PERU
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | Spanish |
| Capital | Lima |
| Area | 1.285.216 km² |
| Population | 33,768,214 (2021) |
| Currency | sol (PEN) |
| Web | .pe |
| Code. | PER |
| Tel. | +51 |

Cities in PERU
| Lima |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Peru (officially: República del Perú) is a republic in South America. The total area of Peru is 1,285,216 km2, including 4997 km2 of the Peruvian part of Lake Titicaca and excluding 95 km2 of the islands in the Pacific Ocean. Peru ranks third in South America in size, behind Brazil and Argentina.
Peru is located along the Pacific coast (2400 km long coastline) and is bordered by Colombia (1496 km) and Ecuador (1420 km) to the north, Brazil (1560 km) to the east and Bolivia (900 km) and Chile (160 km) in the south.
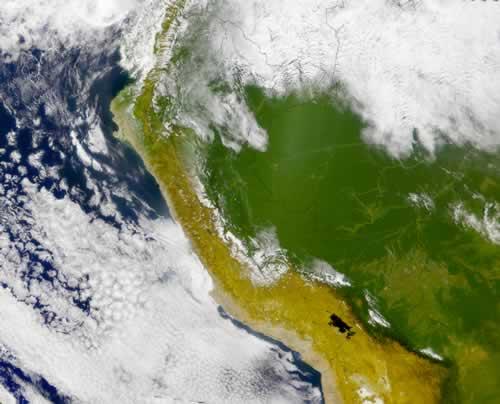

Landscape
Three areas can be distinguished from west to east: the Costa, the Sierra and the Selva.
The Costa comprises the mainly desert-like area along the steep coast between the Pacific Ocean and the western mountain slopes of the Andes (about 11% of the total area of Peru). This 2400 km long coastline is one of the driest areas on earth; in some areas it only rains once every two years. Together with the Atacama Desert in Chile, it forms one of the largest desert areas in the world. The coastal plain is only in the north (sandy desert of Sechura) up to 160 kilometers wide; southward the width varies from 30 to 100 km. The landscape consists partly of plains and sand dunes, partly of hilly land that gradually flows into the Andes mountains.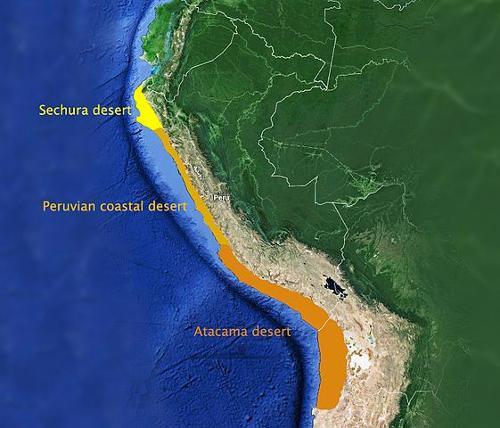 Deserts of PeruPhoto: Hookery CC 4.0 International no changes made
Deserts of PeruPhoto: Hookery CC 4.0 International no changes made
The Sierra comprises the Andean region, consisting of two large chains running from north to south, the Cordillera Occidental and the Cordillera Oriental. The mountains cover about a third of the country and the width varies from 150 to 400 kilometers. In the north of the country these chains are close together, but in southern Peru this distance is great and here is the Altiplano, a large plateau that slopes down to Lake Titicaca and has an average height of about 4000 meters. The plateau continues to southern Bolivia and west of the lake the Cordillera Marítima descends to the coast, with high volcanoes such as the Misti (5822 meters) near Arequipa.
The Cordillera Occidental is an almost continuous chain. The highest part reaches this chain in the Cordillera Blanca, an uninterrupted and highly glazed chain with 29 mountains above 6000 meters, of which Huascarán Sur at 6768 meters is the highest mountain in Peru. In the Cordillera Blanca is also Peru's second mountain, the 6655 meter high Huascarán Norte. The Cordillera Oriental is interrupted by a number of large transverse valleys called quebradas.
 Huascarán Sur, highest mountain in PeruPhoto: ZiaLater in the public domain
Huascarán Sur, highest mountain in PeruPhoto: ZiaLater in the public domain
The discovery of fossils and shells at an altitude of 5000 meters proves that the Andes was once at sea level. The collision of the continental plates created the Andes, and this process is still ongoing. As a result, a lot of volcanic activity can still be observed and earthquakes still occur regularly. Active volcanism only occurs in the vicinity of Arequipa and further south. In the north and center of the Peruvian Andes all volcanoes have been extinguished. Northwest of Arequipa is the Cañón del Colca, with a depth of 3,182 meters, one of the deepest ravines in the world.
The ten highest mountains in Peru:
| name | height | Mountain range |
| Huascarán Sur | 6768 m | Cordillera Blanca |
| Huascarán Norte | 6655 m | Cordillera Blanca |
| Yerupajá Grande | 6634 m | Cordillera Huayhuash |
| Yerupajá Sur | 6515 m | Cordillera Huayhuash |
| Coropuna | 6425 m | Cordillera Chila |
| Huantsan | 6395 m | Cordillera Blanca |
| Huandoy Norte | 6395 m | Cordillera Blanca |
| Ausangate | 6372 m | Cordillera Vilcanota |
| Siula Grande | 6356 m | Cordillera Huayhuash |
| Huanday Oeste | 6356 m | Cordillera Blanca |
The Selva encompasses the area east of the Andes mountains, and can be divided into the Selva Alta (High Selva) or Montaña, the eastern very sharply cut Andean slopes, creating a landscape of sharp ridges between deep valleys, and the Selva Baja ( Low Selva), the Amazon Plain. This tropical lowland covers more than half of the Peruvian territory.
Peru's location on the edge of a tectonically active region is the cause of volcanic phenomena and earthquakes.
A few volcanoes are still active in southern Peru, including El Misti (5835 m). The worst earthquake for centuries occurred in central Peru on May 31, 1970, wreaking havoc in the Río Santa Valley (Huaylas Valley) and wiping out the cities of Huaráz and Yungay.
Rivers and lakes
 Lake Titicata PeruPhoto: Bobistravelling CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Lake Titicata PeruPhoto: Bobistravelling CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
The mighty Amazon River originates in Peru, although its exact origin is still disputed. Measured from Peru to the mouth, the length of the Amazon is approximately 6400 kilometers. The catchment area extends over an area of six million square kilometers. More than five hundred rivers meander through Peru's tropical lowlands (selva), all of which flow into the Amazon River.
Important are the large source branches of the Amazon, which arise high between the Andean chains, the Río Marañón, Río Huallaga and Río Ucayali with Río Apurímac and Río Urubamba. In southern Peru, the east slope of the Cordillera Oriental gives rise to the Madre de Dios, which flows eastwards via the Madeira to the Amazon. The rivers on the west coast, with the exception of the Río Santa, are of little importance as they only contain water for part of the year. Río Marañón, PeruPhoto: Gato Montes CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
Río Marañón, PeruPhoto: Gato Montes CC 3.0 Unported no changes made
The south-flowing Río Ramis is the main source river of Lake Titicaca, the highest navigable lake in the world at 3812 m, of which 4996 km2 (total 8300 km2) belongs to Peru. The water of the lake also comes from many rivers that bring rain and melt water from the Andes. The border with Bolivia runs straight through the lake.
Some more information:
- Length: approx. 175 kilometers
- Width: approx. 50 kilometers
- Average depth: 100 meters
- Largest measured depth: 283 meters
- Water temperature: fairly constant 13 ° C
- Number of islands in the lake: approx. 30
Sources
Le Grand, J.W. / Peru : mensen, politiek, economie, cultuur
Koninklijk Instituut voor de Tropen : Novib
Luft, A. / Peru
Elmar,
Lyle, G. / Peru
Chelsea House Publishers,
Peru
Cambium,
Peru, Bolivia
Lannoo
Rensink, E. / Peru
Gottmer,
Te gast in Peru
Informatie Verre Reizen
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info