MYANMAR


Geography and Landscape
Geography
Myanmar (Burma) is located in Southeast Asia. The surface area of Myanmar is 657,500 km2, making it the largest country on the mainland of Southeast Asia. Myanmar is slightly larger than Great Britain and France combined. The distance between the extreme north and the south is 2090 km; the maximum width is 925 km.
 Myanmar on the world mapPhoto:Addicted 04 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Myanmar on the world mapPhoto:Addicted 04 CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Myanmar borders Bangladesh in the west (193 km), India in the west/northwest (1463 km), China in the north/east (2185 km), Laos in the east (235 km) and Thailand in the east/south (1800). The coastline of Myanmar is 1930 km long and runs from the border with Bangladesh in the west to the city of Kawthoung in the extreme south of the country. The coast of Myanmar is bordered from north to south by the Bay of Bengal, the Gulf of Martaban and the Andaman Sea.
Burma, Burma or Myanmar (myan=fast, mar=strong)?
In 1989, the government decided to change the official name of Burma to Union of Myanmar (Pyidaungse Myanma Naigngandaw). One of the reasons for the change was that the name Burma had too nasty a colonial connotation and one might also think that there were only Burmese living in the country instead of many ethnic groups. Moreover, Myanma was already spoken of in the time of the first Burmese kings. Opponents of the military regime still use the name Burma. The United Nations uses the name Myanmar. The inhabitants of Myanmar are called Burmese, the largest population group are the Burmese. This also often leads to misunderstandings.
Landscape
Myanmar has a varied landscape with mountains, coastal plains, coral islands and many rivers. The north of Myanmar is dominated by the foothills of the eastern Himalayas. In this area, on the border with Tiber, is also the highest mountain in Myanmar and Southeast Asia, the 5883 m high Hkakabo Razi.
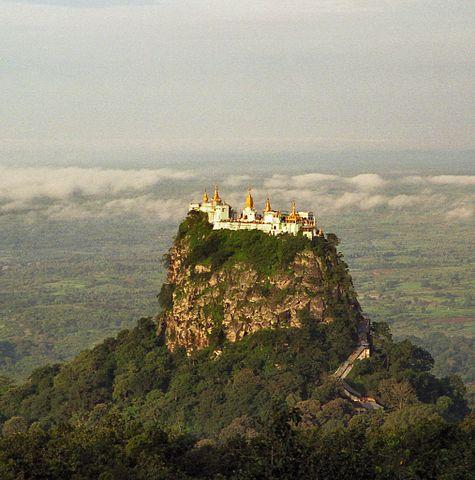
Two mountain ranges running from north to south embrace Myanmar: the Chin Hills and Rakhine Yoma in the west and the Shan Plateau (average altitude 1000 m) and its southern spur Bilauktaing Yoma in the east. The western mountain range also forms the border between Myanmar and the Indian subcontinent; the eastern chain forms the border with Thailand and Laos. Between these two mountain ranges lies the volcanic Bago Yoma mountain range.
 Temple on top of Taung Kalat mountainPhoto:Brian Snelson CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Temple on top of Taung Kalat mountainPhoto:Brian Snelson CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The Ayeyarwady (or Irrawaddy) is the country's most important river and is over 2000 km long. Like other major rivers, it has its source in the mountainous north of Myanmar and flows into the Gulf of Martaban. The Ayeyarwady is very important for Myanmar due to its good navigability and the use of the water for rice cultivation. The river eventually branches off to form a fertile delta of approx. 50,000 km2, one of the largest deltas in the whole of Asia. Other important rivers are the Chindwin (approx. 1000 km), the Sittoung (560 km) and the Thanlwin, the longest river in Myanmar. The world famous Mekong River forms the border between Myanmar and Laos in the northeast.
Myanmar has few lakes; a number of small ones and two large ones, Indawgyi in Kachin State and Inle in Shan State (approx. 242 km2).
The largest coastal plains are in Rakhine State and Tanintharyi District. The Mergui or Myeik Archipelago lies off the extreme south coast of Myanmar in the Andaman Sea. The archipelago consists of more than 800 islands, ranging in size from very small to several hundred square kilometres. Most of the islands are uninhabited, on some islands live sea gypsies, the Salon (they call themselves Moken or Maw Ken).
Sources
Hulst, H. / Birma: (Myanmar)
KIT Publishers/Oxfam Novib
Köllner, H. / Myanmar (Birma)
Het Spectrum
Myat Yin, S. / Burma
Times Books
Peterse, L. / Birma (Myanmar)
Gottmer/Becht
Reid, R. / Myanmar (Burma)
Lonely Planet
Wikipedia
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info