DJIBOUTI
Geography and Landscape
Geography
Djibouti is located in East Africa. Djibouti borders the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea and lies between Eritrea and Somalia. Djibouti also borders on Ethiopia. The surface area of Djibouti is 23,000 square kilometres.
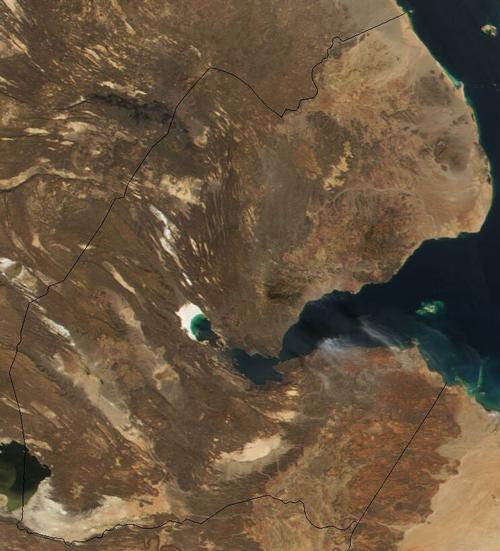 Djibouti Satellite PhotoPhoto: Public domain
Djibouti Satellite PhotoPhoto: Public domain
Landscape
 In the background Mousa Ali, Djibouti's highest pointPhoto :Skilla1st CC 4.0 International no changes made
In the background Mousa Ali, Djibouti's highest pointPhoto :Skilla1st CC 4.0 International no changes made
There are three regions in Djibouti. First, the volcanic desert plateaus in the centre and south of the country; second, the narrow coastal plains; and third, the mountains, with heights from 1,500 to 2,000 metres, in the north of Djibouti. The highest peak is the stratovolcano Mousa Ali (2021 metres) on the border with Ethiopia and Eritrea; the lowest point is Lake Assal (150 metres below sea level).
Djibouti has a coastline of 300 kilometres with many white sandy beaches where no people go. In the hinterland, salt water basins and a few oases interrupt the rough desert landscape. The most important rivers in Djibouti are the Essalou, Ouâhayyi and Sadaï.
Climate and Weather
Djibouti has a pronounced desert climate. July is the hottest month with an average temperature of 36 °C. The hot khamsin wind also blows during this month. Between October and April, the temperatures are more bearable and there may be a shower. In general, it is very dry in Djibouti.
Plants and Animals
Plants
Due to the low rainfall, plant life is limited. On the rocky desert soil, no more grows than thorn bushes and some grass. Here and there are groups of palm trees. Mangrove grows along the coast.
Animals
Wildlife includes hyenas, antelopes, gazelles, donkeys, flamingos, goats, jackals, camels and ostriches. Off the coast live many species of fish, including barracuda and tuna.
Sources
Elmar Landeninformatie
CIA - World Factbook
BBC - Country Profiles
Copyright: Team The World of Info