ZAMBIA

Geography and Landscape
Geography
Zambia (officially: Republic of Zambia) is a republic in south central Africa. The total area of the country is 752,614 km2.
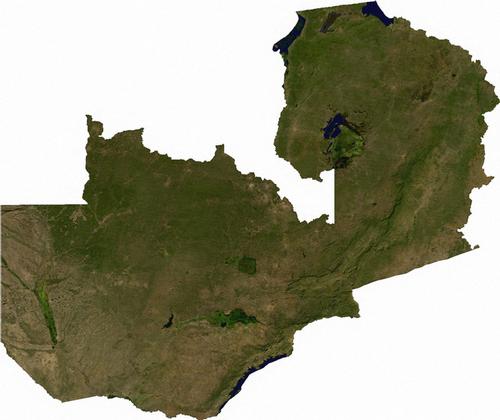 Zambia Satellite PhotoPhoto: Public Domain
Zambia Satellite PhotoPhoto: Public Domain
Zambia is completely surrounded by other countries and borders the Democratic Republic of Congo to the north and north-east (1930 km), Tanzania to the north-west (338 km), Malawi to the east (837 km), Mozambique to the south-east (419 km) and Zimbabwe (797 km), Namibia to the south-west (233 km) and Angola to the west (1110 km).
Landscape
The Zambian landscape consists largely of gently rolling plateaus with an average altitude of 1100 metres above sea level. In the east and north it gradually gets higher and along the border with Malawi the altitude regularly exceeds 1500 metres. Zambia's highest point is found in the Mafinga Hills (2301 metres), on the border with Malawi. On the border with Tanzania around Mbala is an area with an average altitude of 1500 metres.
The valleys of the Central Zambezi in Western Zambia and of the Luangwa in Eastern Zambia are the lowest parts of the country. The point where the Zambezi and Luangwa rivers meet is Zambia's lowest point at 329 metres.
Two of Africa's largest rivers have their source in Zambia, the Zambezi and the Congo River. Zambezi is the fourth largest river in Africa, after the Nile, the Congo and the Niger. In the south, Zambezi forms a border river with Namibia and Zimbabwe and eventually flows into the Indian Ocean after a long journey. About three-quarters of the country belongs to the Zambezi basin and its main tributaries: Kabompo, Kafue and Luangwa. The remainder drains into the Congo and its tributaries the Chambesi and Luapula. The rivers have highly variable water levels and are difficult to navigate because of the rapids and waterfalls. Famous are the Victoria Falls in the Zambezi, over 100 metres high and almost two kilometres wide. Here, the Zambezi thunders down the long zigzagging Batoka Gorge and then flows into the artificial Lake Kariba, which has formed behind the Karaiba Dam. Lake Kariba is 274 kilometres long and up to 48 kilometres wide.
In the extreme north-east is a part of Lake Tanganyika. Lake Tanganyika is 675 kilometres long, the second deepest lake in the world and contains one-sixth of the world's fresh water. To the east of Lake Bangweulu is a swamp that, at 10,000 km2, is one of the largest in the world.
 Tanganyika lake, ZambiaPhoto: Dave Proffer CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Tanganyika lake, ZambiaPhoto: Dave Proffer CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Most of Zambia's soil is a combination of sand and loam; Western Zambia is covered with a thick layer of sand from the Kalahari Desert. Therefore, agriculture is hardly possible in these areas. In the North-East and in the Central, Southern and Eastern Province it rains much more and there we find clay soil.
Sources
Else, D. / Zambia
Lonely Planet
Posthumus, B. / Zambia : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen / Novib
Zuidoost-Afrika
The Reader’s Digest
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info