SWEDEN
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | Swedish |
| Capital | Stockholm |
| Area | 449.964 km² |
| Population | 10,210,538 (2021) |
| Currency | Swedish crown (SEK) |
| Web | .se |
| Code. | SWE |
| Tel. | +46 |

Cities in SWEDEN
| Stockholm |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
The kingdom of Sweden (officially: Konungariket Sverige) is the largest country in the Scandinavian peninsula. Sweden borders Norway in the west and north. Sweden borders Finland in the northeast. In the southwest, Sweden has a coastline of more than 14,000 kilometers along the Gulf of Bothnia, the Baltic Sea, the Sound, the Kattegat and the Skagerrak. Sweden also includes the larger islands of Gotland and Öland. Sweden is a very elongated country. The northernmost point is Frederiksröset, which lies above the Arctic Circle: the southernmost point is Smygehuk opposite Germany's Baltic Sea coast.
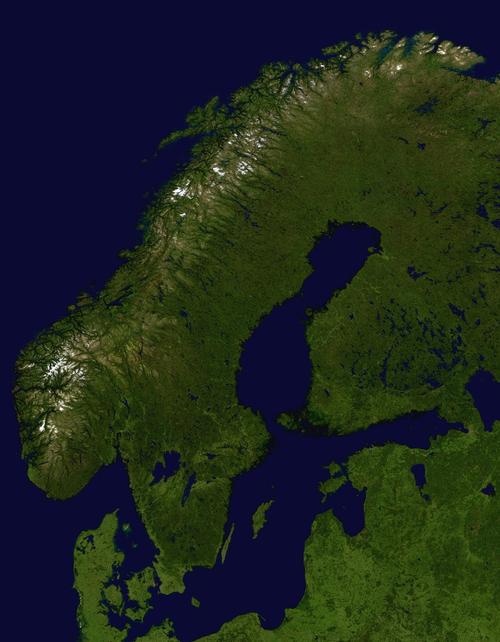 Sweden:Satellite photoPhoto: Public domain
Sweden:Satellite photoPhoto: Public domain
The area of wasteland in Sweden is 31%, including more than 96,000 lakes. 58% of the soil is covered with forests and the cultivated land covers 11%. The longest river is Klarälv-Götaälv, 720 km long. Sweden's highest mountain, the Kebnekaise, is located in Norrland and is over 2100 meters high.
Landscape
The final design of Sweden's landscape came about through the ice ages. The land ice cover had a thickness of 2000 to 4000 m and covered the entire country. The sliding ice polished the bottom, the land was flattened, some harder knobs were ground into so-called hump rocks. In addition, deposition of moraine material took place. Kilometers long and sometimes 100 m high ridges of sand and gravel formed under the ice. After the great pressure of the inland ice disappeared, the land was gradually lifted. As a result, old coastlines were greatly lifted. Even today there is lifting, which in the north is 100 cm per century and at Stockholm 45 cm, while on the south coast no more lifting is measurable. The Swedish coast therefore consists of thousands of small islands and rocky points, which protrude just above water. These skerries are almost completely bare on the west coast, but mostly wooded along the east coast.
 Kebnekaise, Sweden's highest mountainPhoto: Alexander Vujadinovic CC 4.0 Internationano changes
Kebnekaise, Sweden's highest mountainPhoto: Alexander Vujadinovic CC 4.0 Internationano changes
Sweden is divided into three major landscapes: Norrland in the north, Svealand in the middle and Götaland in the south.
Norrland is mountainous with endless forests and many rivers and lakes. Norrland covers almost two-thirds of Sweden's total area.
Svealand in central Sweden has a more open and friendly landscape. Behind a razor belt lies the capital Stockholm on the east coast. Around Stockholm it is overgrown with dense forests. Further inland are open plains where the Swedes have focused on arable farming for thousands of years. However, the fertile fields are alternated with dense forests and swampy plateaus.
Götaland in the south has a very varied landscape with flourishing agricultural areas and beech forests in the southernmost province of Skåne. Furthermore, there are extensive forests on stony ground, hardly suitable for agriculture. The west coast is flat with sometimes long sandy beaches. Furthermore, a skating coast with many islands and inlets. Here are also the large lakes Vänern and Vättern. Vänern is the third largest lake in Europe.
Sources
Best, J. / Zweden
Gottmer
Carlsson, B. / Zweden
Corona
Danse, W. / Zweden
ANWB
Europese Unie
Europees Platform voor het Nederlandse Onderwijs
Meesters, G. / Zweden
ANWB
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info