ROMANIA
Language

Language
Cities in ROMANIA
| Brasov | Bucharest |
Language
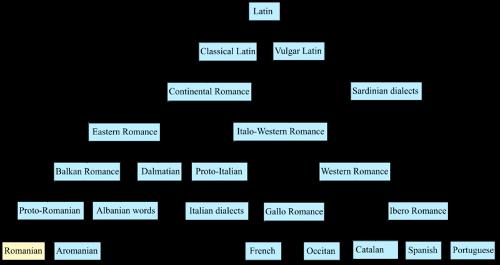 Place of Romanian within the Romanesque language familyPhoto: Maksim CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Place of Romanian within the Romanesque language familyPhoto: Maksim CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The official language of Romania is Romanian, an Eastern Romance language also spoken by the inhabitants of Moldova and minorities in Greece, Albania, Hungary, Bulgaria and Serbia. Romanian, together with Italian and the disappeared Dalmatian, belongs to the Eastern Romance languages, but has developed completely independently due to its isolation. Grammatically and lexicologically, Romanian is strongly influenced by Slavic, especially Bulgarian, but also Russian and Serbian. The influences of Modern Greek, Turkish and Hungarian are mainly on the lexicological level.
Anyone who knows some French or Latin will come across many well-known words in Romanian. Like French, Portuguese, Italian and Spanish, Romanian is a language that originated from Latin.
The first written Romanian dates from the 16th century and in 1688 the complete Bible was first translated into Romanian. It was not until the 19th century that Romanian became the main language of culture of the principalities on the Danube and the first Romanian grammars appeared. The Cyrillic script was officially replaced by the Latin script after the unification of Wallachia and Moldavia in the mid-19th century
There are no real dialects within the borders of Romania. A true variety of Romanian is spoken in the Republic of Moldova. There is also Aromanian, which is spoken in some regions, especially in Northern Greece, and also in Albania, Bulgaria, Macedonia and Serbia.
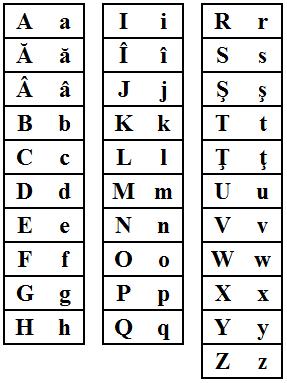 Romanian alphabetPhoto: Public domain
Romanian alphabetPhoto: Public domain
The alphabet consists of 28 letters: the q is missing, but Romanian has the following extra letters, a, â, î, s, and t. With a few exceptions, the pronunciation is almost identical to English.
What is special is that consonants are never doubled, for example: comisar = commissaire.
Some words and phrases:
- A = unu
- Two = doi
- Three = trei
- Ten = zece
- Hundred = o suta
- Good morning = buna dimineata
- See you soon = la reveder
- Monday = luni
- Sunday = duminica
- Forbidden access = access interzis
- No smoking = fumatul interzis
- A single room = o camera cu un pat
- Key = cheie
- Would you like to wake me up at seven? = puteti sa ma treziti la ora sapte?
- A city map = o harta a orasului
The languages of the minorities have the status of an official language in the areas where they live. They therefore have their own education, newspapers and broadcasting time on radio and television.
Sources
Bos, J.W. / Roemenië : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur, milieu
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen
Democratisering aan de Donau : Roemenië na de revolutie van 1989
Instituut voor Publiek en Politiek
Roemenië
Steunpunt Oost-Europa Projecten
Versteegen, J. / Roemenië
Gottmer
Williams, N. / Romania & Moldova
Lonely Planet
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info