INDONESIA
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | Indonesian |
| Capital | Jakarta |
| Area | 1.904.569 km² |
| Population | 278,373,269 (2021) |
| Currency | Indonesian rupiah (IDR) |
| Web | .id |
| Code. | IDN |
| Tel. | +62 |
Cities in INDONESIA
| Jakarta | Yogyakarta |
Popular destinations INDONESIA
| Bali | Java | Sumatra |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Indonesia is a republic in Southeast Asia, located between the Asian mainland and Australia. Indonesia is located in the Australasian Middle Sea between the Indian and the Pacific Oceans. This sea consists of a number of smaller seas, including the Java Sea, Flores Sea, Arufura Sea, Banda Sea, Timor Sea and South China Sea.
The archipelago comprises 17,508 (parts of) islands, of which about 990 are inhabited and only about 6,000 have a name.
Indonesia has a land area of approximately 1.95 million km2, making it the largest country in Southeast Asia. From the islet of Sabang in the west to the border of Irian Jaya near Marauke in the east, Indonesia measures about 5100 kilometers, about one eighth of the earth's circumference. The length of the north-south axis is approximately 1760 km.
The total area of Indonesia, including its territorial waters, is more than 5 million km2. Approx. In fact, 64% of the surface of Indonesia consists of water. Indonesians therefore call their country Tanah Air Kita, "our land and water" for a reason.
The largest islands are Kalimantan (539,460 km2), the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo, Sumatra (473,606 km2), Irian Jaya (421,981 km2), the Indonesian part of New Guinea, Sulawesi (189,216 km2) and Java (132,187 km2) . Together they cover more than 90% of the republic's total territory.
Within the archipelago, some 30 smaller island groups can be distinguished, which are grouped together in four regions: the Grand Sunda Islands, namely Java, Sumatra, Sulawesi (Celebes) and Kalimantan (Borneo); the Lesser Sunda Islands, stretching from Bali to Timor; the Moluccas, a group of approximately 1000 islands and islets including Ambon, Ceram, Ternate, Tidore, the Banda, Aru and Tanimbar Islands, Halmahera and Morotai; and Irian Jaya with surrounding islands.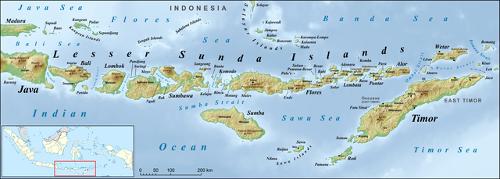 Lesser Sunda Islands belong to IndonesiaPhoto: Lencer CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Lesser Sunda Islands belong to IndonesiaPhoto: Lencer CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Indonesia borders East Timor (228 km), Malaysia (1782 km) and Papua New Guinea (820 km). By sea, Indonesia borders Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, the Philippines and Australia. The total length of the coastline is 108,000 km according to the latest satellite images from February 2003.
Landscape
The enormous variety of landscapes is a result of climatic and geological factors. For example, the islands of Western Indonesia have always been covered with dense tropical rainforests, the East Indonesian islands, on the other hand, are much drier with even savannah landscapes. Most of Indonesia consists of low-lying coastal areas and coral reefs.
Indonesia's highest mountain range, covered with eternal snow, is located in Irian Jaya. Here the Puncak Jaya reaches a height of 5040 meters.
 Puncak Jaya, Indonesia's highest mountainPhoto: Alfrindra Primaldhi CC 2.0 Generikno changes made
Puncak Jaya, Indonesia's highest mountainPhoto: Alfrindra Primaldhi CC 2.0 Generikno changes made
Rainforests
The ecological balance in the rainforest is seriously threatened by human activities or their consequences. For example, logging takes place on a large scale, resulting in increasing erosion. In 1997, huge tracts of rainforest were also lost to forest fires. Indonesia's remaining forest cover covers about 60% of the total land area. This mainly concerns about 100 million hectares of tropical rainforest, the second largest jungle area on earth after Brazil.
Java is one of the most densely populated islands in the world and it is therefore not surprising that more than 90% of its natural vegetation has been destroyed. Most of the remaining primary forest is found only in deserted, mountainous regions above 1,400 meters. Practically all lowland rainforests have been cleared for farms and tree plantations. River and rainforest in Bogor, West-JavaPhoto: Mohd Fahmi Mohd Azmi CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
River and rainforest in Bogor, West-JavaPhoto: Mohd Fahmi Mohd Azmi CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The rainforests of the Lesser Sunda Islands (Nusa Tenggara) are much less lush than those of the rest of Indonesia. There is little rainfall in this area and during the dry season the forests are extremely vulnerable to forest fires. Here you will find a savannah landscape.
Kalimantan in the largest timber export area in all of Southeast Asia. Large parts of the forests have therefore been severely damaged.
Large areas of primary rainforest still exist on the island of Sulawesi.
The most extensive rainforest areas of the Moluccas are found on the islands of Halmahera and Ceram.
The island of New Guinea has the most extensive rainforests in all of Southeast Asia, in total about 700,000 km2. About 80-85% of the tropical forest of Irian Jaya, the western part of the island of New Guinea, and 75-80% of that of Papua New Guinea is still in its original state.
The whole of Irian Jaya, with the exception of the southeastern part, is covered with rainforest.
Rivers and Lakes
The large islands are intersected by large rivers that arise in the mountains and flow into the lowlands as broad streams. Some major rivers are the Kapuas and Barito in Borneo, the Musi in Sumatra and the Brantas in Java. Most of the rivers in Java flow to the north and flow into the Java Sea. The rivers in Java are relatively long. The Solo River has its source in Central Java, near the island's south coast, and winds for a distance of about 600 km before flowing into the Java Sea at Surabaya. Kalimantan's river system is impressive, including Indonesia's longest rivers. The west-flowing Sungai Kapuas is longer than 600 km, the east-draining Mahakam and the south-flowing Sungai Barito are about 500 km long.
Lake Danau Toba is the largest lake in Southeast Asia at 1700 km2; with 450 meters one of the deepest and also one of the highest (900 m) lakes in the world. Lake Danau Toba is with 1700 km² the largest lake in Southeast AsiaPhoto: PL 05 SIGIT CC 4.0 International no changes made
Lake Danau Toba is with 1700 km² the largest lake in Southeast AsiaPhoto: PL 05 SIGIT CC 4.0 International no changes made
Borneo has a total of approximately 110 lakes, including some large ones such as that of Jempang (15,000 ha), Semayang (13,000 ha) and Melintang (11,000 ha). The largest lakes of Irian Jaya are the Danau Paniai, formerly the Exchange Lakes, and the Danau Sentani at Jayapura.
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
More than 100 volcanoes are still active on Indonesia. The most famous is the Krakatau or Rakata, an island volcano located between Sumatra and Java. Other well-known volcanoes are the Agung in Bali, the Merapi, Kelud, Semeru, Pangranro and Gede in Java, the Rinjani in Lombok and the Galunggung in West Java. The most active volcano is the Tambora on the island of Sumbawa. The area where all these volcanoes are located is also called the "Ring of Fire". On average, a large eruption is registered about 10 times a year.
This not only causes problems, but also has a positive side. The mineral-rich ash that is emitted spreads through rivers and irrigation canals all over the country. This makes Indonesia one of the most fertile countries in the world. In particular, the young volcanic ash soils of East and West Java are excellent agricultural land, including for wet rice cultivation. The terraced fields or rice fields, so characteristic of the landscape, are often even situated against the slopes of volcanoes. Only Kalimantan has no suitable agricultural land. This is not a volcanic island and the parent rocks present mainly consist of sandstone and granite. Less suitable for agriculture are also the red-yellow leached soils in the wet northwest of Java and the terra-rassa soils on the south coast of the island. In addition to cone-shaped volcanoes, there are also volcanoes with multiple craters and volcanoes with a whole series of secondary cones. Mount Bromo on Java, IndonesiaPhoto: Sara Marlowe CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Mount Bromo on Java, IndonesiaPhoto: Sara Marlowe CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
When Krakatau erupted in 1883, the force of the eruption was comparable to the detonation of several hydrogen bombs. The eruption caused tidal waves that killed more than 35,000 people in Java.
The explosion of Krakatau was surpassed by the 1815 eruption of Tambora volcano on Sumbawa, which killed 90,000 people and ejected ashes darkening the sun for many months.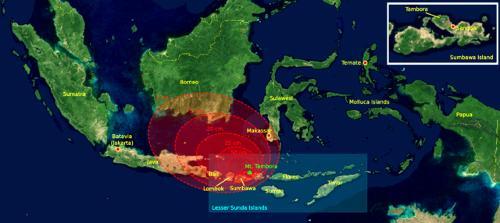 The eruption of Mount Tambora in 1815. The red areas on the map indicate the thickness of the volcanic ashPhoto: Myself CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The eruption of Mount Tambora in 1815. The red areas on the map indicate the thickness of the volcanic ashPhoto: Myself CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
In addition to volcanic eruptions, numerous earthquakes also occur. Every year an average of 500 to 1000 tremors are recorded throughout Indonesia, most of which fortunately have only a limited force.
However, when the epicenter of an earthquake is in the sea, such a quake can create a devastating tidal wave or "tsunami," which is often much more dangerous than the quake itself.
Sources
Dalton, B. / De Indonesië reisgids
Elmar
Darmawie-van Oijen, J. / Indonesië : handboek voor reizigers
Babylon-De Geus
Homburg, E. / Indonesië
Elmar,
Indonesië
Cambium
Lyle, G. / Indonesia
Chelsea House
Martyr, D. / Indonesië
Van Reemst
Mastenbroek, B. / Kijk op Indonesië
Elsevier
Muller, K. / Indonesië : het 13.000 eilandenrijk
Becht
Oosterman, I. / Indonesië
ANWB Media
Schulte Nordholt, N. / Indonesië : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen / NOVIB
Te gast in Indonesië
Informatie Verre Reizen
Wassing, R. S. / Indonesië : Java, Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Komodo, Flores, Sumba, Timor, Sumatra, Zuid- en Oost-Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Singapore
Gottmer
Witjes, B. / Indonesië
Stichting Teleac
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info