HAITI
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | French, Creole |
| Capital | Port-au-Prince |
| Area | 27.750 km² |
| Population | 11,635,679 (2021) |
| Currency | gourde (HTG) |
| Web | .ht |
| Code. | HTI |
| Tel. | +509 |

Geography and Landscape
Geography
Haiti officially the Republic of Haiti (French: République d'Haiti, Kreyòl: Repiblik Ayiti), occupies the western part of the island of Hispaniola and a number of smaller islands, of which Île de la Gonâve, Île de la Tortue and Île à Vache are the largest.
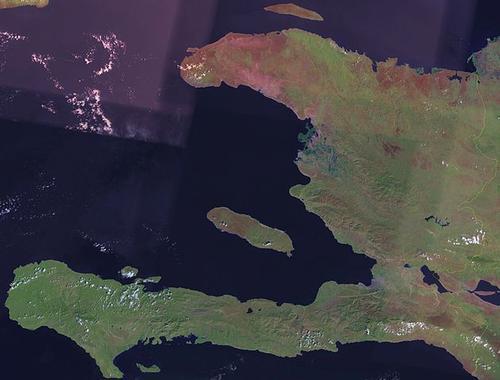
Haiti is part of the Greater Antilles. On the eastern part of the island is the Dominican Republic. With a surface area of 27,750 square kilometres, Haiti is roughly the size of Belgium.
Haiti lies south of the Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. To the north-west of Haiti is Cuba and to the west is Jamaica. To the east is Puerto Rico. Finally, far south of Haiti are the Leeward Islands of the Netherlands Antilles: Aruba, Bonaire and Curacao.
Landscape
Haiti has a landscape of rugged rocky coasts, white beaches and plains where sugar cane and coffee are grown. Furthermore, there are impressive mountain areas with the southern Massif du Sus having the highest peak at 2674 metres: Pic la Selle. Other mountain ranges are the Chaine des Marheaux, the Montagnes du Trou d'Eau and the Montagnes Noires. In the north lies the Massif du Nord.
 Landscape around Pignon, HaitiPhoto: Public domain
Landscape around Pignon, HaitiPhoto: Public domain
Climate and Weather
Haiti has a subtropical climate with daytime temperatures ranging between 25 and 30 degrees throughout the year. The island has a dry period and a rainy season. The rainy season runs from June to November and is also mostly sunny. Rain showers are often short but heavy. There is much less rain in the lee of the mountains than on the slopes. From September to November is the hurricane season.
Plants and Animals
Plants
The country has some plains, but mostly hills and mountains. Originally, the land was covered with forests. However, these were burnt down to gain agricultural land and to make charcoal to cook on. Today, only two percent of the original forest remains. Deforestation of the steep slopes caused mudslides and erosion. This was at the expense of agriculture and makes the country extra vulnerable to hurricanes and cyclones. On the savannahs, palms grow here and there, and in the driest areas cacti dominate the picture. The mangrove forests along the coast are particularly beautiful. Some fertile locations on the mountain slopes are covered with mountain mangroves. The lowlands are dotted with picturesque sugar cane and coffee plantations. The vegetation further consists of bluewood, cedar, pine, mahogany, orchid, palm and rosewood.
Animals
Many animals have lost their natural habitat due to deforestation and have subsequently become extinct. The animal world is not very varied. In the mangrove forests, there are still quite a few water birds. There are also a few crocodiles. The surrounding waters are teeming with multicoloured fish. Other animals that occur in Haiti are agouta, flamingo, hummingbird, parrot, peregrine falcon and bat.
Sources
Elmar Landeninformatie
Wikipedia
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info