CC 2.5 Generic no changes made
Landscape
Geographically, Afghanistan pertain to the northeastern part of the Iranian Highlands, almost half of which (1.2 million km2) lies in Afghanistan. In the flat northern steppe region of Afghanistan there are fertile valleys, irrigated by rivers, with some important cities such as Mazar-e Sharif and Kunduz. The south of Afghanistan, with peaks of at most about 1000 meters, is desert area (Registan desert with many sand dunes and Dasjt-i Margo desert) or desert-like and the rivers flowing there are often dry. Afghanistan mountain landscapePhoto: Master Sgt. Andy Dunaway U.S. Air Force in het publieke domein
Afghanistan mountain landscapePhoto: Master Sgt. Andy Dunaway U.S. Air Force in het publieke domein
Between the landscapes described above is a mountain landscape with mountain ranges that run from the southwest to the northeast and cover about two thirds of the surface of Afghanistan. The main mountain range is the Hindu Kush mountain range (length 1100 km), located just north of the capital, Kabul, which extends into the north of Pakistan. The highest peak of the entire mountain range is Tirich Mir (7699 m) in Pakistan, the highest mountain in Afghanistan is Noshaq (7485 m). This mountain is located at the beginning of the Wakhan Corridor, a narrow strip of land that reaches as far as China, and is the most westerly mountain in the world at over 7,000 meters high. Other high mountains in Afghanistan are the Urgend II (6940 m), the Yamit (6940 m), the Tirgaran (6755 m), the Koheandaras (6628 m) and the Lasht (6504 m). Afghanistan has more than 100 mountains that are higher than 6100 meters and almost 50% of the country is above 2000 meters.
 Noshaq, the highest mountain in AfghanistanPhoto: Khwahan CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Noshaq, the highest mountain in AfghanistanPhoto: Khwahan CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The central part of the Afghan mountain area is formed by the Koh-i Baba, a mountain range with peaks up to 5200 m. The eastern mountain area, with peaks up to 4877 meters, is called Sefid-Koeh and here at an altitude of about 1100 m is the famous Khyber Pass, a 48 km long and sometimes three meters wide pass that connects the Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia with Pakistan and the subcontinent of India. The mountains of Afghanistan join in the northeast with the Karakoram Mountains, which in turn form part of the Himalayas.
This area is geologically very active, with frequent (severe) earthquakes. Earthquakes in 1955, 1998 (6.9 on the Richter scale) and 2002 (7.2) left villages destroyed, thousands of deaths, tens of thousands injured and many homeless. On April 24, 2013, an earthquake hit an area 24 km northwest of the Nangarhar provincial capital of Jalalabad (5.7); 18 people were killed, 141 injured and 676 houses were damaged.
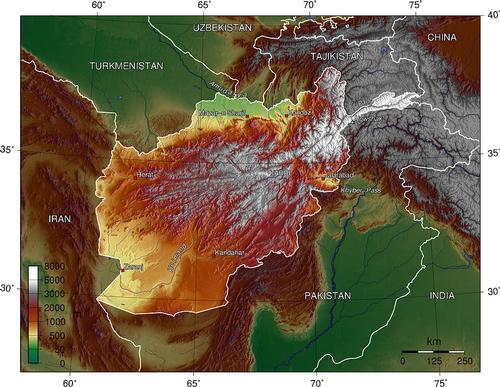 Map of Afghanistan with elevation changes Photo: Thuresson CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Map of Afghanistan with elevation changes Photo: Thuresson CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Rivers and lakes
South of the Hindu Kush is the Kabul Valley through which the Kabul River flows. It is of course no coincidence that the most important city of Afghanistan was founded here. The Kabul (600 km), with tributaries such as the Ghorband, the Panjshir, the Logar and the Kuna, is the only river that flows through the Indus into the Arabian Sea, part of the Indian Ocean. Other Afghan rivers, including the Helmand with tributary Arghandab, the longest river in Afghanistan (1,449 km), flow into inland seas or water basins like that of Sistan in southwestern Afghanistan.
The Hari-Rud (640 km) flows west from Central Afghanistan, then forms the border between Afghanistan and Iran and flows into a water basin in neighboring Turkmenistan. The Amu Darya River in North Afghanistan (1100 km) forms the border between Afghanistan and the neighboring countries of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and flows into Aral Lake. Smaller rivers in the north are the Balkhab, the Samangan and the Kunduz.
 River KabulPhoto: Khalid Mahmood CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
River KabulPhoto: Khalid Mahmood CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Afghanistan does not have many bigger lakes. In the extreme southwest is Afghanistan's largest lake, Lake Hamun-e-Saberi. In this area there are also the lakes Daryacha-e-Namakzar and Hamun-e-Pusak. This lake is also largely located in Iran. In the southeast lies the salt lake Istadeh-ye Moqor and in the Baba mountains in the central region of Bamiyan at an altitude of 2,900 meters there are five small lakes, the Band-e-Mir lakes Haybat, Ghulaman, Zulfiqar, Qanbar and Panir . In the northeast, in the Wakhan corridor, is Lake Sar-e-Qul. To the east, south of the town of Ghazni, is the salt lake Ab-e-Istada (130 km2). To the north of the northeastern city of Faizabad is the beautifully situated Lake Shewa.
Sources
CIA World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Elmar Landeninformatie
Clammer, Paul / Afghanistan
Lonely Planet
Copyright: Team The World of Info