NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS

Geography and Landscape
Geography
Micronesia (from the Greek: small islands) consists of approximately 2300 large and small islands. The islands are scattered in the Western Pacific between Hawaii and the Philippines. Geographically, Micronesia consists of four archipelagos: the Marshall Islands, the Mariana Islands, the Gilbert Islands and the Caroline Islands. Kiribati, which is part of Micronesia, also includes the Line Islands and Phoenix Islands, which are officially part of Polynesia. The distance from north to south is 2572 km and from east to west 5056 km. This means that the islands are spread over an area of more than 13 million km2.
The Northern Mariana Islands (officially: Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands), is a United States-associated archipelago in the North Pacific and part of the Mariana Islands. The Mariana Islands is a group of islands and atolls in the Pacific Ocean, with a total land area of 1081 km2 and a total population of 158,000. The Northern Mariana Islands belong to the continent of Oceania.
The group is divided into the American territory of Guam and the equally American Northern Mariana Islands. The Northern Mariana Islands consist of 14 of the 15 islands of the Mariana Islands. The fifteenth and southernmost island is Guam. The Northern Mariana Islands stretch north of Guam for 645 km. Some of the islands lie in the Pacific and the rest in the Philippine Sea. All the islands are of volcanic or limestone origin.
 Location Northern Mariana IslandsPhoto:TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Location Northern Mariana IslandsPhoto:TUBS CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The total area of the Northern Mariana Islands is 476 km2. The main and largest islands are Saipan (185 km2) with the main town Garapan, Rota (125 km2), Tinian (98 km2) and Pagan (32 km2). The smaller islands lie to the north of Saipan and are rugged volcanic islands. The highest point (964 metres) is on the islet of Agrihan, but is unnamed.
Landscape
Pagan is the largest of the smaller islands. The Maug Islands and Sarigan are protected areas. Farallon de Medinilla is still used by the Americans as a military training area. The only active volcanoes in Micronesia lie between these islands. In 1981, an eruption covered half of Pagan with lava. In 1990, all 21 inhabitants of Anatakan were evacuated to Saipan after an earthquake measuring 7.4 on the Richter scale. Farallon de Pajaros and Asuncion also have volcanic activity.
The Marianas Trench is an underwater canyon 2593 km long and has the greatest ocean depth in the world, 11,770 metres. In fact, the Marianas are the summits of underwater mountains. Measured from the bottom of the Mariana Trench, these mountains are therefore much larger than Mount Everest.
Saipan is the fastest growing island in terms of population and golf courses and tourist hotels are springing up like mushrooms. The number of tourists and guest workers already exceeds the number of indigenous people on the island. It is a pity that the typical Micronesian character of the island is slowly being lost. Saipan has beautiful beaches on the south and west coast, a rough and rocky east coast, a hilly interior and steep cliffs on the north coast.
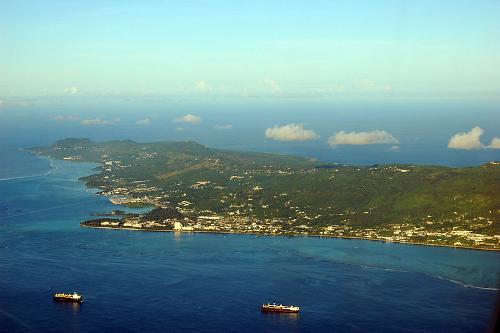 Aerial photo of Saipan, Northern Mariana IslandsPhoto P. Miller (Pdmiller) in het publieke domein
Aerial photo of Saipan, Northern Mariana IslandsPhoto P. Miller (Pdmiller) in het publieke domein
Tinian has been known since World War II as the island from which the planes that would drop the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki took off. Tinian is the most "mountainous" of the islands, with its highest peak at 210 metres. Tinian is also an island with green meadows, deserted beaches and beautiful views. During the Japanese occupation in World War II, many trees were felled and Tinian's fertile soil was used to plant sugar cane fields.
After the war, cattle breeding was resumed and currently Tinian exports meat and milk products to the other islands. In the mid-1990s, the islanders agreed to the establishment of a casino in order to bring in more foreign currency. The northern part of the island was leased to the Americans, who might establish a military base there. Since the closure of military bases in the Philippines, this part of Tinian is regularly used for military exercises.
Rota, situated halfway between Guam and Saipan, has only recently been visited by tourists from other islands. Meanwhile, a few hotels have been built. Rota even has a youth hostel for backpackers. Rota has a hilly landscape with small farms and good spring water. In the hunting season, deer can be hunted.
Songsong is the most important town on the island. The economic crisis in Asia had a major impact on the island's economy; tourists stayed away and revenues fell drastically. Due to the many construction activities, foreign workers (especially from the Philippines) flooded the island.
Sources
Galbraith, K. / Micronesia
Lonely Planet
Levy, N. / Micronesia handbook
Moon
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info