RUSSIA
Geography and Landscape

Geography and Landscape
| Basic information | |
| Official language | Russian |
| Capital | Moscow |
| Area | 17.098.242 km² |
| Population | 146,042,988 (2021) |
| Currency | rouble (RUB) |
| Web | .ru |
| Code. | RUS |
| Tel. | +7 |
Cities in RUSSIA
| Moscow | Saint-petersburg |
Geography and Landscape
Geography
The Russian Federation (Russian: Rossiskaja Federacija; also: Russian Federative Republic [Russian: Rossiskaja Federativnaja Respoeblika]) or Russia (Russian: Rossija), is a republic located in the continents of Europe and Asia.
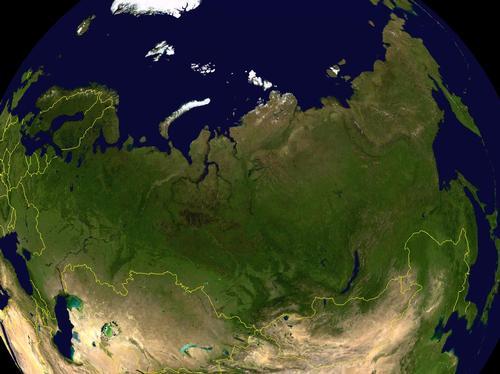
The total area of Russia is 17,075,200 km2, making it the largest country in the world. The maximum distance from east to west is no less than approximately 10,000 km (from Poland to the Bering Strait), and Russia therefore has ten time zones. The European part of Russia covers about a quarter of Russia's total territory.
The border between Europe and Asia is formed by the Ural Mountains. Russia further borders the following countries: Norway (196 km), Finland (1340 km), Estonia (294 km) and Latvia (217 km) to the north and west, and via the exclave Kaliningrad to Lithuania (227 km) and Poland (206 km), in the southwest to Belarus (959 km) and Ukraine (1576 km) and in the south to Georgia (723 km), Azerbaijan (284 km) and Kazakhstan (6846 km). In the far east, Russia borders China (3645 km), Mongolia (3845 km) and North Korea (19 km).
Russia is surrounded in the north by a large number of Arctic Ocean fringes, such as the Barents Sea, the White Sea, the Carian Sea, the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea. To the east, Russia borders the Bering Sea, the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan; to the south on the Caspian Sea; in the west on the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Finland. Russia's coastline totals 20,017 km.
Russia also includes Kaliningrad (German: Königsberg; Polish: Krolewice), an exclave between Lithuania and Poland in the Bight of Gdansk.
The following islands and archipelagos also belong to Russia: Nova Zembla, Francois Joseph Islands, Northland, New Siberian Islands, Vrangel, Commander Islands, Kuril and Sakhalin.
The northernmost point of the Eurasian landmass, and in fact the northernmost part of the Earth's mainland, is the Tajmyr Peninsula. The peninsula extends up to 1100 km north of the Arctic Circle. The most northerly point in Russia is Cape Rodolfo on one of the French Joseph Islands near Novaya Zemlya.
Landscape
 Tundra landscape RussiaPhoto: Ninaras CC 4.0 International no changes made
Tundra landscape RussiaPhoto: Ninaras CC 4.0 International no changes made
The Eastern European plain is a gently undulating area that rises slightly towards the east and is bounded there by the Ural Mountains. This plain lies mostly at an altitude of less than 200 meters, but some hilly areas reach heights of 300 to 400 meters (including the Timan Ridge, the Valdaj Heights and the North Russian Ridge). The highest peak of the Ural Mountains is the Narodnaja with 1894 meters, the rest of the mountain is much lower.
Three landscape types are found to the east of the Ural Mountains. In the far north is the treeless tundra, which on a permanently frozen subsoil, the permafrost, covers the Eurasian landmass for a length of 4000 km. To the south of this, extensive coniferous forests (spruce, pine and also birch) of the taiga make way for extensive grasslands, the steppes.
The tundra is a desolate cold desert that covers the northern part of the Eurasian landmass from the tree line to the Arctic Ocean like a hood. Because of the intense cold and the long winters, only mosses, lichens and, in the southern part, dwarf shrubs grow. The average annual temperature is around -10 °C. During the three summer months, the soil surface is thawed several decimeters. Below it is the permafrost or "Vetchnaya Mertslota", a permanently frozen layer of earth several tens to hundreds of meters thick.
The forests (mainly birch and coniferous) of the taiga stretch from the Baltic Sea to the Bering Strait and from the Arctic Circle to the central Siberian highlands north of Lake Baikal; a total of 6.5 million km2, making it one of the largest continuous forest areas in the world. The taiga is intersected by rivers that have been frozen over for more than half the year.
The steppes of Russia form a vast belt of open grassland stretching from the Black Sea to Manchuria. Over millennia, the plant material has broken down into a dark, humus-rich soil, the "black soil" (chernozhom), which is very suitable for agriculture.
Rivers, lakes and channels
 River Ob, RussiaPhoto: Andrew Kudin CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
River Ob, RussiaPhoto: Andrew Kudin CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Russia has about 100,000 rivers. Many of these rivers are inaccessible, but they have great hydropower potential, especially the rivers in Siberia. Shipping traffic on the major rivers of European Russia and Siberia is struggling due to the long periods that the rivers under ice. In European Russia, the ice period lasts 100 to 135 days; the mouths of the Siberian rivers have been frozen for 190 days (Ob) to 260 days (Lena).
In spring, major floods occur in both the European and Siberian rivers due to the large supply of melt water and, in the Siberian rivers, due to the backwater of the river level through the estuary ice. The Volga is the longest river in Europe (3531 km). Other important rivers are the Urals (2428 km) and in the Asian part of Russia the Lena (4313 km), the Irtysch (4248 km) and the Ob (3650 km).
Russia has a large number of lakes (about 270,000), of which five have an area of more than 1000 km2. The largest lakes are Lake Baikal near Irkutsk and Lake Ladoga near St. Petersburg; other well-known lakes are the Caspian Sea and the Aral Sea. The lakes and swamps of the Siberian plains are a result of the lack of drainage and the occurrence of frozen soils that prevent the infiltration of melt and rainwater. There are also a number of artificial reservoirs with a total area of approximately 70,000 km2.
The channels mainly serve shipping. The White Sea, Baltic Sea and Black Sea are interconnected via the channels of the Volga system.
Miscellaneous
LAKE BAIKAL
 Lake Baikal, RussiaPhoto: Aleksandr Zykov CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Lake Baikal, RussiaPhoto: Aleksandr Zykov CC 2.0 Generic no changes made
Lake Baikal is about 25 million old and therefore possibly the oldest lake in the world. The lake has an area of 31,500 km2 and a coastline of 2000 km in length. In terms of surface, Lake Baikal is the eighth lake in the world.
It is the deepest lake in the world at a depth of 1,600 meters and contains about 31,500 km2 of water, the same amount as all the major North American lakes combined and one fifth of all fresh water on Earth.
336 rivers flow into the lake, but it has only one discharge river, the Angara. The lake has about 45 islands, of which Olkhon is the largest with even a 1268 meter high mountain.
CAUCASUS
 Elbrus, Russia's highest mountainPhoto: Jialiang Gao CC 3.0 Unportedno changes made
Elbrus, Russia's highest mountainPhoto: Jialiang Gao CC 3.0 Unportedno changes made
The Caucasus is a mountain range in Russia, Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan, also known as a land bridge between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. The Caucasus is divided into the Lesser Caucasus and the Greater Caucasus. In the Greater Caucasus you will find the highest mountains in Europe, the Elbrus (5642 meters), the Dych Taoe (5204 meters), the Kosjtan Taoe (5145 meters) and the Kazbek (5047 meters). There are more than 1000 glaciers of which the Bezengi is the longest at 18 km.
KOERILEN ARCHIPELAGO
Off the far east coast of Siberia lies the Kuril archipelago, 56 islands with about 100 volcano peaks of which 38 are still active. They stretch for 1,200 km from the Kamchatka Peninsula to the Japanese island of Hokkaido.
Sources
Graaf, A. van der / Reis-handboek Sovjet-Unie
Elmar
Rusland, Centraal-Azië en de Kaukasus
The Reader’s Digest,
Russia & Belarus
Lonely Planet
Te gast in Rusland
Informatie Verre Reizen
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info