MEXICO
Society

Society

Cities in MEXICO
| Mexico city | Playa del carmen | Riviera maya |
Society
State organization
Mexico (Estados Unidos Mexicanos) is a federal democratic republic with a great deal of autonomy for the individual states. All this is laid down in the 1917 constitution, which has since been amended many times.
The president heads the executive branch. He is elected in direct elections for no more than one six-year term. The cabinet consists of fifteen ministers, three secretaries of state and an attorney general. The president is a powerful man because he appoints the ministers himself, but can also dismiss governors, for example.
Legislative power rests with the parliament (Congreso de la Unión), consisting of a Senate (Cámara de Senadores) with 128 members (4 per state), elected for six years, and a Chamber of Deputies (Cámara de Diputados) with 500 members , of which 300 are elected every three years by the district system and 200 by the proportional representation system from lists of candidates submitted by registered parties. "Cámara de Diputados" MexicoPhoto: EdwinDlacruz CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
"Cámara de Diputados" MexicoPhoto: EdwinDlacruz CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The right to vote is open to all citizens aged eighteen and older, and married persons from the age of 16. Women have only had the right to vote since 1953.
Mexico is politically divided into five regions with 31 states and the Federal District in which the capital Mexico City is located with twelve surrounding so-called delegaciones. Each state has its own constitution, its own taxes and an elected governor who remains in office for six years and is elected by the residents of the state themselves. The Governor of the Federal District is appointed by the President. The states are subdivided into approx. 2300 municipios (municipalities).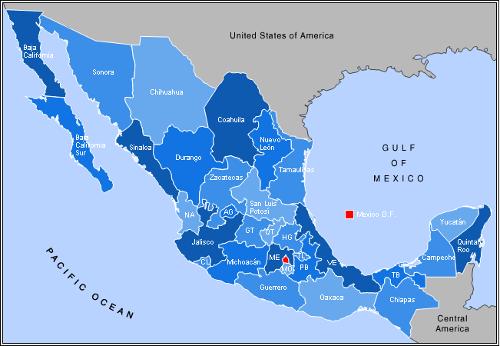 States MexicoPhoto: Alex Covarrubias CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
States MexicoPhoto: Alex Covarrubias CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
In 1997 there were been elections for the office of mayor of Mexico City for the first time in history. Until then, the mayor of Mexico City was directly appointed by the president. At the municipal level, the mayor still has the option of appointing his own civil servants and police officers. For the current political situation see chapter history.
Education
Public primary education is free and now compulsory for children aged 6 to 15 years. Yet only about 60% of the children finish primary school. Especially in the traditional Indian communities, work is often much more important to boost the income of the parents. Elementary school Ignacio Zaragoza, MexicoPhoto: Oskarale CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Elementary school Ignacio Zaragoza, MexicoPhoto: Oskarale CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
In the Indian areas, the educational level is also low due to too few teaching materials. School buildings also usually do not meet the standards and there are too few teachers who have often had a poor education. Furthermore, there are 60 children in one class, especially in rural areas. Secondary education is almost impossible for the poor part of the population to afford and many children drop out after primary education. Of the thousand children in primary school, only eighty go to secondary education. Only half of these eighty will graduate!
Education continues to suffer from annual strikes and demonstrations by teaching staff for higher salaries and better educational facilities.
For the wealthier Mexican children there are private schools, both for primary and higher education.
There are 85 universities and nearly 4,000 higher education institutions in Mexico. The UNAM (Universidad Nacional de Autónoma) is the largest university in the world with more than 300,000 students and more than 20,000 teachers. Building of the Universidad Nacional de Autónoma de México (UNAM), largest university in the worldPhoto: Armineaghayan CC 4.0 International no changes made
Building of the Universidad Nacional de Autónoma de México (UNAM), largest university in the worldPhoto: Armineaghayan CC 4.0 International no changes made
Nationally, illiteracy rates are about 8% among men and 13% among women. Among the indigenous population, this percentage is generally considerably higher, up to 80% in some village communities.
Sources
Daling, T. / Mexico : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur, milieu
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen / Novib
Dunlop, F. / Mexico
Van Reemst,
Mexico
Cambium
Rokebrand, R. / Mexico
Gottmer/Becht
Rummel, J. / Mexico
Chelsea House Publishers
Wagenvoort, E. / Reishandboek Mexico
Elmar
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info