MEXICO

Cities in MEXICO
| Mexico city | Playa del carmen | Riviera maya |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Mexico (Spanish: México; officially: Estados Unidos Mexicanos, = United States of Mexico) is a federated republic in Central America. Geographically, Mexico is part of the continent of North America, culturally it is part of Latin America (Central and South America).
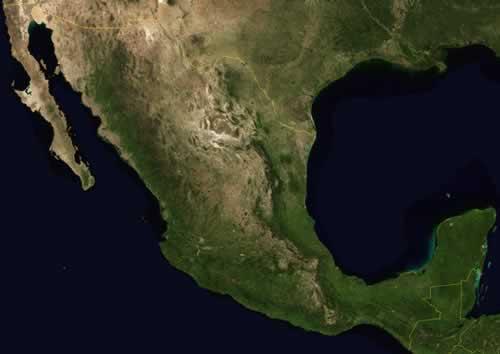
The total area, including 5364 km² of islands, is 1,958,201 km². Mexico takes fourteenth place in the world ranking of major countries. Mexico is the third largest country in Latin America after Brazil and Argentina.
Mexico is bordered to the north by the US states of California, Arizona, New Mexico and Texas. This border is 3326 kilometers long, two thirds of which is formed by the river Río Bravo del Norte (United States: Rio Grande). In the south, Mexico borders the Central American states of Guatemala (962 km) and Belize (250 km). Border with Mexico near San DiegoPhoto: Roman Eugeniusz CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Border with Mexico near San DiegoPhoto: Roman Eugeniusz CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
To the west, Mexico borders the Pacific or Pacific Ocean (7360 kilometers). In the east, the country borders the Atantic Ocean (2600 km). The Atlantic Ocean here is called Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea.
Mexico includes many islands, of which Guadeloupe, Revillagigedo and Isla de Cedros in the Pacific Ocean, Tiburón, Tres Marías and Angel de la Guarda in the Gulf of California, and Cozumel Island in the Caribbean Sea are the largest. There are two main peninsulas: Baja California in the northwest and Yucatán in the southeast. The capital of Mexico is Ciudad de México (internationally known as Mexico City). Mexico City is located at an altitude of 2,200 meters in a valley surrounded by the Sierra Madre and a number of volcanoes. Isla de Cedros, MexicoPhoto: WCCasey CC 4.0 International no changes made
Isla de Cedros, MexicoPhoto: WCCasey CC 4.0 International no changes made
Landscape
Mexico is generally a very mountainous country with narrow valleys in between where agriculture is possible. Approx. 80% of the country is covered with mountains and no less than 26% of the country has a slope of 25% or more.
The Central Plateau or Mesa Central (also called Meseta de México) occupies three quarters of Mexico and is bordered by the Sierra Madre Oriental (continuation of the Rocky Mountains), the Sierra Volcánica Transversal and the Sierra Madre Occidental (continuation of the American Sierra Nevada). This plateau is intersected by hills, valleys and mountain ranges. The altitude varies from 1500 meters in the north to 2500 meters in the south. Sierra Madre Oriental, MexicoPhoto: Boligrafoazul CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Sierra Madre Oriental, MexicoPhoto: Boligrafoazul CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The pine-forested Sierra Madre Occidental runs parallel to the west coast from the United States border to the south and the Sierra Madre Oriental runs parallel to the east coast. Many canyons in the Sierra Madre Occidental are 1500 to 2000 meters deep, such as the Baranca del Cobre in the state of Chiapas. To the west of the Sierra Madre Occidental is a savanna area with large, irrigated agricultural valleys. Sierra Madre Occidental, MexicoPhoto: Christian Frausto Bernal CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Sierra Madre Occidental, MexicoPhoto: Christian Frausto Bernal CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
South of the plateau lies the Sierra Volcánica Transversal chain of volcanoes. Some volcanoes are still active, for example the Popocatépetl, the "smoking mountain" (5452 meters high). In June 1997 the volcano became active again after 67 years and the capital was covered with a thick layer of ash. Other high volcanoes are the Nevada de Toluca (4577 meters), the Ixtaccíhuatl (5286 meters: sleeping woman) and the eternally snow-covered Citlaltépetl (mountain of the star) or Pico de Orizaba, at 5700 meters the highest point in Mexico. Characteristic of this area are crater lakes and lava flows. To the south of this volcanic area lies the coastal mountain range Sierra Madre del Sur. This mountain range is separated by the isthmus of Tehuantepec from the mountainous region of the state of Chiapas. To the west is the volcanic belt of Michoacán, where a volcano was formed in 1943, the Volcán de Paricutín. In total there are about 3,000 volcanoes in Mexico, of which fourteen are active.
 Pico de Orizaba, Mexico's highest mountainPhoto: Pacomexico CC BY 2.0 no changes made
Pico de Orizaba, Mexico's highest mountainPhoto: Pacomexico CC BY 2.0 no changes made
South of the plateau lies the valley of Oaxaca at an altitude of 1350 meters. In the state of Tabasco there are swamps and tropical rainforests, which also cover much of the relatively flat Yucatán peninsula. To the east of Yucatán are the fantastic sandy beaches that are very popular with tourists.
Along the Gulf of Mexico is a long coastal plain from the Río Grande to the Yucatán peninsula. This coastal plain is about 1280 km long and the width varies from a few kilometers to about 150 kilometers. This lowland consists largely of lagoons and swamps. Also along the coasts of the Pacific Ocean is a lowland, consisting of long hills and plains that merge into the Sonoran Desert in the north.
The mountainous, arid and desert peninsula of Baja California has steep slopes to the Gulf of California and fairly wide coastal plains to the Pacific Ocean. It is the largest peninsula in the world, approximately 1300 kilometers long and 65 to 300 kilometers wide.
In northwestern Mexico is the Sonoran Desert and to the east is the Chihuahua Desert. Both deserts consist equally of sand, gravel and bedrock. The dry northeast was once the bottom of a sea. The soil here usually consists of limestone, a sedimentary rock formed from shells or skeletons of aquatic organisms, such as shellfish and corals. Caves often form in this type of rock. Chihuahua desert, MexicoPhoto: Ricraider CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Chihuahua desert, MexicoPhoto: Ricraider CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Due to the shifting of the ocean floor in relation to the continental plate, there are quite a lot of earthquakes in Mexico. Very severe earthquakes occur sporadically, the most recent being September 19, 1985 when an earthquake measuring 7.8 on the Richter scale caused thousands of deaths and billions of damage in Mexico City. Approx. 150,000 houses were damaged by the natural disaster.
About 575 kilometers west of Mexico is the Revillagigedos archipelago, whose volcano Mariano Barcena exploded in 1952. Another volcano that exploded was the Chichonal in Chiapas in 1982.
From the island of Isla Contoy off the coast of Yucatán to the port city of Chetumal on the border with Belize is the second largest barrier reef in the world, 700 kilometers long. Isla Contoy, MexicoPhoto: Peter Maas CC 2.5 Generic no changes made
Isla Contoy, MexicoPhoto: Peter Maas CC 2.5 Generic no changes made
The largest underwater cave system in the world is that of Nohoch, southwest of Akumal, with 18 kilometers of interconnected underwater corridors and caves.
Rivers and lakes
Due to the dry climate, there are hardly any rivers in the north. After heavy rainfall, lakes may temporarily form basins or valleys. To the south, three large river systems drain the Central Plateau. The river system of the Balsas has carved deep valleys and drains to the Pacific. The Rio Pánuco system flows through a rocky area to the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. The Santiago System drains into the Pacific Ocean through Lago Chapala. Rio Panuco, MexicoPhoto: Edgar Galindo CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Rio Panuco, MexicoPhoto: Edgar Galindo CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Major rivers are also the Río Usumacinta, the Río Grijalva and the Río Grande de Santiago. Large lakes are Lago Chapala (1690 km2) and the Falcon Reservoir. Lago Chapala, MexicoPhoto: AlejandradlT CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Lago Chapala, MexicoPhoto: AlejandradlT CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Sources
Daling, T. / Mexico : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur, milieu
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen / Novib
Dunlop, F. / Mexico
Van Reemst,
Mexico
Cambium
Rokebrand, R. / Mexico
Gottmer/Becht
Rummel, J. / Mexico
Chelsea House Publishers
Wagenvoort, E. / Reishandboek Mexico
Elmar
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info